SBOS926H January 2021 – November 2024 OPA2392 , OPA392
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.7 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = 5.5 V, VCM = VS / 2, RLOAD = 10 kΩ connected to VS / 2, and CL = 100 pF (unless otherwise noted)
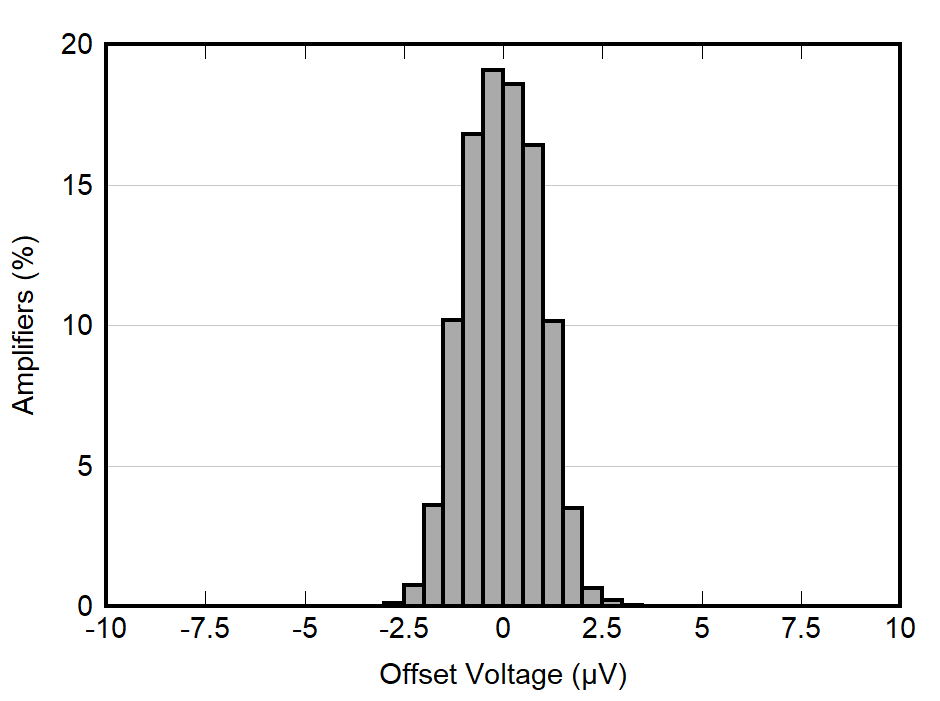
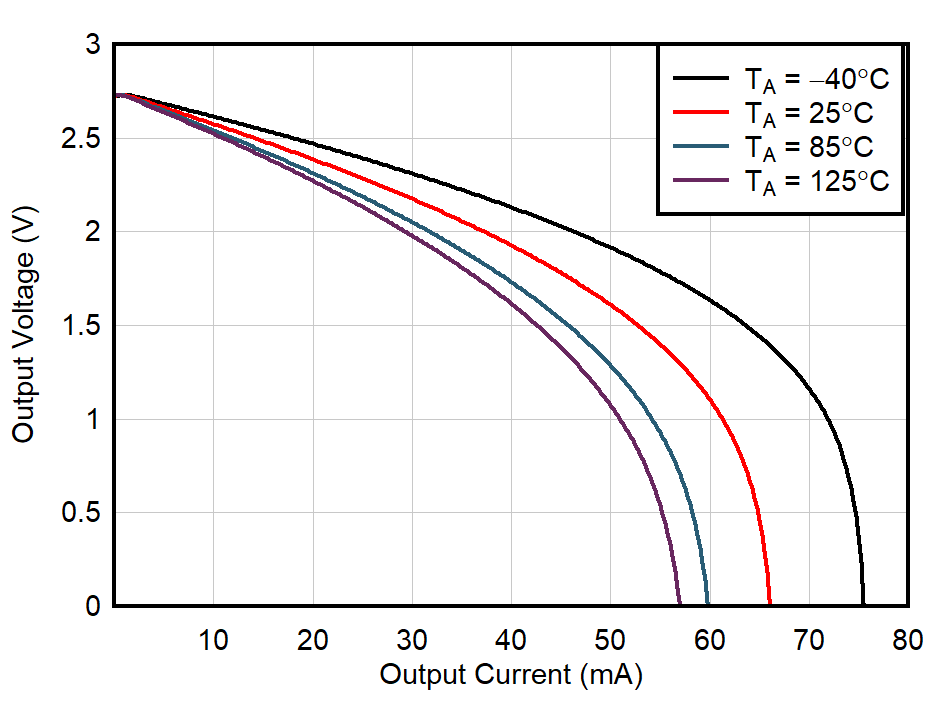
| VS = 5.0 V |
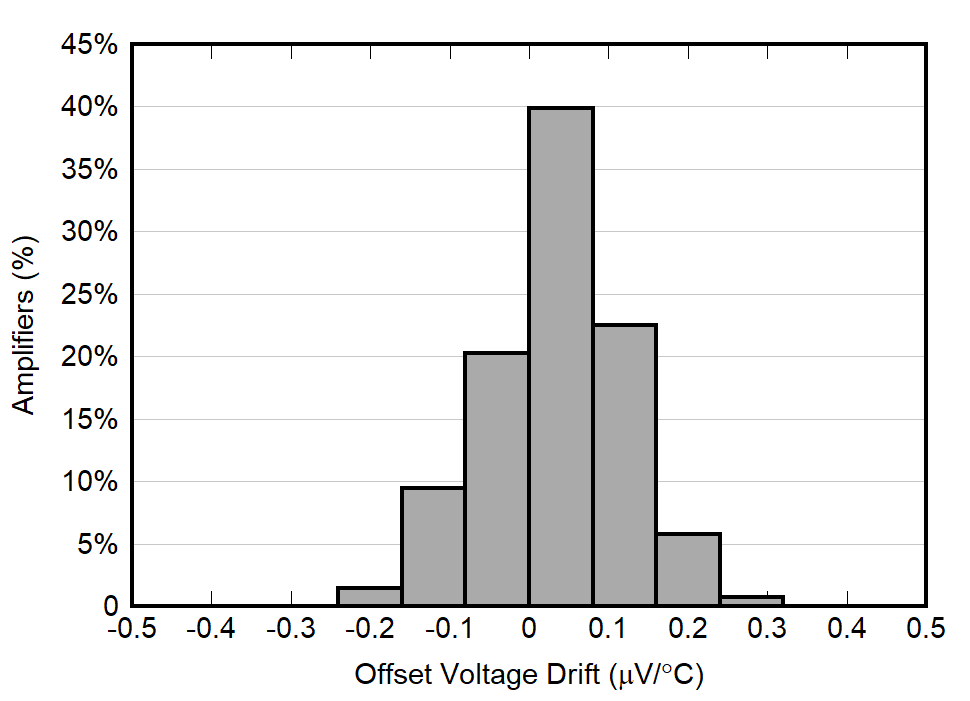
| VS = 5.0 V |
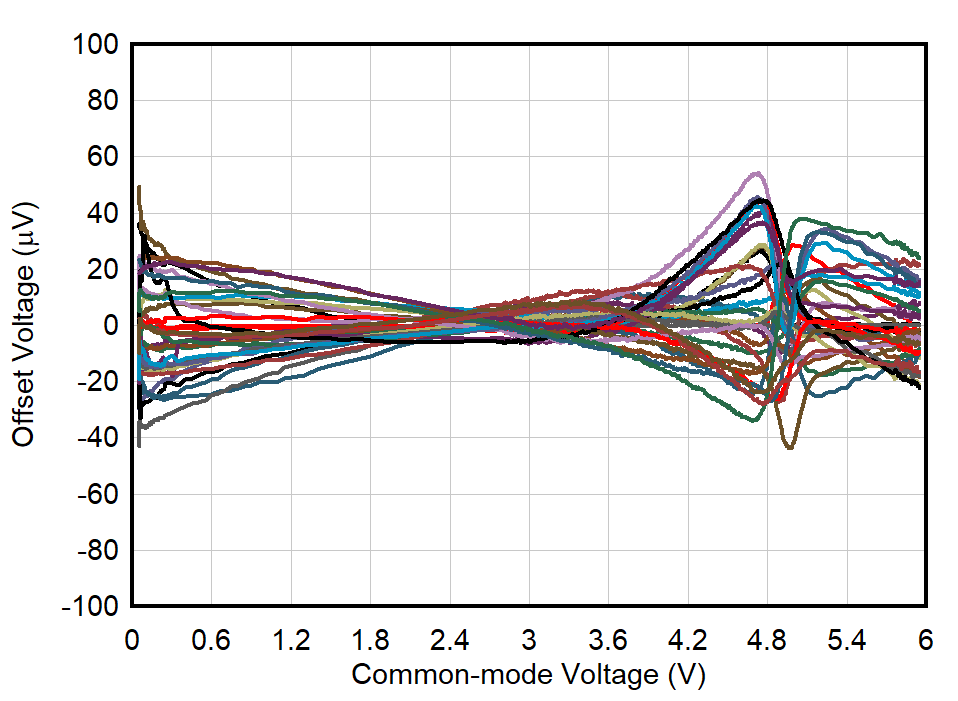

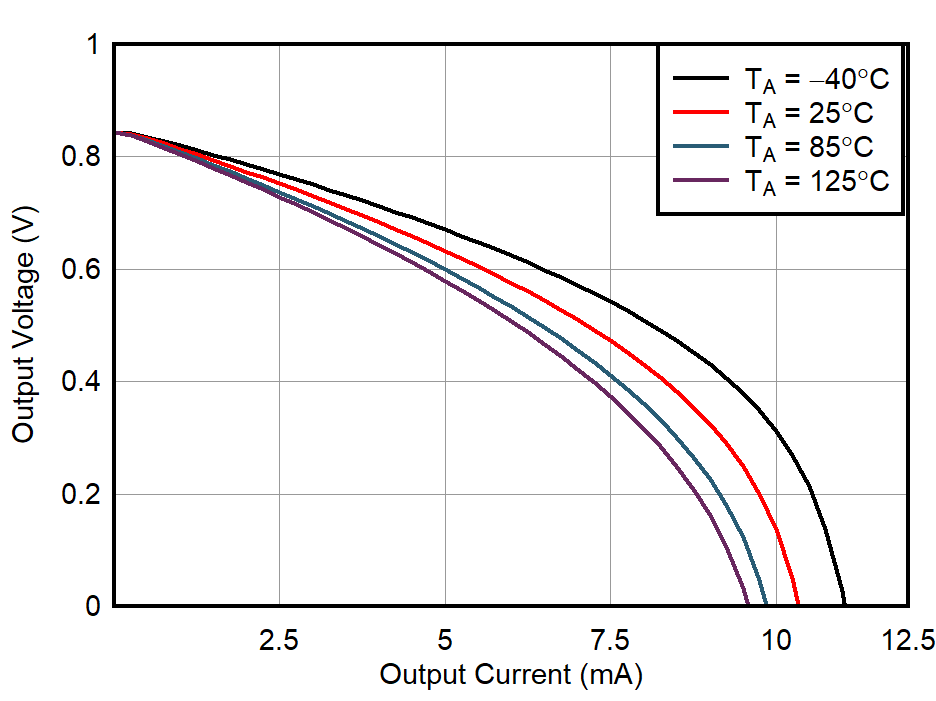
| VS = 1.7 V |
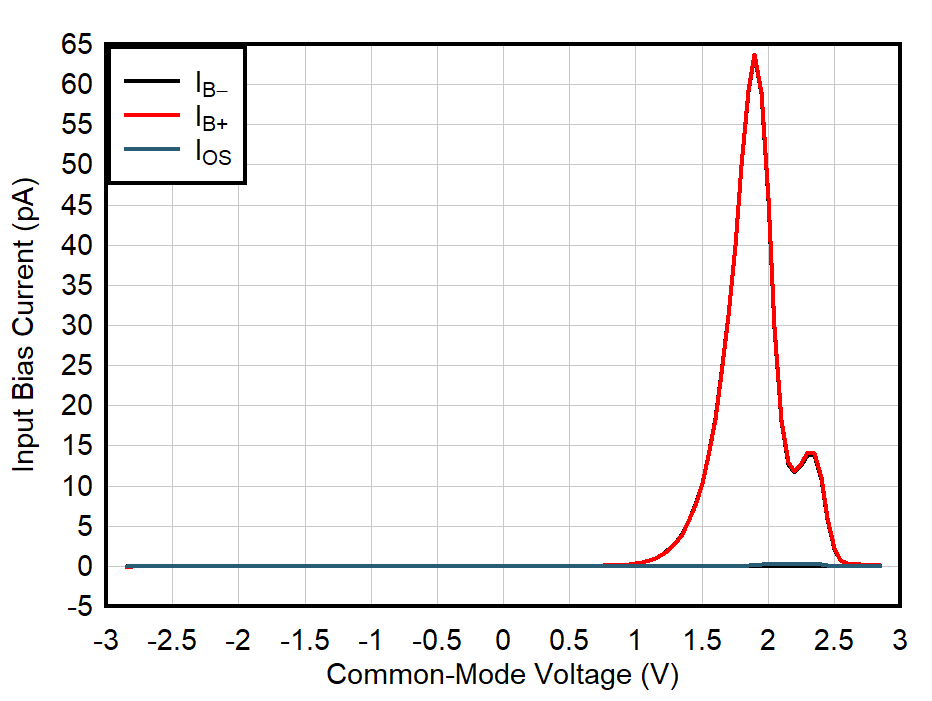
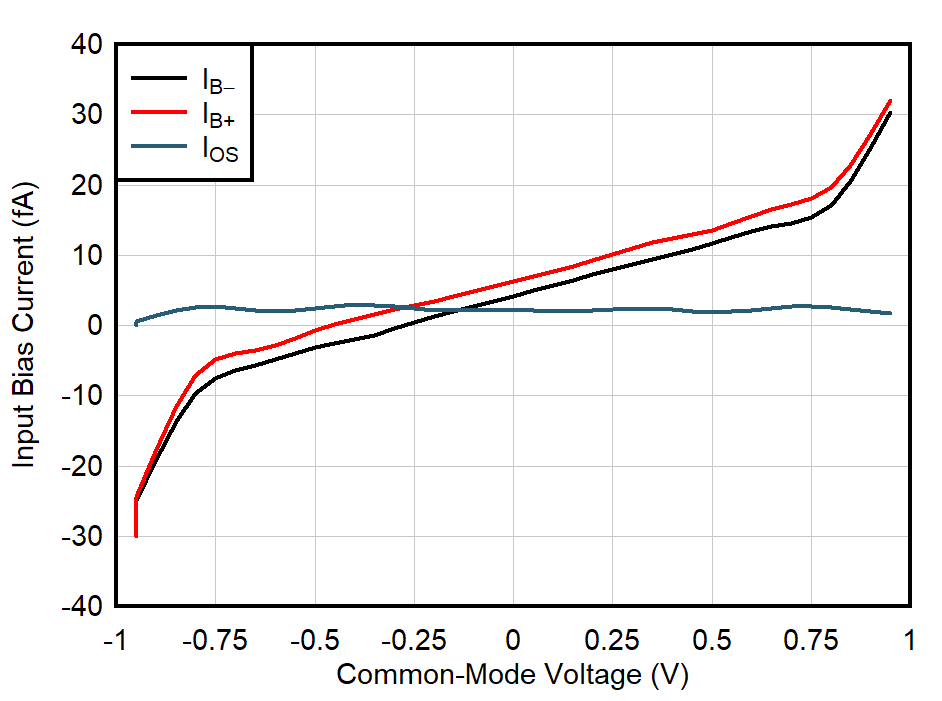
| VS = ±0.85 V |
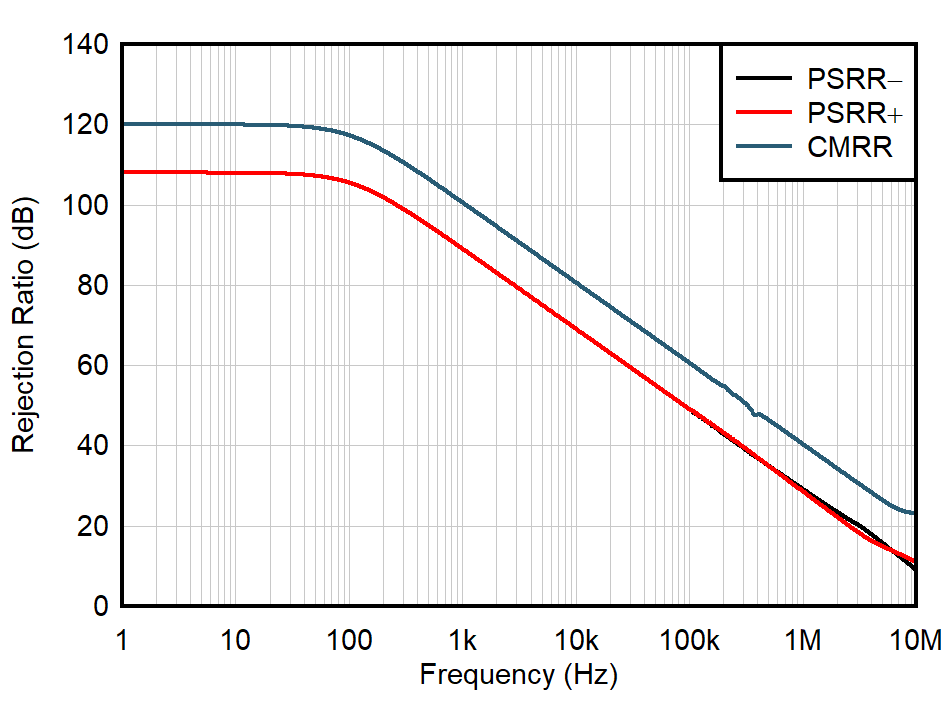
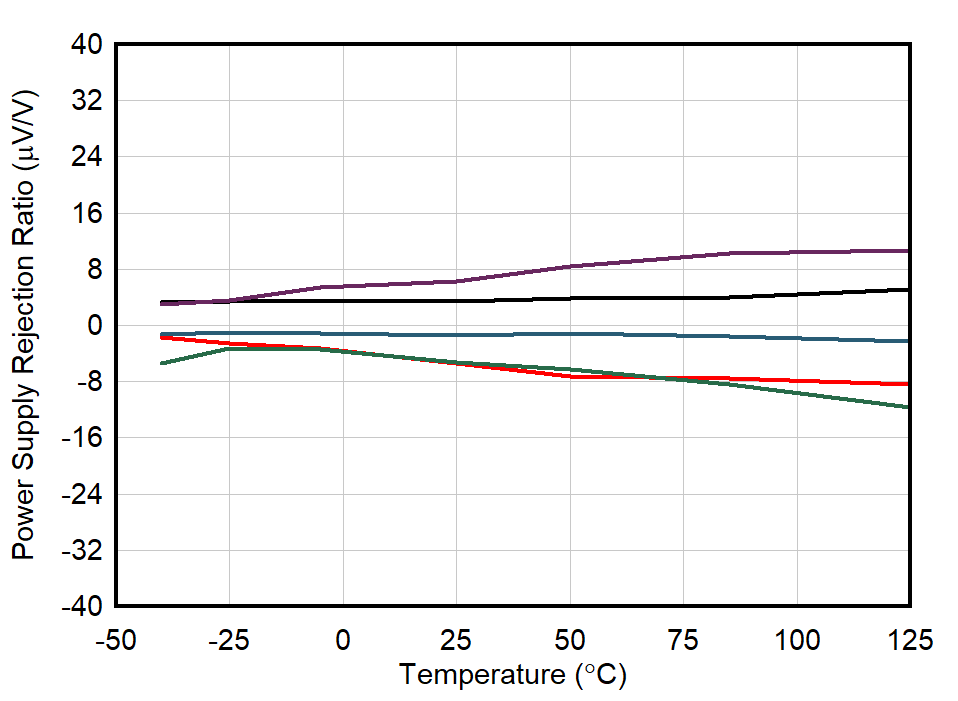
| 5 Units |
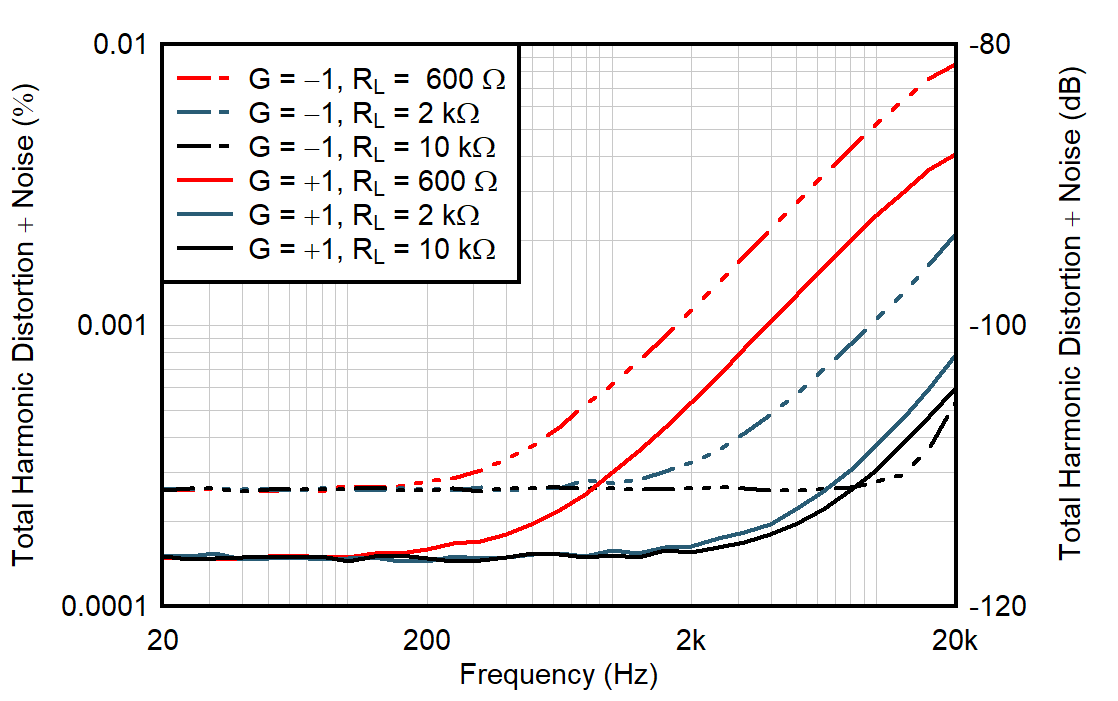
| VOUT = 1 VRMS |
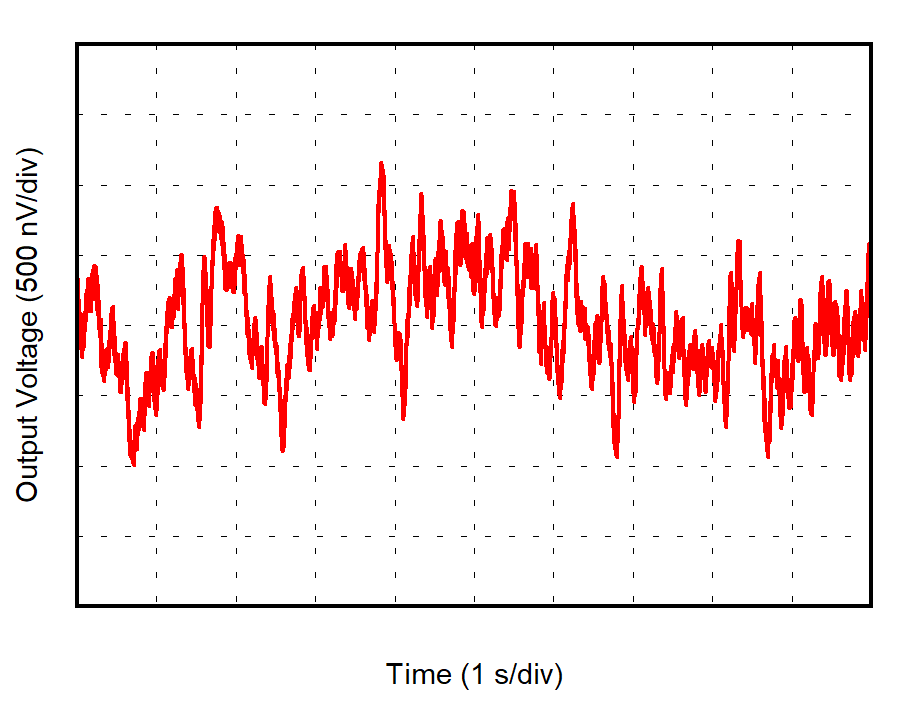
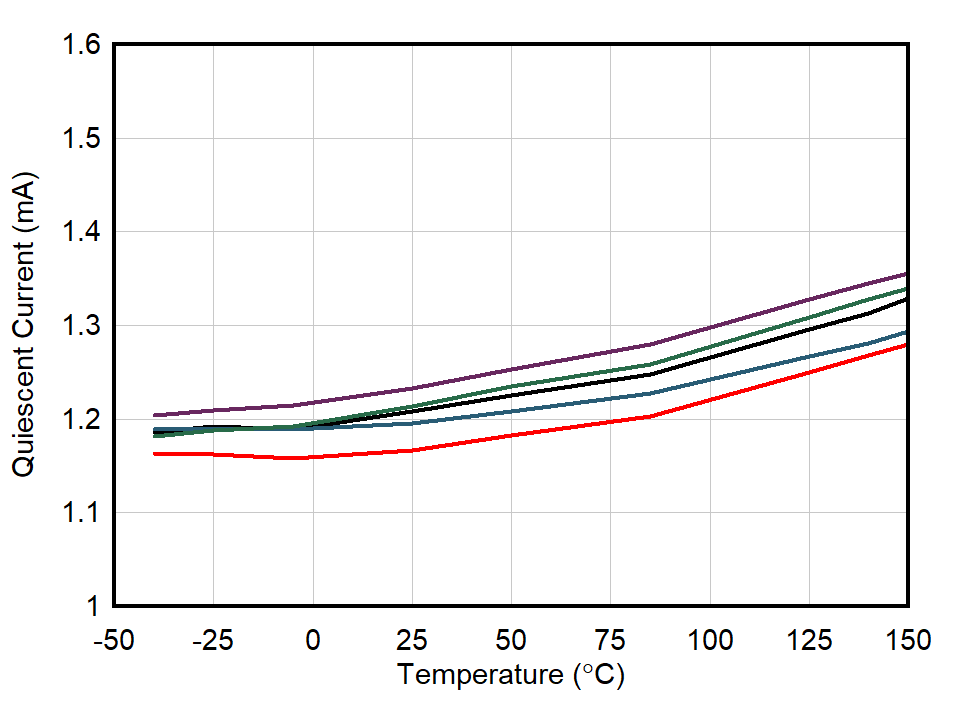
| 5 Units |
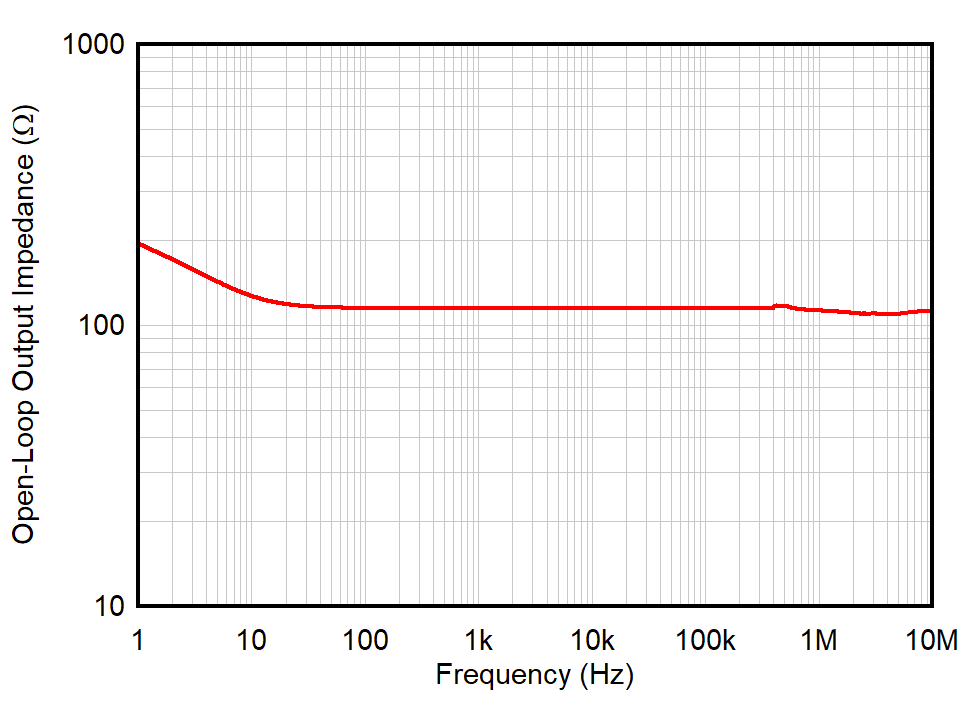
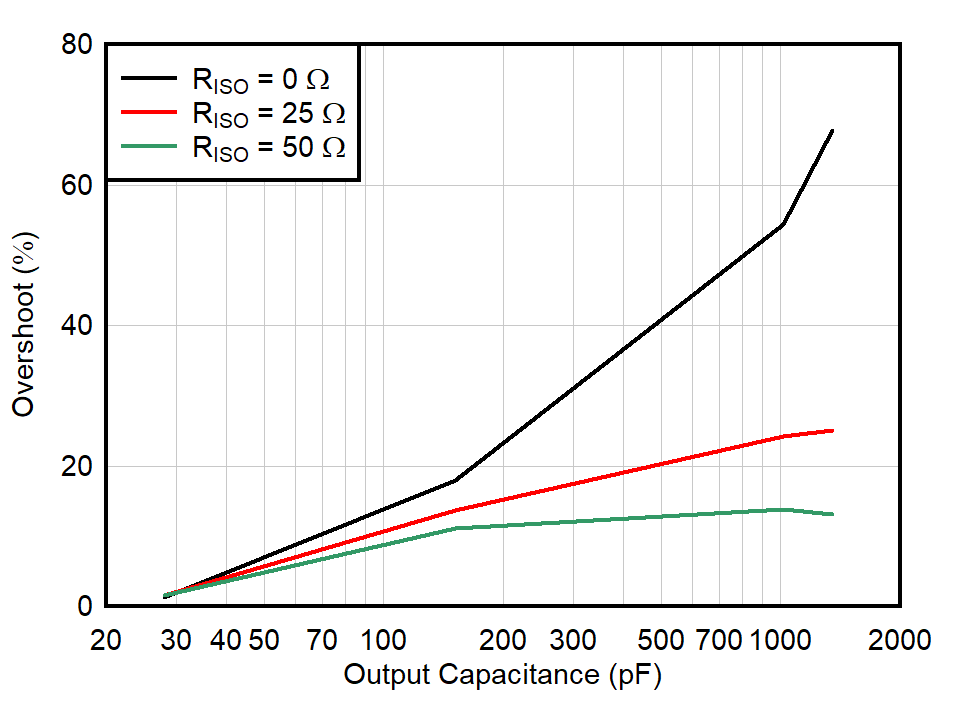
| G = 1 |
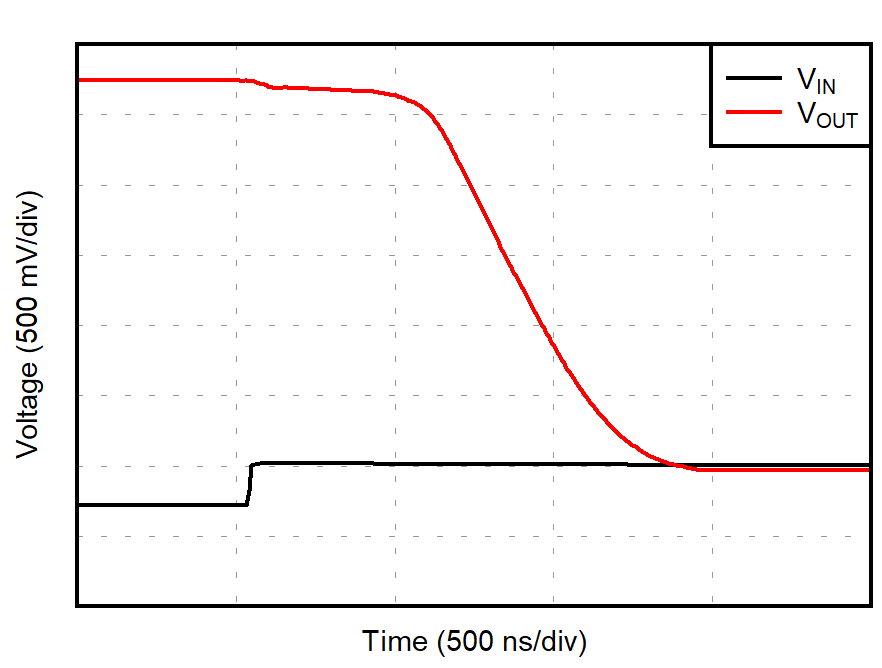
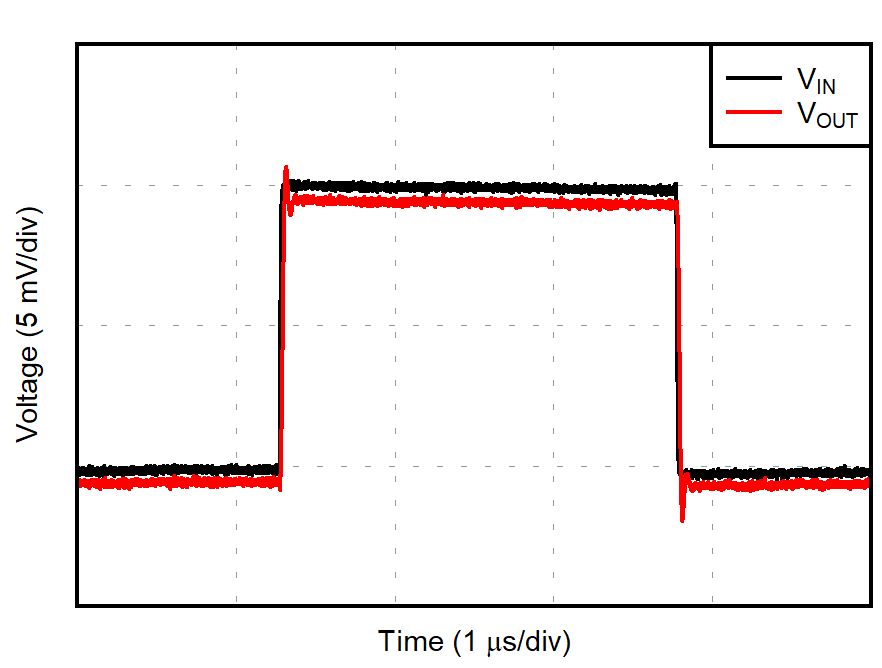
| G = 1 |
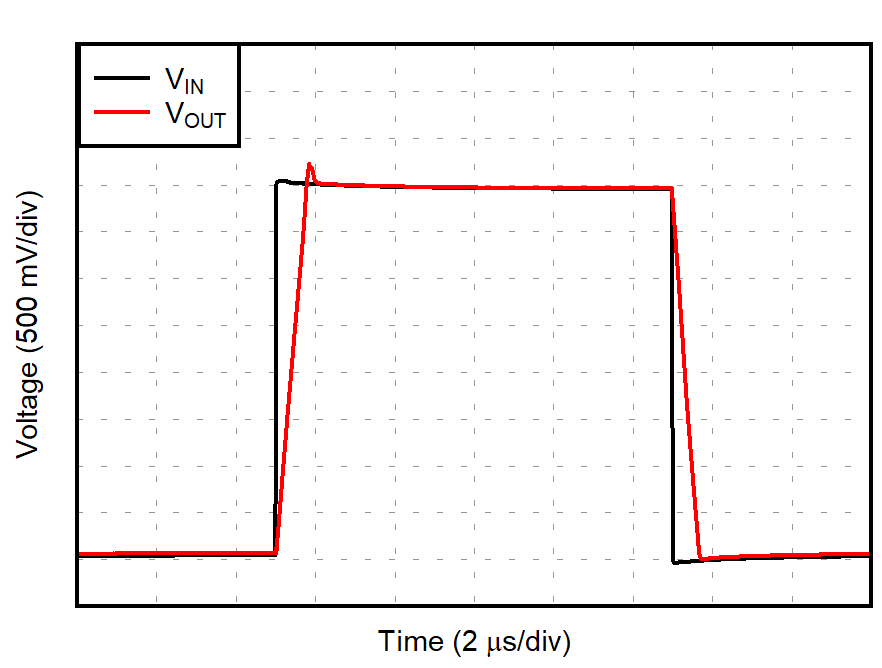
| G = 1 |
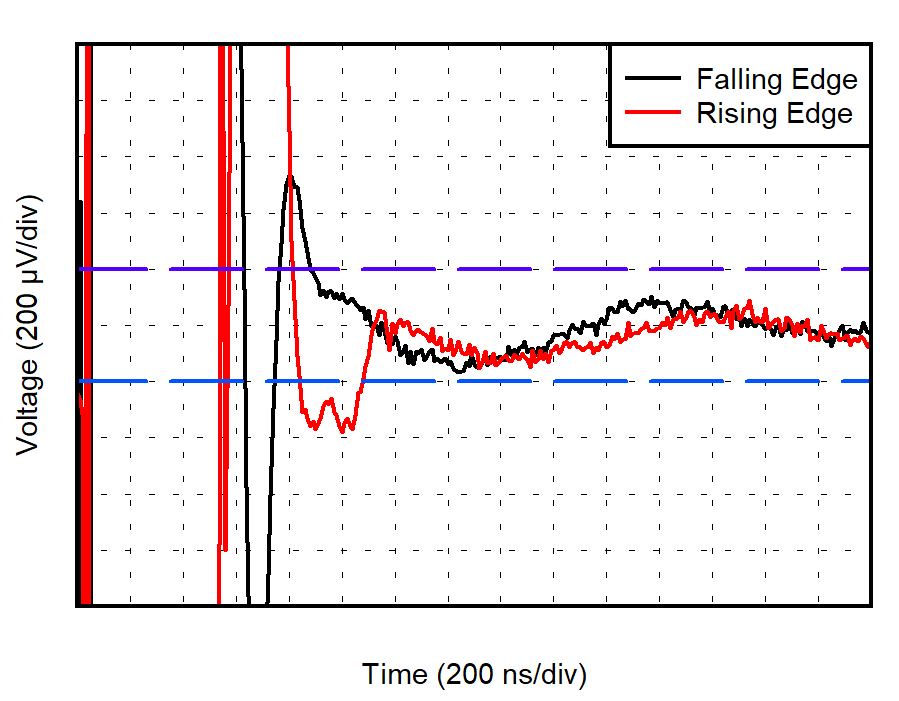
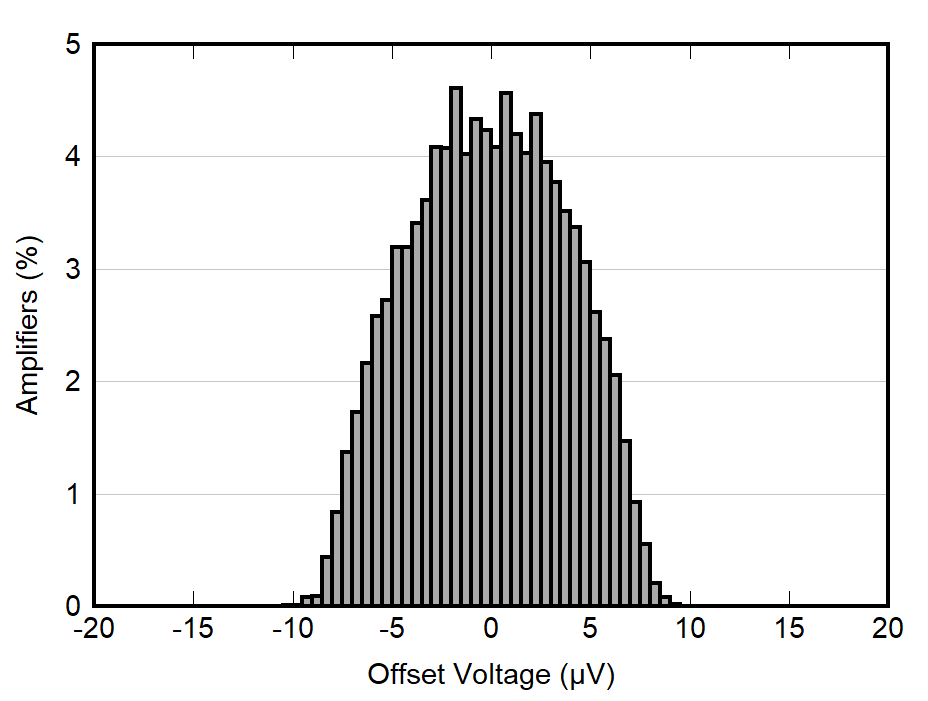
| VS = 5.0 V, VCM = 4.8 V |
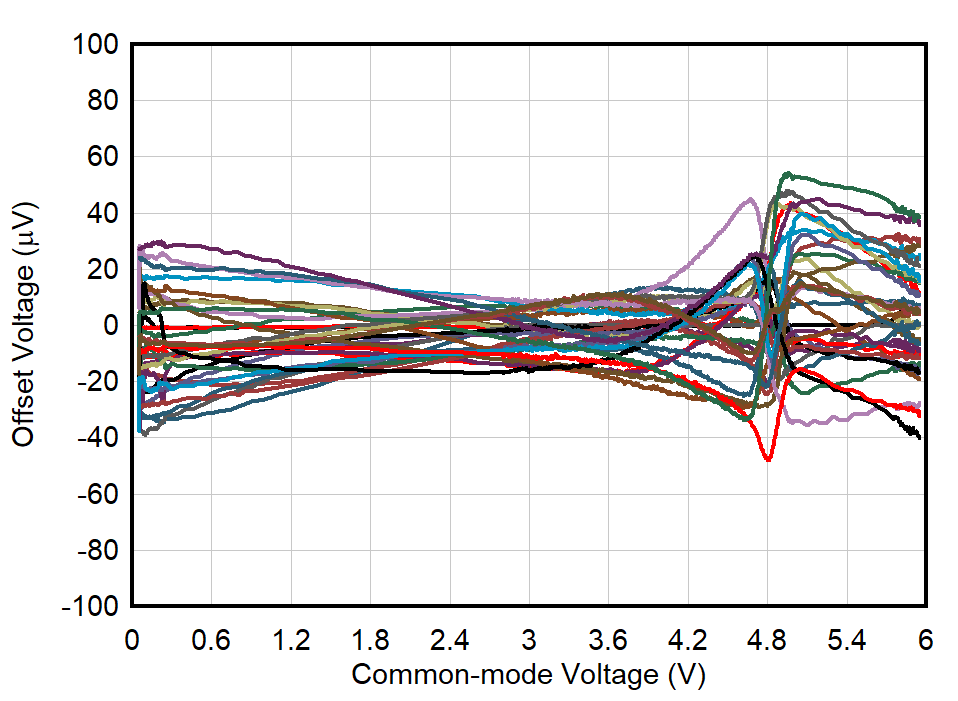
| TA = –40°C |
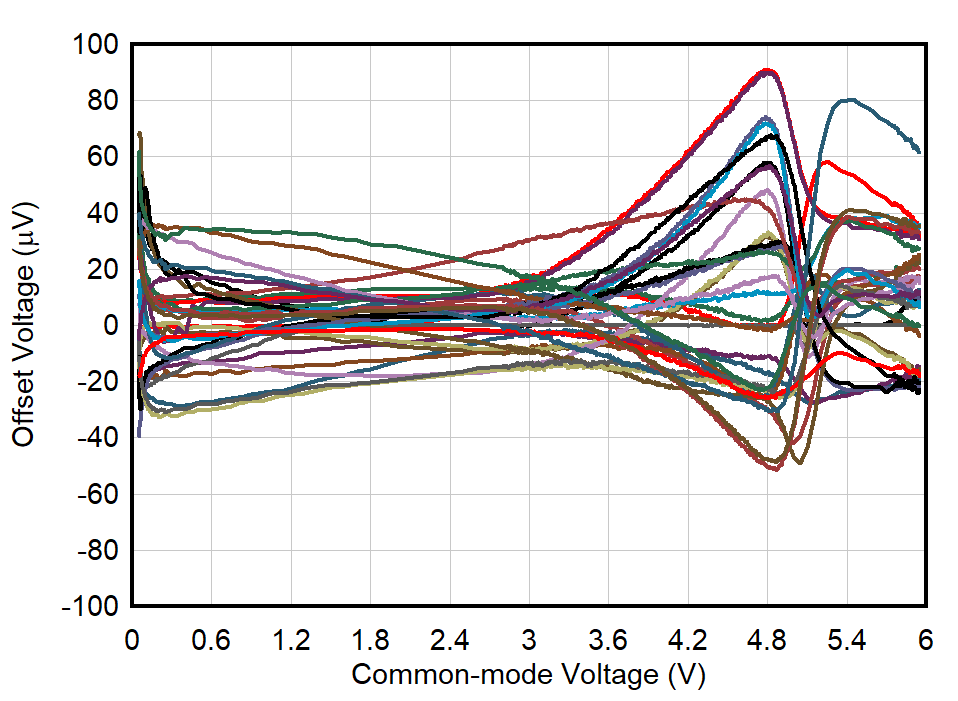
| TA = +125°C |
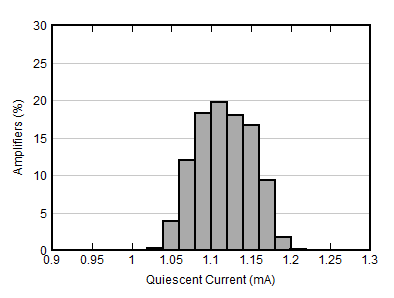
| VS = 1.7 V |
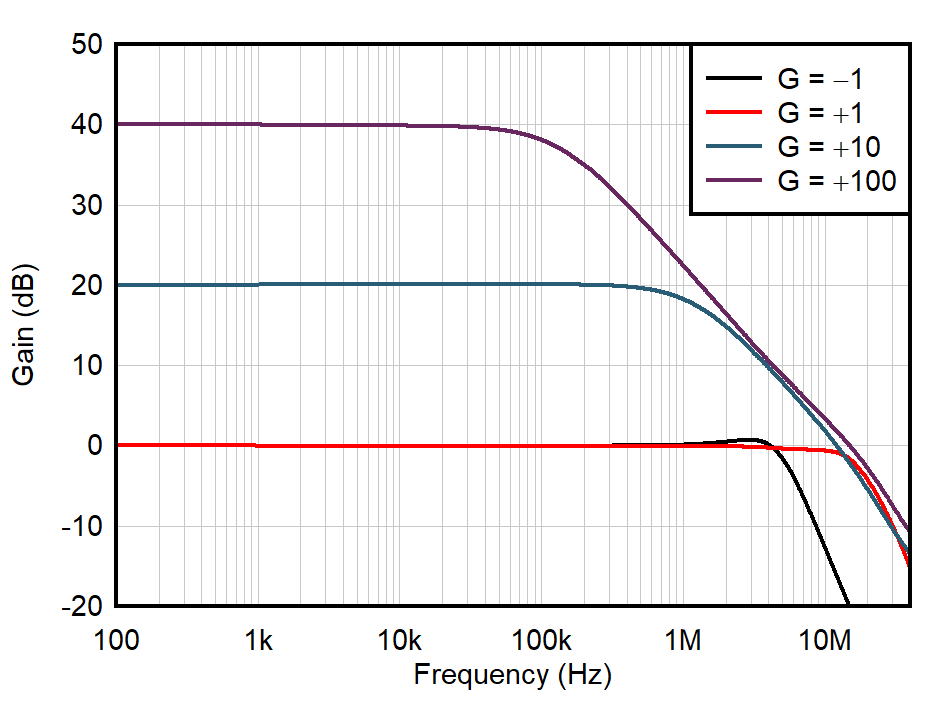
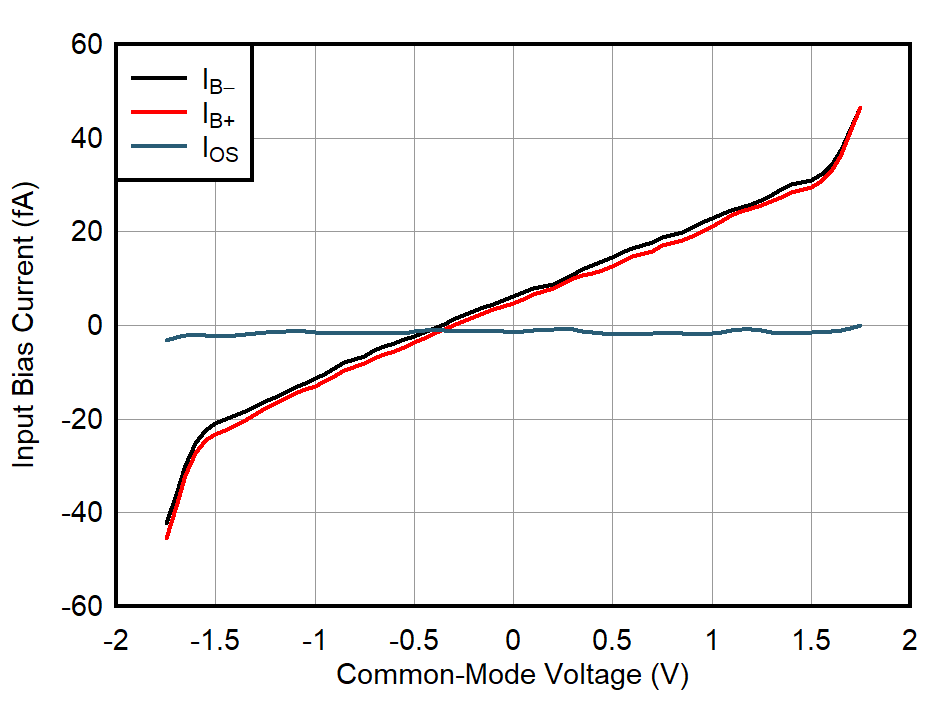
| VS = 3.3 V |
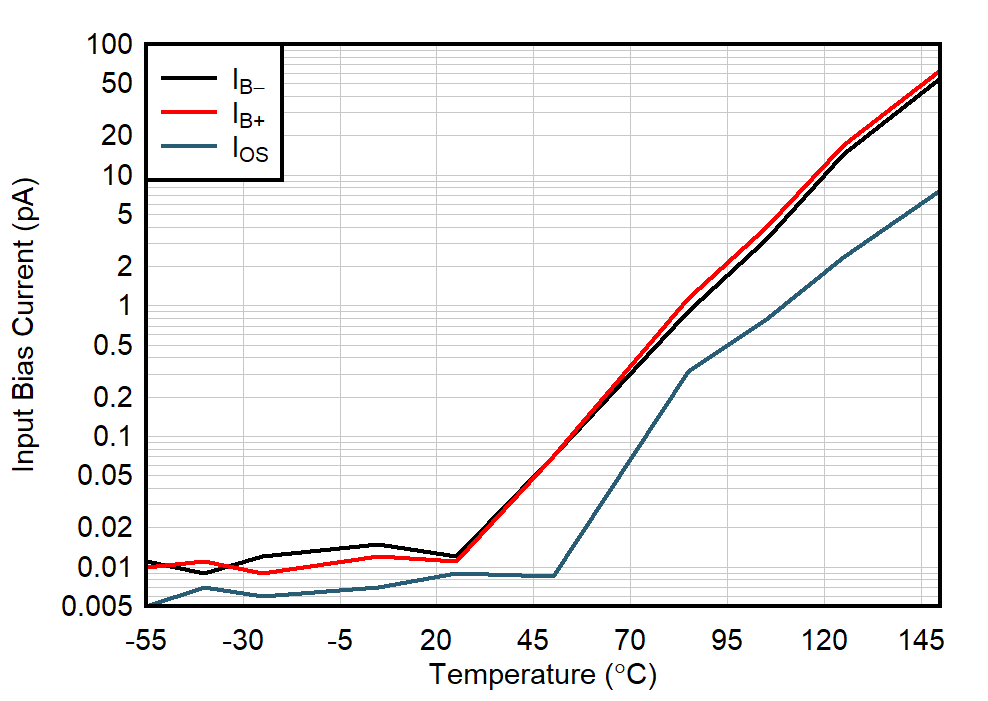
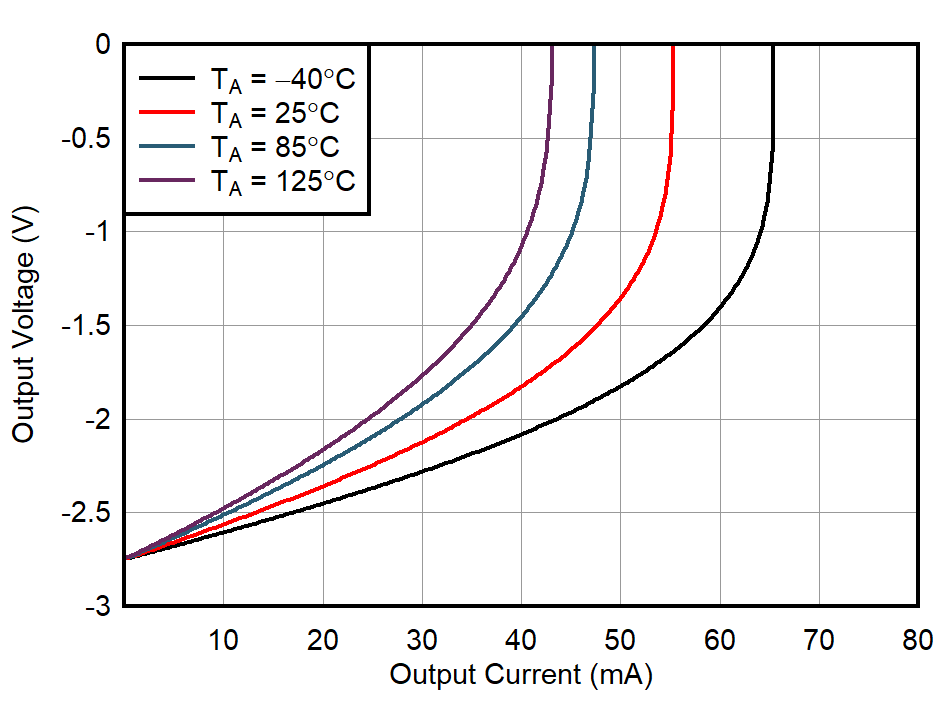
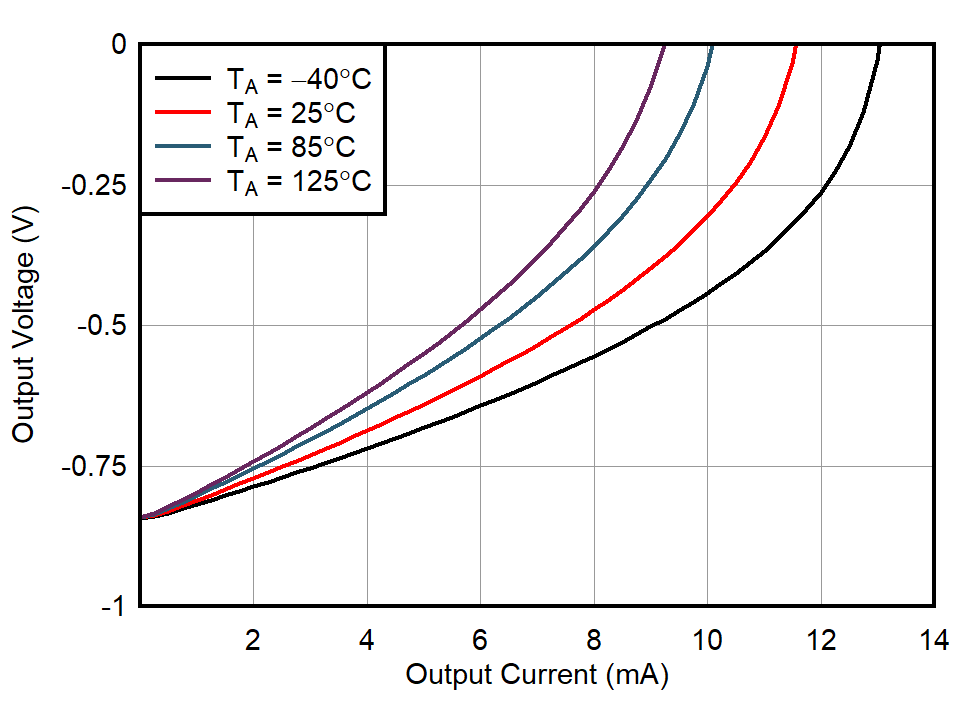
| VS = ±0.85 V |
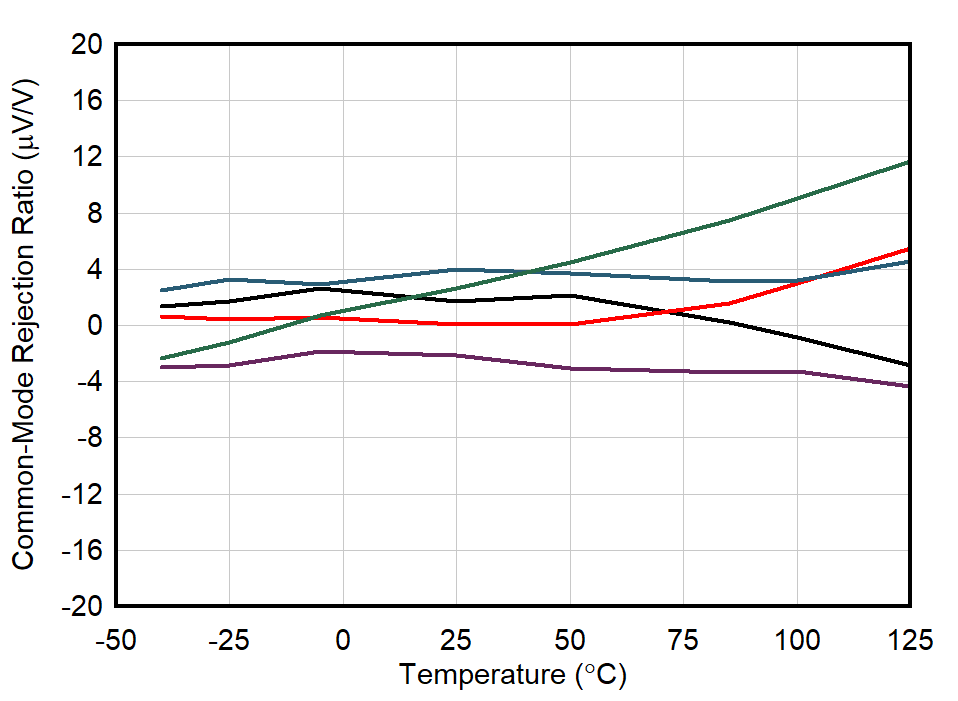
| 5 Units |
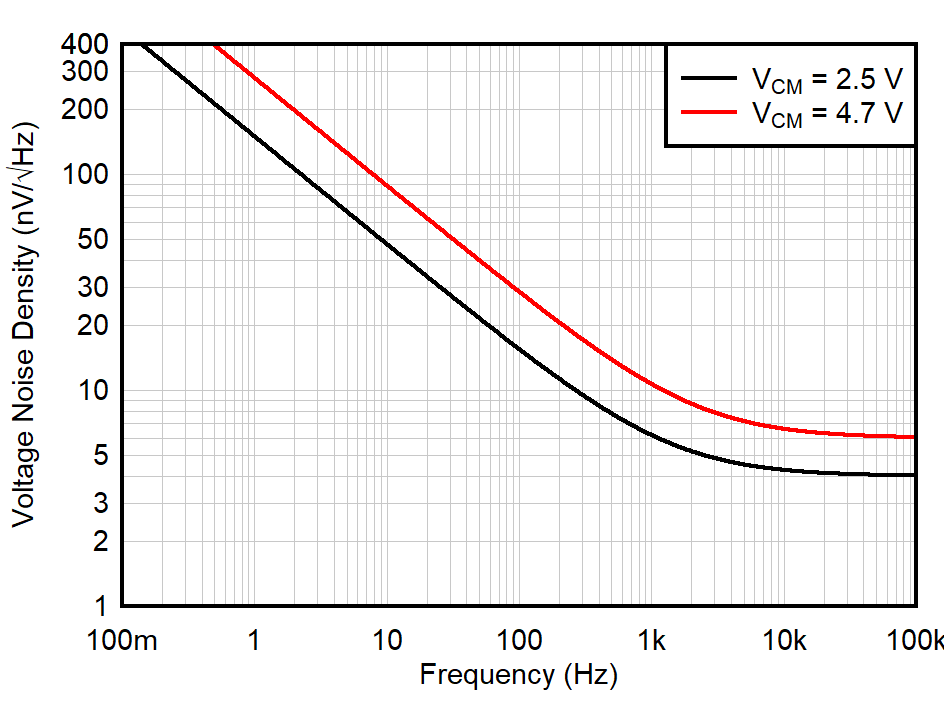
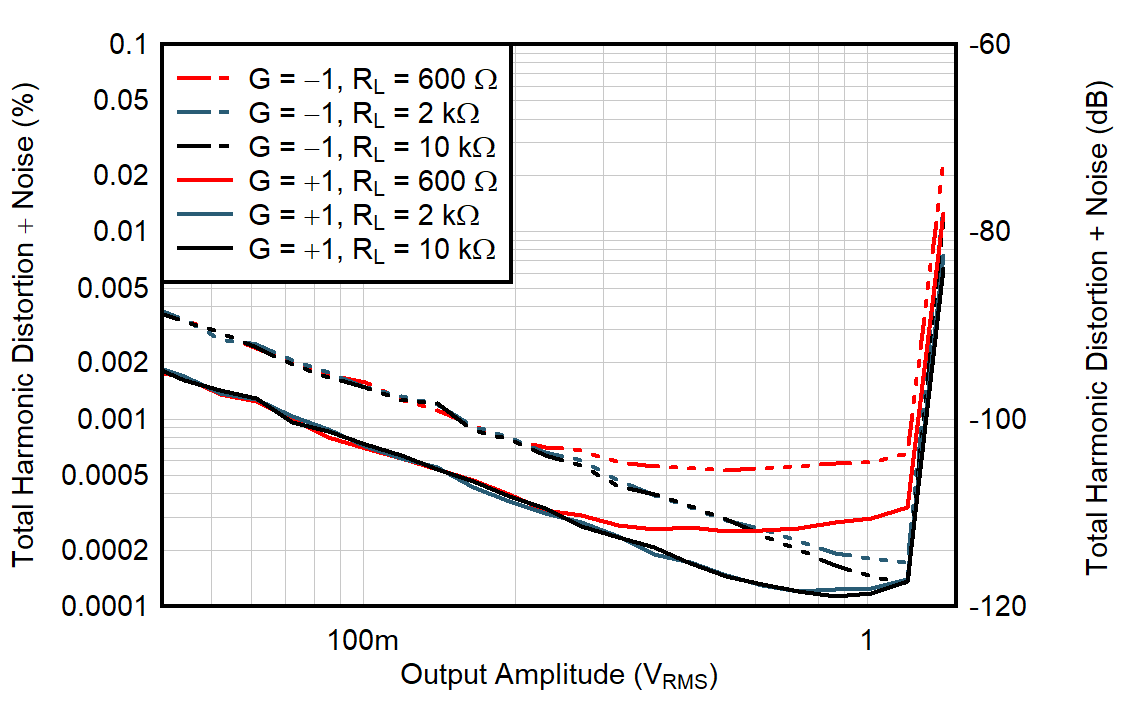
| f = 1 kHz |
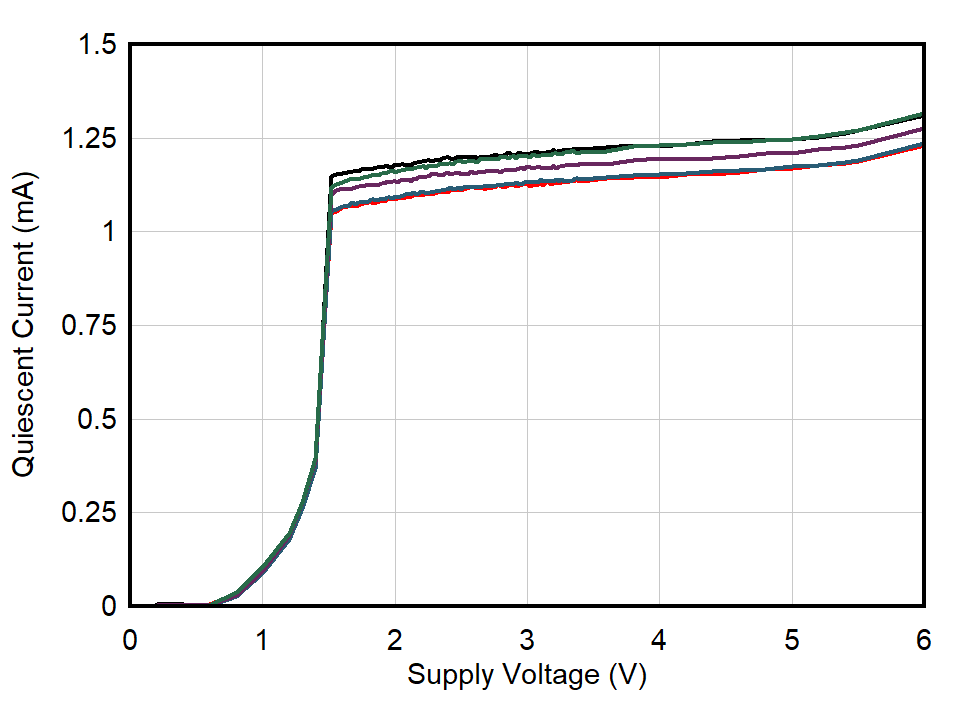
| 5 Units |
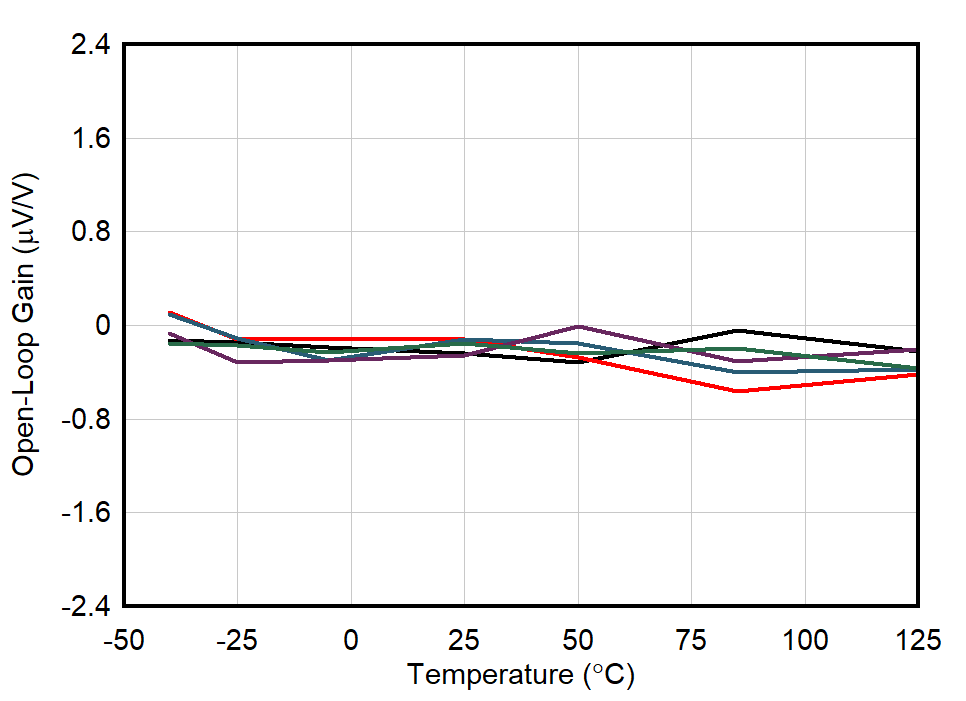
| 5 Units |
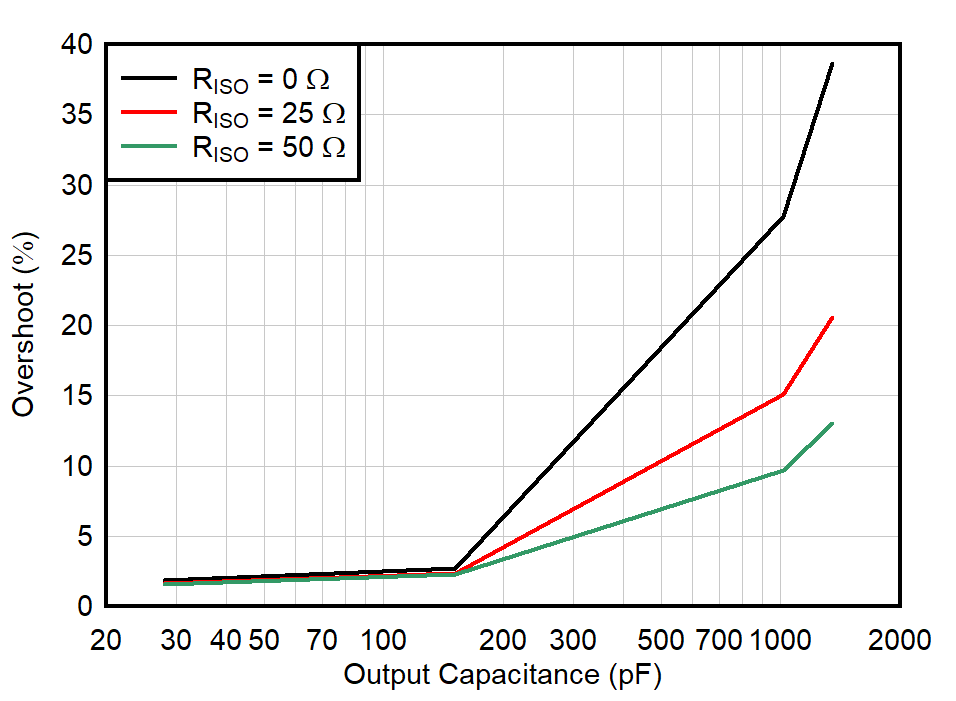
| G = –1 |
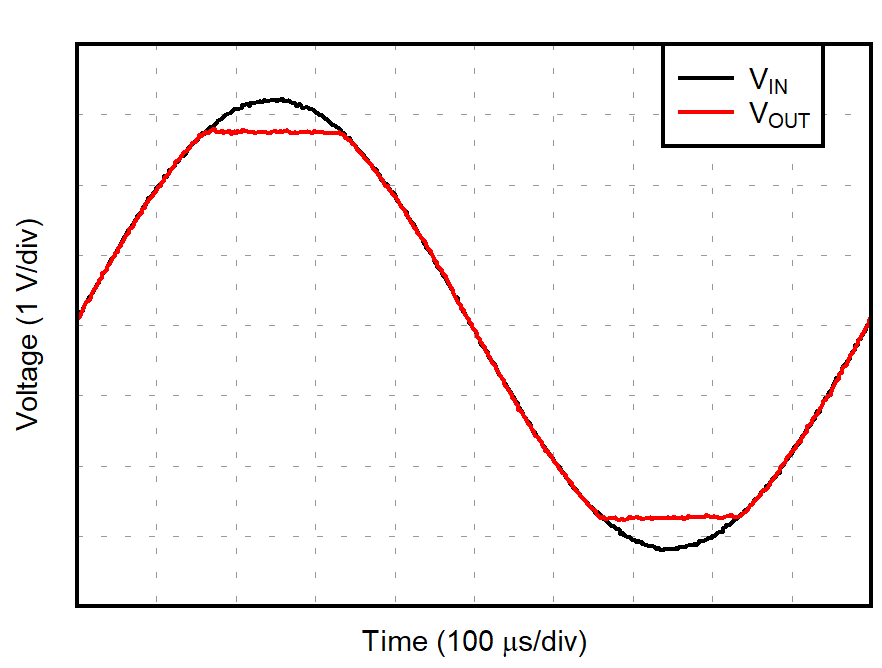
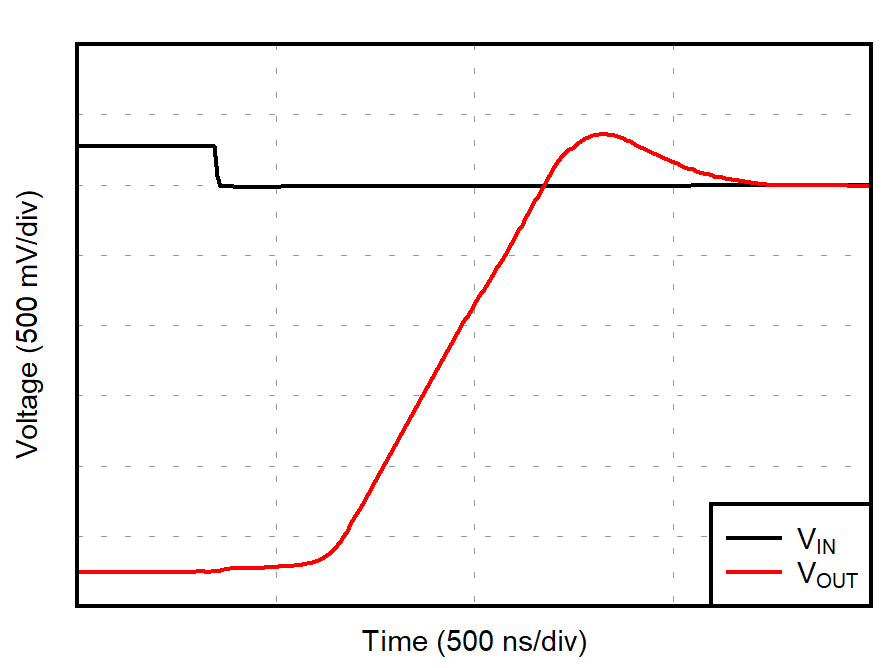
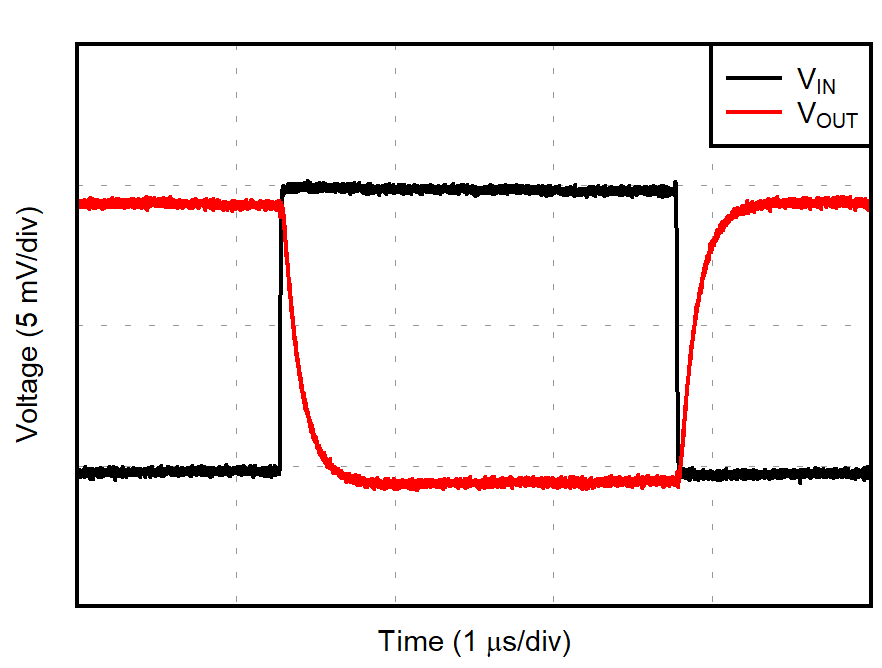
| G = –1 |
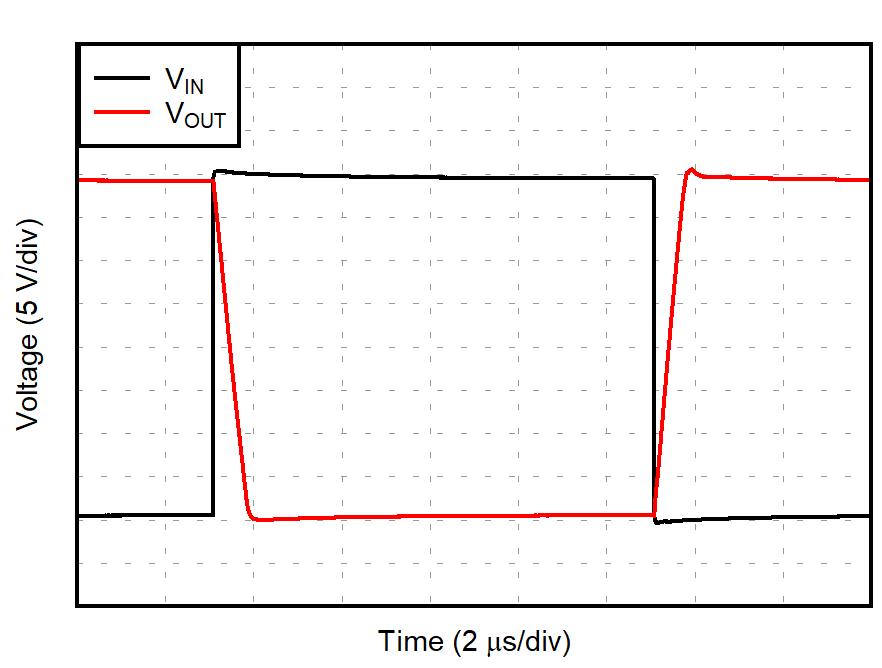
| G = –1 |
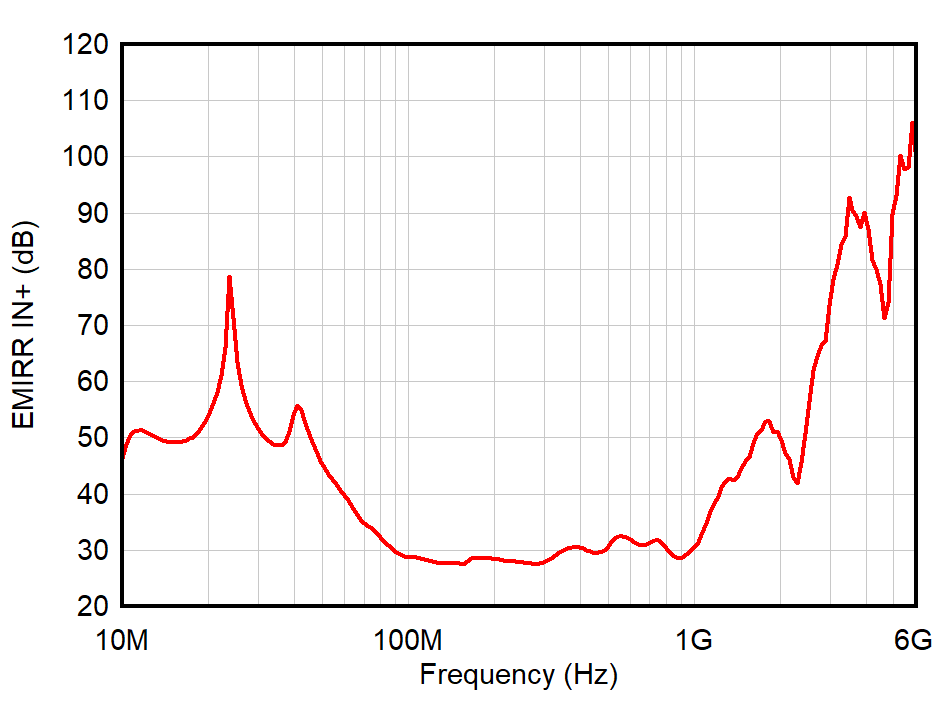
| PRF = –10 dBm |