SBASA34B June 2020 – August 2024 AMC3330
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Power Ratings
- 5.6 Insulation Specifications
- 5.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 5.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 5.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.10 Switching Characteristics
- 5.11 Timing Diagram
- 5.12 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 5.13 Typical Characteristics
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
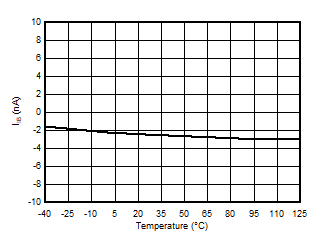
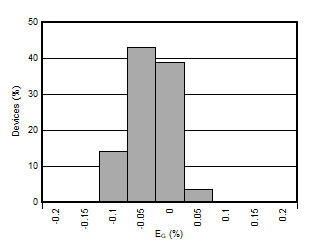
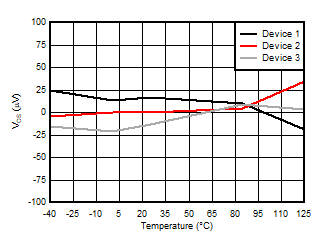
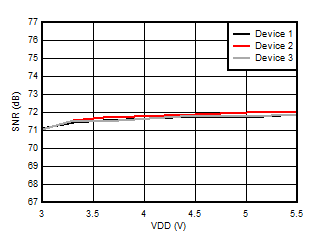
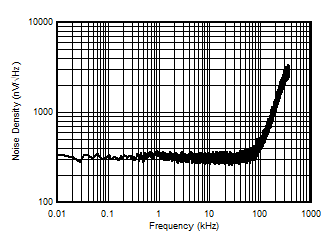
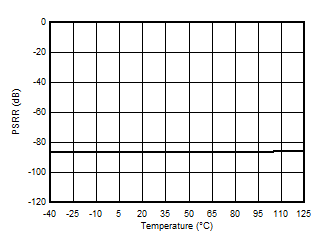
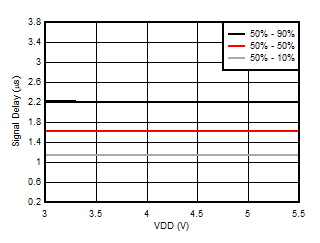
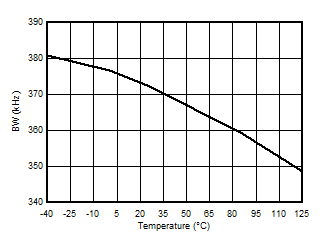
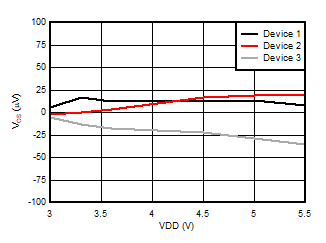
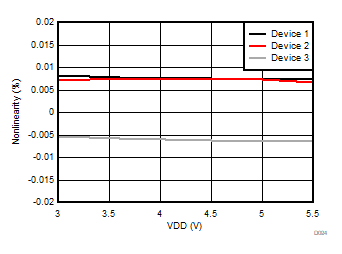
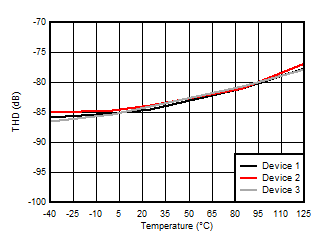
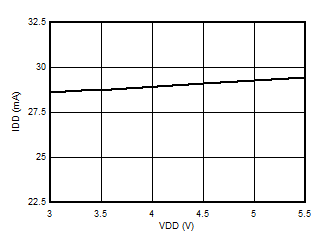
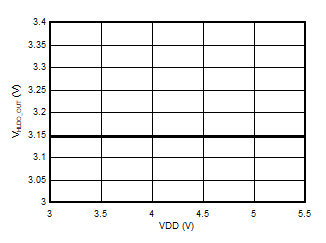
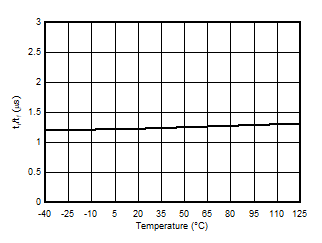
5.13 Typical Characteristics
at VDD = 3.3 V, INP = –1 V to 1 V, INN = HGND = 0V, and fIN = 10 kHz (unless otherwise noted)