SBAU193E June 2011 – May 2021 ADS8568
6.6 Histogram Display
Noise degrades ADC resolution and the histogram tool can be used to estimate effective resolution, which is an indicator of the number of bits of ADC resolution losses resulting from noise generated by the various sources connected to the ADC when measuring a DC signal. The cumulative effect of noise coupling to the ADC output from sources such as the input drive circuits, the reference drive circuit, the ADC power supply, and the ADC itself is reflected in the standard deviation of the ADC output code histogram that is obtained by performing multiple conversions of a DC input applied to a given channel. As shown in Figure 6-6, the histogram corresponding to a DC input is displayed on clicking the Capture button.
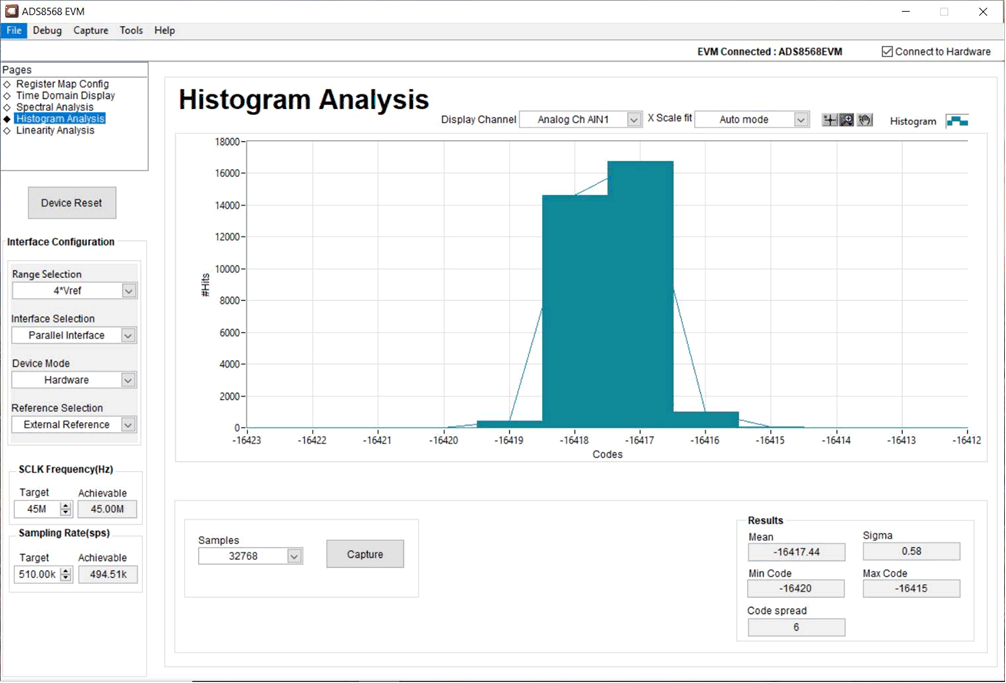 Figure 6-6 Histogram Display
Figure 6-6 Histogram Display