SBASAM0B March 2024 – November 2024 ADS127L18
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Parameter Measurement Information
- 6.1 Offset Error Measurement
- 6.2 Offset Drift Measurement
- 6.3 Gain Error Measurement
- 6.4 Gain Drift Measurement
- 6.5 NMRR Measurement
- 6.6 CMRR Measurement
- 6.7 PSRR Measurement
- 6.8 SNR Measurement
- 6.9 INL Error Measurement
- 6.10 THD Measurement
- 6.11 IMD Measurement
- 6.12 SFDR Measurement
- 6.13 Noise Performance
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.3 Application Curves
The following figures are produced by the TINA-TI™, SPICE-based analog simulation program. Download the THS4551 SPICE model at the THS4551 product folder.
Figure 9-2 shows the frequency response of the antialias filter and the total response of the antialias filter and ADC. As shown in this image, the filter provides 90dB stop-band attenuation from the Nyquist frequency to the 12.8MHz fMOD frequency.
Figure 9-3 shows the analog filter group delay. The 0.575μs group delay is small in comparison to the 85μs group delay of the ADC digital filter (34 / fDATA). The analog filter group delay linearity is 0.017μs, peaking at the edge of the 165kHz pass band.
 Figure 9-2 Antialias Filter Frequency
Response
Figure 9-2 Antialias Filter Frequency
Response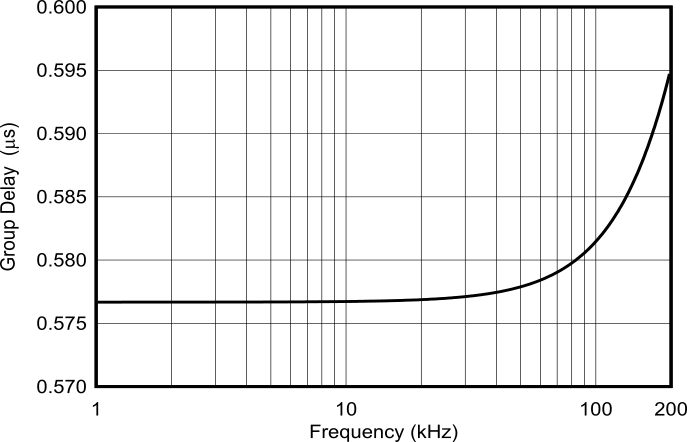 Figure 9-3 Antialias Filter Group
Delay
Figure 9-3 Antialias Filter Group
DelayFigure 9-4 shows the noise density of the antialias filter circuit, the noise density of the ADC, and the combined noise density of the filter and ADC. Noise density is the noise voltage per √Hz of bandwidth plotted versus frequency.
Figure 9-5 shows the total noise from the 1Hz start frequency up to the ADC final bandwidth. Below 200Hz, noise is dominated by 1 / f voltage and current noise of the THS4551 amplifier. Above 200Hz, noise is dominated by ADC noise. The integrated noise of the filter and ADC over the 165kHz bandwidth is 11.8μV, meeting the 12μV target value.
 Figure 9-4 Noise Density
Figure 9-4 Noise Density Figure 9-5 Total Noise
Figure 9-5 Total Noise