SBOS561C March 2012 – May 2024 TLV3201 , TLV3202
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.1.2.2 Noninverting Comparator With Hysteresis
A noninverting comparator with hysteresis requires a two-resistor network, as shown in Figure 8-5, and a voltage reference (VREF) at the inverting input. When VIN is low, the output is also low. For the output to switch from low to high, VIN must rise up to VIN1. VIN1 is calculated by Equation 4.
Equation 4. 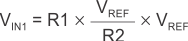
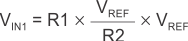
When VIN is high, the output is also high. In order for the comparator to switch back to a low state, VIN must equal VREF before VA is again equal to VREF. VIN can be calculated by Equation 5.
Equation 5. 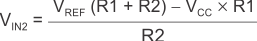
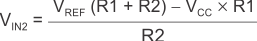
The hysteresis of this circuit is the difference between VIN1 and VIN2, as defined by Equation 6.
Equation 6. 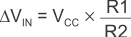
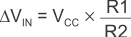
 Figure 8-5 TLV3201 in Noninverting Configuration With Hysteresis
Figure 8-5 TLV3201 in Noninverting Configuration With Hysteresis