SBVS291C April 2017 – December 2020 TPS7A84A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: TPS7A8400A
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: TPS7A8401A
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: TPS7A8400A
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: TPS7A8401A
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1
External Component Selection
- 8.1.1.1 Adjustable Operation
- 8.1.1.2 ANY-OUT Programmable Output Voltage
- 8.1.1.3 ANY-OUT Operation
- 8.1.1.4 Increasing ANY-OUT Resolution for LILO Conditions
- 8.1.1.5 Current Sharing
- 8.1.1.6 Recommended Capacitor Types
- 8.1.1.7 Input and Output Capacitor Requirements (CIN and COUT)
- 8.1.1.8 Feed-Forward Capacitor (CFF)
- 8.1.1.9 Noise-Reduction and Soft-Start Capacitor (CNR/SS)
- 8.1.2 Start-Up
- 8.1.3 AC and Transient Performance
- 8.1.4 DC Performance
- 8.1.5 Sequencing Requirements
- 8.1.6 Negatively Biased Output
- 8.1.7 Reverse Current Protection
- 8.1.8 Power Dissipation (PD)
- 8.1.1
External Component Selection
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
8.1.8.2 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation (RACO)
The operational area of an LDO is limited by the dropout voltage, output current, junction temperature, and input voltage. The recommended area for continuous operation for a linear regulator can be separated into the following parts, shown in Figure 8-14:
- Limited by dropout: Dropout voltage limits the minimum differential voltage between the input and the output (VIN – VOUT) at a given output current level; see the Section 8.1.4.2 section for more details.
- Limited by rated output current: The rated output current limits the maximum recommended output current level. Exceeding this rating causes the device to fall out of specification.
- Limited by thermals: The shape of the slope is given by Equation 13. The slope is nonlinear because the junction temperature of the LDO is controlled by the power dissipation across the LDO; therefore, when VIN – VOUT increases, the output current must decrease in order to ensure that the rated junction temperature of the device is not exceeded. Exceeding this rating can cause the device to fall out of specifications and reduces long-term reliability.
- Limited by VIN range: The rated input voltage range governs both the minimum and maximum of VIN – VOUT.
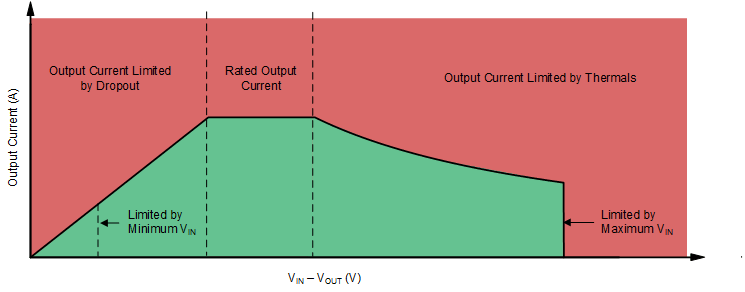 Figure 8-14 Continuous Operation Slope Region Description
Figure 8-14 Continuous Operation Slope Region DescriptionFigure 8-15 to Figure 8-20 show the recommended area of operation curves for this device on a JEDEC-standard, high-K board with a RθJA = 43.4°C/W, as given in the Thermal Information table in the Section 6 section.
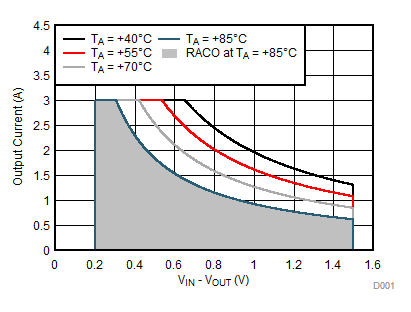 Figure 8-15 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 0.9 V
Figure 8-15 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 0.9 V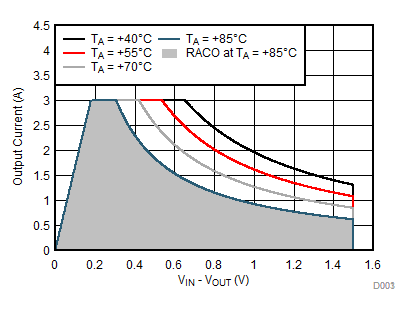 Figure 8-17 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 1.8 V
Figure 8-17 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 1.8 V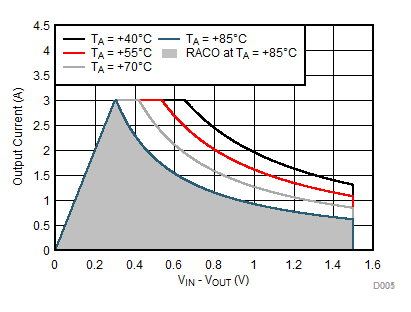 Figure 8-19 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 8-19 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 3.3 V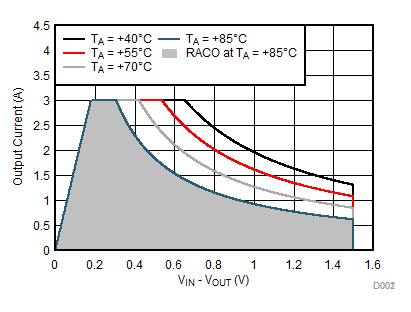 Figure 8-16 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 1.2 V
Figure 8-16 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 1.2 V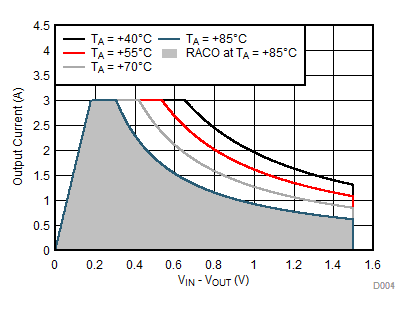 Figure 8-18 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 2.5 V
Figure 8-18 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 2.5 V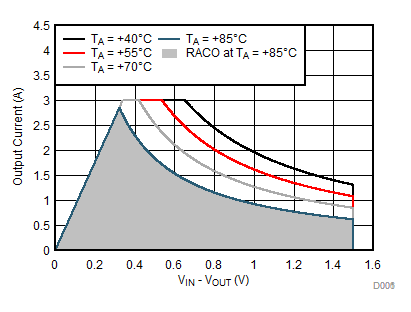 Figure 8-20 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 5 V
Figure 8-20 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation for VOUT = 5 V