SBVA103 September 2023 TPS25762-Q1 , TPS25772-Q1
Application Brief
The battery supply voltage in automotive applications can vary widely depending on a number of factors such as battery condition, engine operation and system architecture. Specifically during power up, electronic devices like the TPS257x2-Q1 USB Type-C® Power Delivery (PD) controller family have specified voltage ranges for proper device power up and operation. In cases when the supply voltage can vary outside this range, device operation can be affected. The TPS257x2-Q1 USB PD controller family offers different device options to provide a wide range of possible supply voltage requirements. This application brief is intended to provide understanding of those requirements and compatible devices for use in USB PD systems.
TVSP and Boot Mode
The TPS257x2-Q1 device family supports up to nine boot modes that are detected at power up. These modes provide flexibility to meet system requirements for different use cases. More information about these boot modes can be found in the device data sheet and are summarized in Table 1.
| RTVSP (1%) | TVSP Index | I2C Addr | Logic Level | Boot Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open | 0 | 0x22 | 3.3 V | EEPROM |
| 93.1 kΩ | 1 | 0x23 | 3.3 V | External Hub/MCU |
| 47.5 kΩ | 2 | 0x22 | 1.8 V | EEPROM |
| 29.4 kΩ | 3 | 0x23 | 1.8 V | External Hub/MCU |
| 20.0 kΩ | 4 | 0x23 | 3.3 V | EEPROM |
| 14.7 kΩ | 5 | 0x22 | 3.3 V | External Hub/MCU |
| 11.0 kΩ | 6 | 0x23 | 1.38V | EEPROM |
| 8.45 kΩ | 7 | 0x22 | 1.8 V | External Hub/MCU |
| 6.65 kΩ | 8 | 0x22 | 3.3 V | Firmware Update |
The boot mode is selected by external configuration of the Transient Voltage protection and firmware Setting Pin (TVSP). Refer to the respective device data sheet for a complete description of the TVSP pin, external components and functionality. The most common boot mode is TVSP0 and is entered when there is no bias resistance to ground connected. In this mode, the TPS257x2-Q1 is connected to an external EEPROM that provides the initial configuration payload at startup required to enable the desired operation.
Device Startup
When the TPS257x2-Q1 is initially powered, the device is held in a reset state until a minimum supply voltage on VIN of 5.3V (typ) and the enable threshold at the EN/UVLO pin is achieved. At this point, the internal circuitry is enabled and VIN is monitored for a valid threshold required for TVSP boot mode detection. Once the supply voltage at the VIN pin is ≥ 7.6V, the TVSP boot mode detection is initiated and the current flowing through RTVSP is measured. This process takes approximately 300msec to complete and the result determines the configured boot index.
Supply Voltage Dependency
For a stable, monotonically increasing supply voltage, the TVSP boot mode measurement is completed as described. However, when VIN is allowed to fall below 7.6 V after device startup and initiation of the TVSP measurement, an incorrect boot mode can be detected. This process can result in undesired device startup and inability to properly initiate USB system charging when sink devices are connected to the charging port or multiple ports.
An example of such a supply variation that can affect device startup is crank testing as defined by ISO 16750-2 Road vehicles – Environmental conditions and testing for electrical and electronic equipment applicable to automotive applications.
Cranking tests are performed to simulate the droop in supply voltage when a combustion engine is started due to the load of the starter motor. Battery voltage levels are temperature-dependent during start-up, with severe cold causing the largest drop in voltage, also referred to as Cold Crank. Figure 1 represents a typical starting profile. Voltage thresholds and timing can vary based on specific OEM requirements for a given system.
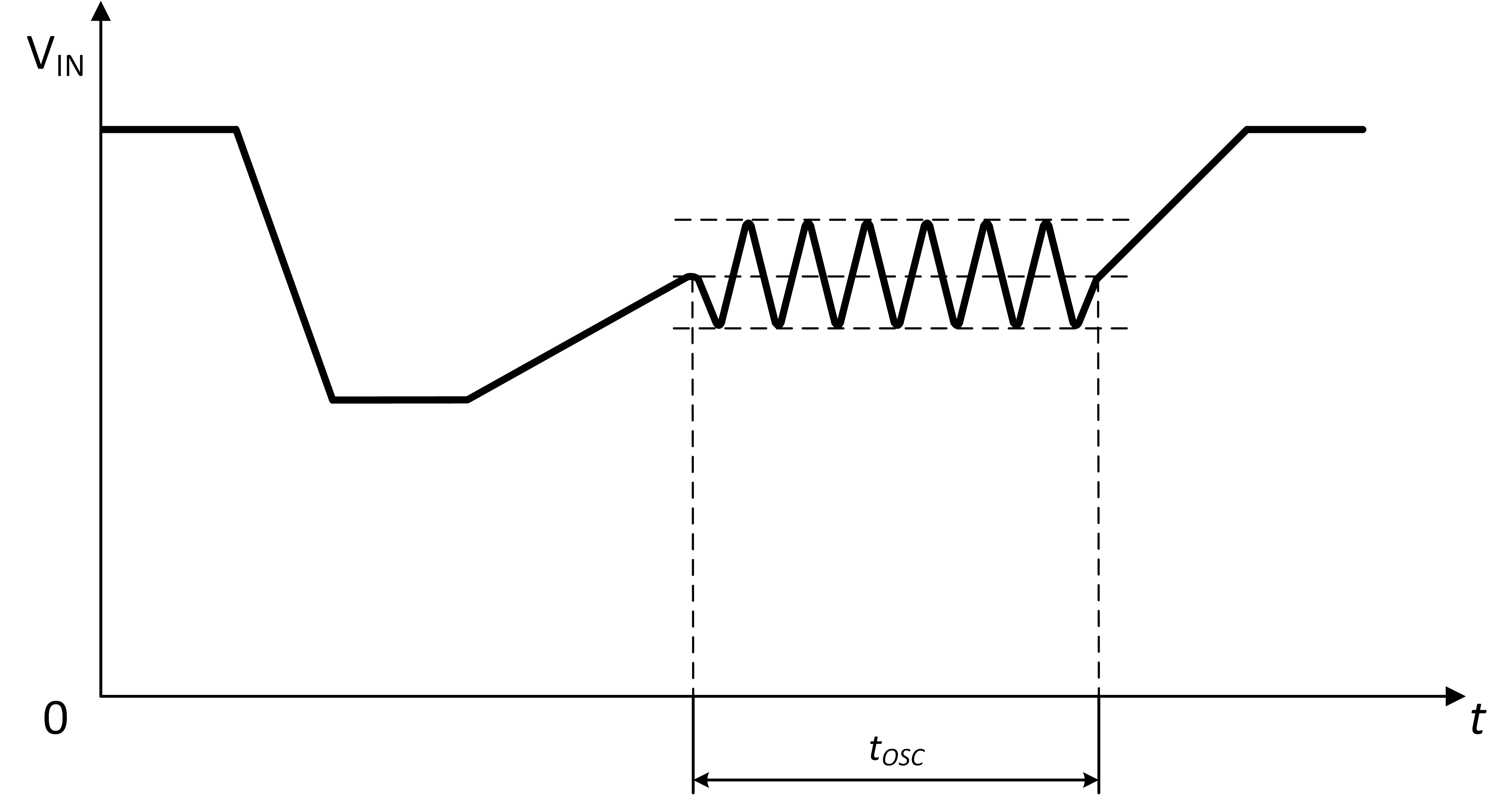 Figure 1 Typical Automotive Starting Profile
Figure 1 Typical Automotive Starting ProfileDuring cold crank, VIN of the TPS257x2-Q1 supplied by the battery can become astable as the starter motor is engaged to start the engine. For the purposes of this document, astable is defined as oscillating between two states. During the time, tOSC, the voltage of VIN can rise and fall periodically until the engine is started and VIN reaches a steady-state, operational level.
Device Selection
The TPS257x2-Q1 device family provides support for such system supply voltage variations as outlined in Table 2.
| Generic Part Number (GPN) | Orderable Part Number (OPN) | Astable VIN Boot Support | Configurable Boot Mode Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| TPS25762-Q1 | TPS25762CQRQLRQ1 | VIN-dependent | Yes |
| TPS25762-Q1 | TPS25762CAQRQLRQ1 | Yes | No |
| TPS25772-Q1 | TPS25772CQRQLRQ1 | VIN-dependent | Yes |
| TPS25772-Q1 | TPS25772CAQRQLRQ1 | Yes | No |
For systems providing a supply voltage, VIN, that stays at or above 7.6 V after reaching this threshold, the TPS257x2CQx devices are recommended. These devices provide full boot mode support for a wide range of application use cases. For use cases with an astable VIN profile (for example, cold crank), if VIN does not fall below 7.6 V during TVSP boot mode detection at power up, the TPS257x2CQx devices remain a valid option. Depending on the required boot mode required, the TPS257x2CAQx devices are also applicable for such VIN supply use cases.
However, for systems that can experience an astable supply voltage at power up where VIN both rises above and falls below 7.6V during TVSP boot mode detection, the TPS257x2CAQx devices are recommended. These device variants are configured to support TVSP0 for typical operation and TVSP8 for firmware update and do not support boot modes 1 through 7. Modes supported by the TPS257x2CAQx are defined in Table 3. The boot methodology of the TPS257x2CAQx devices is designed to tolerate the lower VIN supply instability in such applications to boot correctly into TVSP0.
| RTVSP (1%) | TVSP Index | I2C Addr | Logic Level | Boot Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open | 0 | 0x22 | 3.3 V | EEPROM |
| 5.6 kΩ | 8 | 0x22 | 3.3 V | Firmware Update |
While these device variants limit boot mode support, they are useful for application use cases where VIN can vary across the 7.6 V threshold at power on during boot mode detection.
For applications that can experience astable supply behavior AND require boot support from an external hub/MCU (for example, TVSP indices 1, 3, 5, or 7), the recommendation is to use external control to achieve correct device bootup. For example, a retry methodology can be designed into the hub or MCU operation to toggle the TPS257x2CQx EN input pin to restart boot operation in case I2C communication by the hub/MCU is not acknowledged as expected for normal operation. Alternately, the hub or MCU can hold the EN pin during power up for the TPS257x2CQx device until stable VIN is detected and then begin I2C communication once the device is enabled. Such system-level controls can be implemented in cases where the device can boot incorrectly due to the previously described astable VIN supply upon initial power up.
References
- ISO 16750-2:2012 Road vehicles – Environmental conditions and testing for electrical and electronic equipment – Part 2: Electrical loads, section 4.6
- Texas Instruments, TPS25772-Q1 Automotive Dual USB Type-C® Power Delivery Controller with Buck- Boost Regulator, data sheet.
- Texas Instruments, TPS25762-Q1 Automotive USB Type-C® Power Delivery Controller with Buck-Boost Regulator, data sheet.