SBOA411 December 2020 INA3221-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a Failure Mode Analysis (FMA) for the pins of the INA3221-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to Ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to VS (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1 TI Classification of Failure Effects
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance |
Figure 4-1 shows the INA3221-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the 'Pin Configuration and Functions' section in the INA3221-Q1 datasheet.
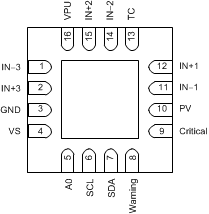 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- TA = -40°C to +125°C
- VS = 3.3 V
- VBUS = 12 V
Table 4-2 Pin FMA for Device Pins Short-Circuited to Ground
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN-3 | 1 | In high-side configuration, a short from the bus supply to ground will occur. High current will flow from bus supply to ground. In low side configuration, normal operation. | B for high-side; D for low-side |
| IN+3 | 2 | In high-side configuration, a short from the bus supply to ground will occur. High current will flow from bus supply to ground. In low side configuration, input pins are shorted. | B |
| GND | 3 | Normal operation. | D |
| VS | 4 | Power supply shorted to ground. | B |
| A0 | 5 | Address pin shorted to ground. Normal operation if this is intended, otherwise loss of pin functionality. | D if A0 = GND by design; B otherwise |
| SCL | 6 | I2C clock pin shorted to ground. Loss of I2C communication. | B |
| SDA | 7 | I2C data pin shorted to ground. Loss of I2C communication. | B |
| Warning | 8 | Warning pin shorted to ground. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| Critical | 9 | Critical pin shorted to ground. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| PV | 10 | PV pin shorted to ground. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| IN-1 | 11 | In high-side configuration, a short from the bus supply to ground will occur. High current will flow from bus supply to ground. In low side configuration, normal operation. | B for high-side; D for low-side |
| IN+1 | 12 | In high-side configuration, a short from the bus supply to ground will occur. High current will flow from bus supply to ground. In low side configuration, input pins are shorted. | B |
| TC | 13 | TC pin shorted to ground. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| IN-2 | 14 | In high-side configuration, a short from the bus supply to ground will occur. High current will flow from bus supply to ground. In low side configuration, normal operation. | B for high-side; D for low-side |
| IN+2 | 15 | In high-side configuration, a short from the bus supply to ground will occur. High current will flow from bus supply to ground. In low side configuration, input pins are shorted. | B |
| VPU | 16 | VPU pin shorted to ground. Loss of power to internal power valid circuitry. | B |
Table 4-3 Pin FMA for Device Pins Open-Circuited
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN-3 | 1 | IN-3 will be at the same potential as IN+3. Differential input voltage is effectively 0V. | B |
| IN+3 | 2 | IN+3 will be at the same potential as IN-3. Differential input voltage is effectively 0V. | B |
| GND | 3 | GND is floating. Output will be incorrect as it is no longer referenced to ground. | B |
| VS | 4 | No power supply to device. | B |
| A0 | 5 | Address pin is open. Undefined device address. | B |
| SCL | 6 | I2C clock pin is open. Loss of I2C communication. | B |
| SDA | 7 | I2C data pin is open. Loss of I2C communication. | B |
| Warning | 8 | Warning pin is open. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| Critical | 9 | Critical pin is open. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| PV | 10 | PV pin is open. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| IN-1 | 11 | IN-1 will be at the same potential as IN+1. Differential input voltage is effectively 0V. | B |
| IN+1 | 12 | IN+1 will be at the same potential as IN-1. Differential input voltage is effectively 0V. | B |
| TC | 13 | TC pin is open. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| IN-2 | 14 | IN-2 will be at the same potential as IN+2. Differential input voltage is effectively 0V. | B |
| IN+2 | 15 | IN+2 will be at the same potential as IN-2. Differential input voltage is effectively 0V. | B |
| VPU | 16 | VPU pin is open. Loss of power to internal power valid circuitry | B |
Table 4-4 Pin FMA for Device Pins Short-Circuited to Adjacent Pin
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IN-3 | 1 | 2 - IN+3 | Differential input voltage is 0V. | B |
| IN+3 | 2 | 3 - GND | In high-side configuration, a short from the bus supply to ground will occur. In low-side configuration, differential input voltage is 0V . | B |
| GND | 3 | 4 - VS | Power supply shorted to ground. | B |
| VS | 4 | 5 - A0 | Address pin shorted to VS. Normal operation if this is intended, otherwise loss of pin functionality. | D if A0 = VS by design; B otherwise |
| A0 | 5 | 6 - SCL | Address pin shorted to SCL. Normal operation if this is intended, otherwise loss of pin functionality. | D if A0 = SCL by design; B otherwise |
| SCL | 6 | 7 - SDA | I2C clock pin shorted to data pin. Loss of I2C communication. | B |
| SDA | 7 | 8 - Warning | I2C data pin shorted to Warning pin. Loss of I2C communication. | B |
| Warning | 8 | 9 - Critical | Warning pin shorted to Critical pin. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| Critical | 9 | 10 - PV | Critical pin shorted to PV pin. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| PV | 10 | 11 - IN-1 | PV pin shorted to bus voltage. In high-side configuration, damage can occur. In low-side configuration, loss of pin functionality. | A for high-side; B for low-side |
| IN-1 | 11 | 12 - IN+1 | Differential input voltage is 0V. | B |
| IN+1 | 12 | 13 - TC | TC pin shorted to bus voltage. In high-side configuration, damage can occur. In low-side configuration, loss of pin functionality. | A for high-side; B for low-side |
| TC | 13 | 14 - IN-2 | TC pin shorted to bus voltage. In high-side configuration, damage can occur. In low-side configuration, loss of pin functionality. | A for high-side; B for low-side |
| IN-2 | 14 | 15 - IN+2 | Differential input voltage is 0V. | B |
| IN+2 | 15 | 16 - VPU | VPU pin shorted to bus voltage. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| VPU | 16 | 1 - IN-3 | VPU pin shorted to bus voltage. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
Table 4-5 Pin FMA for Device Pins Short-Circuited to VS
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN-3 | 1 | In high-side configuration, VS shorted to bus voltage. High current will flow from bus supply to VS or vice versa. Device could be damaged. | A |
| IN+3 | 2 | In high-side configuration, VS shorted to bus voltage. High current will flow from bus supply to VS or vice versa. Device could be damaged. | A |
| GND | 3 | Power supply shorted to ground. | B |
| VS | 4 | Normal operation. | D |
| A0 | 5 | Address pin shorted to VS. Normal operation if this is intended, otherwise loss of pin functionality. | D if A0 = VS by design; B otherwise |
| SCL | 6 | I2C clock pin shorted to VS. Loss of I2C communication. | B |
| SDA | 7 | I2C data pin shorted to VS. Loss of I2C communication. | B |
| Warning | 8 | Warning pin shorted to VS. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| Critical | 9 | Critical pin shorted to VS. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| PV | 10 | PV pin shorted to VS. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| IN-1 | 11 | In high-side configuration, VS shorted to bus voltage. High current will flow from bus supply to VS or vice versa. Device could be damaged. | A |
| IN+1 | 12 | In high-side configuration, VS shorted to bus voltage. High current will flow from bus supply to VS or vice versa. Device could be damaged. | A |
| TC | 13 | TC pin shorted to VS. Loss of pin functionality. | B |
| IN-2 | 14 | In high-side configuration, VS shorted to bus voltage. High current will flow from bus supply to VS or vice versa. Device could be damaged. | A |
| IN+2 | 15 | In high-side configuration, VS shorted to bus voltage. High current will flow from bus supply to VS or vice versa. Device could be damaged. | A |
| VPU | 16 | Normal operation. | D |