SBOU264B May 2021 – December 2022 INA232 , INA234 , INA236
4.2.3.1 Without Shunt Resistor
To configure a measurement evaluation without a shunt resistor, follow these steps:
- Connect a differential voltage across the IN+ and
IN– terminals (see Figure 4-14). Note that INA234EVM or INA236EVM is used for illustration. In screw terminal J1, IN+
and IN– are swapped for the INA232EVM (see Figure 4-15).
- If the differential voltage supply is a floating supply, connect a –0.3-V to 48-V common-mode voltage (leave powered off until finished setting up) to the inputs by connecting the positive lead of the external voltage source to either the IN+ or IN– terminal. This action effectively raises the absolute common-mode voltage of the input pins. Make sure that the differential voltage plus or minus the common-mode voltage within the –0.3-V to 48-V range.
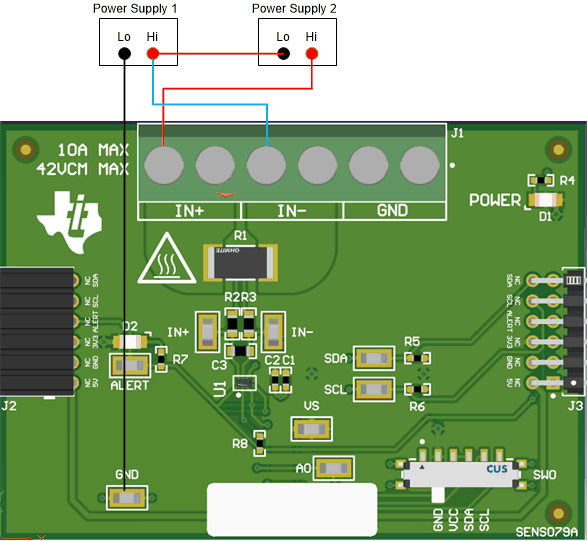 Figure 4-14 IN+ and IN– Wiring Without a Shunt
Resistor
Figure 4-14 IN+ and IN– Wiring Without a Shunt
Resistor
Figure 4-15 INA232EVM
- Connect the VBUS terminal (J1 pin 2) to the desired bus voltage (likely either IN+ or IN–).
- Connect the source ground to the GND terminal (J1 pin 1).
- Power on the system, and observe the device states and outputs through the GUI.