SBOU024C august 2004 – july 2023 PGA309
- 1
- Read This First
-
1Introduction
- 1.1 PGA309 Functional Description
- 1.2 Sensor Error Adjustment Range
- 1.3 Gain Scaling
- 1.4 Offset Adjustment
- 1.5 Voltage Reference
- 1.6 Sensor Excitation and Linearization
- 1.7 ADC for Temperature Sensing
- 1.8 External EEPROM and Temperature Coefficients
- 1.9 Fault Monitor
- 1.10 Over-Scale and Under-Scale Limits
- 1.11 Power-Up and Normal Operation
- 1.12 Digital Interface
- 1.13 Pin Configuration
- 2Detailed Description
- 3Operating Modes
-
4Digital Interface
- 4.1 Description
- 4.2 Two-Wire Interface
- 4.3 One-Wire Interface
- 4.4 One-Wire Interface Timeout
- 4.5 One-Wire Interface Timing Considerations
- 4.6 Two-Wire Access to External EEPROM
- 4.7 One-Wire Interface Initiated Two-Wire EEPROM Transactions
- 4.8 PGA309 Stand-Alone Mode and Two-Wire Transactions
- 4.9 PGA309 Two-Wire Bus Master Operation and Bus Sharing Considerations
- 4.10 One-Wire Operation with PRG Connected to VOUT
- 4.11 Four-Wire Modules and One-Wire Interface (PRG)
- 5Application Background
-
6Register Descriptions
- 6.1 Internal Register Overview
- 6.2
Internal Register Map
- 6.2.1 Register 0: Temp ADC Output Register (Read Only, Address Pointer = 00000)
- 6.2.2 Register 1: Fine Offset Adjust (Zero DAC) Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00001)
- 6.2.3 Register 2: Fine Gain Adjust (Gain DAC) Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00010)
- 6.2.4 Register 3: Reference Control and Linearization Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00011)
- 6.2.5 Register 4: PGA Coarse Offset Adjust and Gain Select/Output Amplifier Gain Select Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00100)
- 6.2.6 Register 5: PGA Configuration and Over/Under-Scale Limit Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00101)
- 6.2.7 Register 6: Temp ADC Control Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00110)
- 6.2.8 Register 7: Output Enable Counter Control Register (Read/Write, Address Pointer = 00111)
- 6.2.9 Register 8: Alarm Status Register (Read Only, Address Pointer = 01000)
- A External EEPROM Example
- B Detailed Block Diagram
- C Glossary
- Revision History
4.2 Two-Wire Interface
The industry standard Two-Wire timing diagram is shown in Figure 4-1, with the timing diagram definitions in Table 4-1. The key operating states are:
- Bus Idle: Both SDA and SCL lines remain high.
- START Condition: A START condition is defined by a change from high to low in the state of the SDA line, while the SCL line is high. Each data transfer is initiated with a START condition (see Figure 4-1).
- STOP Condition: A STOP condition is defined by a change from low to high in the state of the SDA line, while the SCL line is high. Each data transfer is terminated with a repeated START or STOP condition (see Figure 4-1).
- Data Transfer: The number of data bytes transferred between a START and a STOP condition is not limited and is determined by the master device. The receiver acknowledges the transfer of each 8-bit byte of data.
- Acknowledge: Each receiving device, when addressed, is obliged to generate an Acknowledge bit. A device acknowledges by pulling down the SDA line during the Acknowledge clock pulse in such a way that the SDA line is stable low during the high period of the Acknowledge clock pulse. Setup and hold times must be taken into account. On a master receive, the master may terminate the transaction by generating a Not Acknowledge on the last byte that has been transmitted by the slave (see Figure 4-2).
Table 4-1 Two-Wire Timing Diagram Definitions
| Parameter | Min | Max | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCL Operating Frequency | fSCL | 1 | 400 | kHz |
| Bus Free Time Between STOP and START Conditions | tBUF | 600 | ns | |
| Hold Time After Repeated START Condition. After this period, the first clock is generated. | tHDSTA | 600 | ns | |
| Repeated START Condition Setup Time | tSUSTA | 600 | ns | |
| STOP Condition Setup Time | tSUSTO | 600 | ns | |
| Data Hold Time | tHDDAT | 0 | ns | |
| Data Setup Time | tSUDAT | 100 | ns | |
| SCL Clock LOW Period | tLOW | 1300 | ns | |
| SCL Clock HIGH Period | tHIGH | 600 | ns | |
| Clock/Data Fall Time | tF | 300 | ns | |
| Clock/Data Rise Time | tR | 300 | ns | |
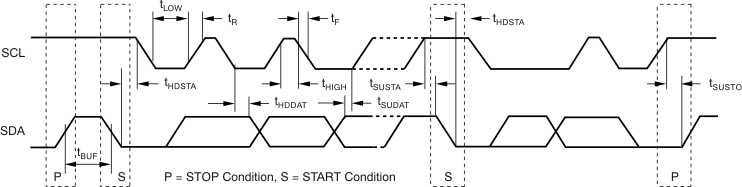 Figure 4-1 Two-Wire Timing Diagram
Figure 4-1 Two-Wire Timing Diagram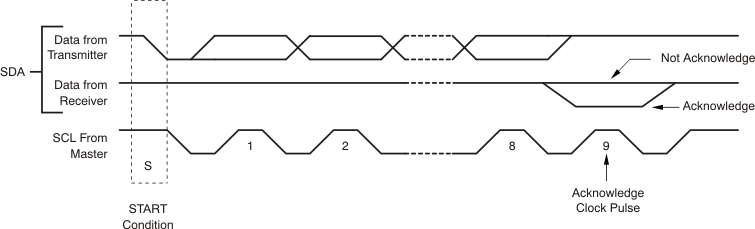 Figure 4-2 Two-Wire Start and Acknowledge
Figure 4-2 Two-Wire Start and Acknowledge