SBOSA08 February 2021 INA183
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
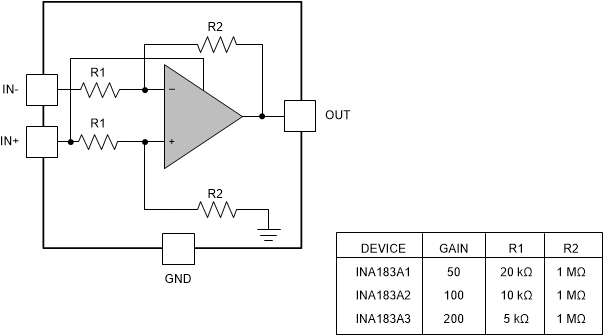
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
The simplified functional diagram below shows the device power is provided by the voltage on the IN+ pin. This diagram also shows the nominal values for the internal gain set resistors. The nominal value of these resistors can vary by 20% or more; however, the matching between these resistors is tightly controlled. The matching of these internal resistors results in a precise fixed gain that varies very little over temperature.