SBOA463 December 2020 OPA2376-Q1
4.2 OPA2376QDGKRQ1 (DGK) Package
Figure 4-2 shows the OPA2376-Q1 pin diagram for the OPA2376QDGKRQ1 (DGK) package. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the OPA2376-Q1 data sheet.
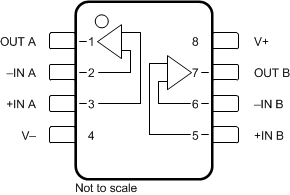 Figure 4-2 Pin Diagram (OPA2376QDGKRQ1 (DGK) Package)
Figure 4-2 Pin Diagram (OPA2376QDGKRQ1 (DGK) Package)| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
OUT A | 1 | Depending on circuit configuration, device will likely be forced into short circuit condition with OUT A voltage ultimately forced to V‒ voltage. Prolonged exposure to short circuit conditions could result in long term reliability issues. | A |
‒IN A | 2 | Negative feedback not present to device. Depending on circuit configuration, output will most likely move to negative supply. | B |
+IN A | 3 | Device common‒mode tied to negative rail. Depending on circuit configuration, output will likely not respond due to the device being put in an invalid common‒mode condition. | C |
+IN B | 5 | Device common‒mode tied to negative rail. Depending on circuit configuration, output will likely not respond due to the device being put in an invalid common‒mode condition. | C |
‒IN B | 6 | Negative feedback not present to device. Depending on circuit configuration, output will most likely move to negative supply. | B |
OUT B | 7 | Depending on circuit configuration, device will likely be forced into short circuit condition with OUT B voltage ultimately forced to V‒ voltage. Prolonged exposure to short circuit conditions could result in long term reliability issues. | A |
V+ | 8 | Op‒Amp supplies will be shorted together leaving V+ pin at some voltage between V+ and V‒ sources (depending on source impedance). | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
OUT A | 1 | No negative feedback or ability for OUT A to drive application. | B |
‒IN A | 2 | Inverting pin of Op‒Amp left floating. Negative feedback will not be provided to device, likely resulting in device output moving between positive and negative rail. ‒IN A pin voltage will likely end up at positive or negative rail due to leakage on ESD diodes. | B |
+IN A | 3 | Input common‒mode left floating. Op‒Amp will not be provided with common‒mode bias, device output will likely end up at positive or negative rail. +IN A pin voltage will likely end up at positive or negative rail due to leakage on ESD diodes. | B |
V‒ | 4 | Negative supply left floating. Op‒Amp will cease to function as no current can source/sink to the device. | A |
+IN B | 5 | Input common‒mode left floating. Op‒Amp will not be provided with common‒mode bias, device output will likely end up at positive or negative rail. +IN B pin voltage will likely end up at positive or negative rail due to leakage on ESD diodes. | B |
‒IN B | 6 | Inverting pin of Op‒Amp left floating. Negative feedback will not be provided to device, likely resulting in device output moving between positive and negative rail. ‒IN B pin voltage will likely end up at positive or negative rail due to leakage on ESD diodes. | B |
OUT B | 7 | No negative feedback or ability for OUT B to drive application. | B |
V+ | 8 | Positive supply left floating. Op‒Amp will cease to function as no current can source/sink to the device. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
OUT A | 1 | ‒IN A | Depending on circuit configuration, gain of circuit will be reduced to unity gain and application may not function as intended | B |
‒IN A | 2 | +IN A | Both inputs will be tied together. Depending on the offset of the device, this will likely move the output voltage near mid supply. | D |
+IN A | 3 | V‒ | Device common‒mode tied to negative rail. Depending on circuit configuration, output will likely not respond due to the device being put in an invalid common‒mode condition. | C |
V‒ | 4 | +IN B | Device common‒mode tied to negative rail. Depending on circuit configuration, output will likely not respond due to the device being put in an invalid common‒mode condition. | C |
+IN B | 5 | ‒IN B | Both inputs will be tied together. Depending on the offset of the device, this will likely move the output voltage near mid supply. | D |
‒IN B | 6 | OUT B | Depending on circuit configuration, gain of circuit will be reduced to unity gain and application may not function as intended | B |
OUT B | 7 | V+ | Depending on circuit configuration, device will likely be forced into short circuit condition with OUT B voltage ultimately forced to V+ voltage. Prolonged exposure to short circuit conditions could result in long term reliability issues. | A |
V+ | 8 | OUT A | Depending on circuit configuration, device will likely be forced into short circuit condition with V+ voltage ultimately forced to OUT A voltage. Prolonged exposure to short circuit conditions could result in long term reliability issues. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
OUT A | 1 | Depending on circuit configuration, device will likely be forced into short circuit condition with OUT A voltage ultimately forced to V+ voltage. Prolonged exposure to short circuit conditions could result in long term reliability issues. | A |
‒IN A | 2 | Negative feedback not present to device. Depending on non‒inverting input voltage and circuit configuration, output will most likely move to negative supply. | B |
+IN A | 3 | Depending on circuit configuration, application will likely not function due to the device common‒mode being connected to +IN A. | B |
V‒ | 4 | Op‒Amp supplies will be shorted together leaving V‒ pin at some voltage between V‒ and V+ sources (depending on source impedance). | A |
+IN B | 5 | Depending on circuit configuration, application will likely not function due to the device common‒mode being connected to +IN B. | B |
‒IN B | 6 | Negative feedback not present to device. Depending on non‒inverting input voltage and circuit configuration, output will most likely move to negative supply. | B |
OUT B | 7 | Depending on circuit configuration, device will likely be forced into short circuit condition with OUT B voltage ultimately forced to V+ voltage. Prolonged exposure to short circuit conditions could result in long term reliability issues. | A |