SBVS082K June 2007 – June 2024 TPS74901
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.1.3 Dropout Voltage
The TPS74901 offers very low dropout performance, making the device designed for high-current low VIN and low VOUT applications. The low dropout of the TPS74901 allows the device to be used in place of a DC/DC converter and still achieve good efficiencies. This capability provides designers with the power architecture for applications to achieve the smallest, simplest, and lowest-cost solution.
There are two different specifications for dropout voltage with the TPS74901. The first specification (see Figure 7-1) is referred to as VIN dropout and is used when an external bias voltage is applied to achieve low dropout. This specification assumes that VBIAS is at least 3.25V above VOUT, which is the case for VBIAS when powered by a 5V rail with 5% tolerance and with VOUT = 1.5V (3.25V is a test condition of this device and can be adjusted by referring to Figure 5-11). If VBIAS is higher than VOUT + 3.25V, VIN dropout is less than specified.
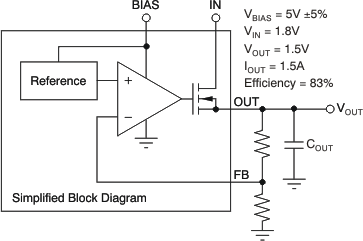 Figure 7-1 Typical Application of the TPS74901 Using an Auxiliary Bias Rail
Figure 7-1 Typical Application of the TPS74901 Using an Auxiliary Bias RailThe second specification (shown in Figure 7-2) is referred to as VBIAS dropout and is applied to applications where IN and BIAS are tied together. This option allows the device to be used in applications where an auxiliary bias voltage is not available or low dropout is not required. Dropout is limited by BIAS in these applications because VBIAS provides the gate drive to the pass transistor; therefore, VBIAS must be 1.75V above VOUT. Because of this usage, IN and BIAS tied together easily consume a huge amount of power. Pay attention not to exceed the power rating of the device package.
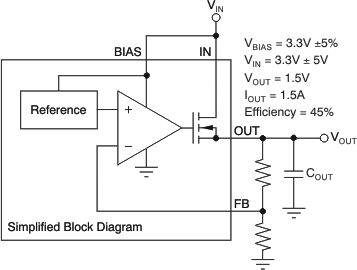 Figure 7-2 Typical Application of the TPS74901 Without an Auxiliary Bias
Figure 7-2 Typical Application of the TPS74901 Without an Auxiliary Bias