SBVS296B September 2017 – June 2018 TPS7A52-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Recommended Capacitor Types
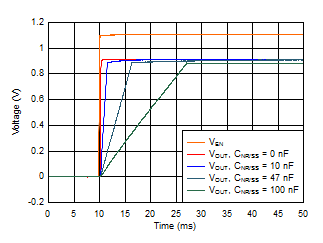
- 8.1.2 Soft-Start and Inrush Current
- 8.1.3 Optimizing Noise and PSRR
- 8.1.4 Charge Pump Noise
- 8.1.5 Current Sharing
- 8.1.6 Adjustable Operation
- 8.1.7 Power-Good Operation
- 8.1.8 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Operation
- 8.1.9 Dropout Voltage (VDO)
- 8.1.10 Load Transient Response
- 8.1.11 Reverse Current Protection Considerations
- 8.1.12 Power Dissipation (PD)
- 8.1.13 Estimating Junction Temperature
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.6 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VIN = 1.4 V or VIN = VOUT(NOM) + 0.4 V (whichever is greater), VBIAS = open, VOUT(NOM) = 0.8 V, VEN = 1.1 V, COUT = 22 µF, CNR/SS = 0 nF, CFF = 0 nF, and PG pin pulled up to VIN with 100 kΩ (unless otherwise noted)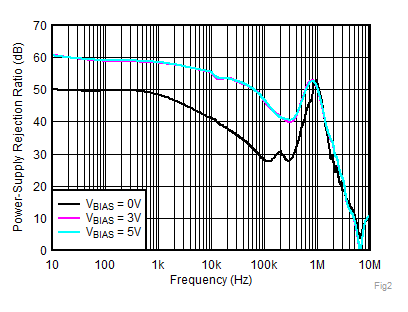
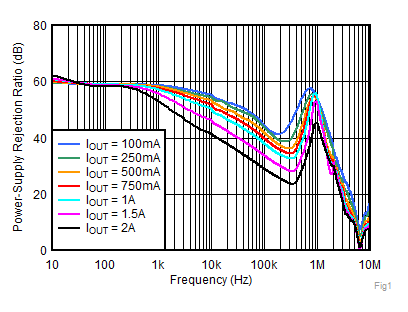
| VIN = 1.4 V, IOUT = 1 A,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10 nF |
| VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V, VBIAS = 5.0 V, IOUT = 2 A,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10 nF |
| VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V, VOUT = 1 V, IOUT = 2 A,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10 nF |
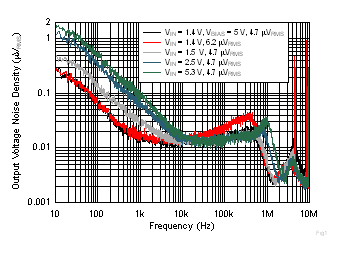
| IOUT = 2 A, CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10 nF,
RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz |
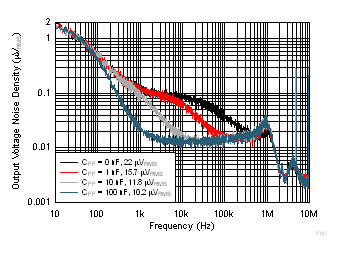
| VIN = 1.2 V, VOUT = 0.9 V, VBIAS = 5.0 V, IOUT = 2 A,
CFF = 10 nF |
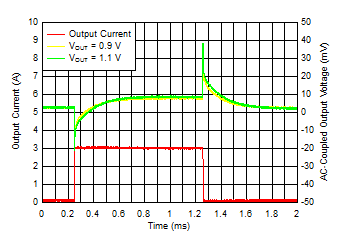
| IOUT, DC = 100 mA,
CNR/SS = CFF = 10 nF, slew rate = 1 A/µs |
| RGR package, VOUT = 0.9 V, VIN = 1.2 V, VBIAS = 5.0 V,
CNR/SS = CFF = 10 nF, slew rate = 1 A/µs |
| RGR package, IOUT = 2 A, VBIAS = 6.5 V |
| RGR package, VIN = 1.1 V, VBIAS = 3 V |
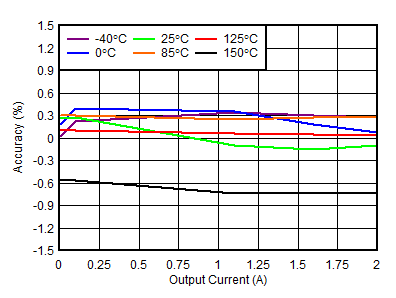
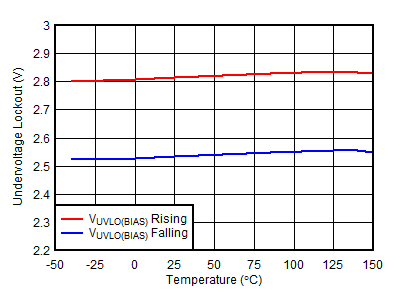
| VIN = 1.4 V, VBIAS = 0 V |
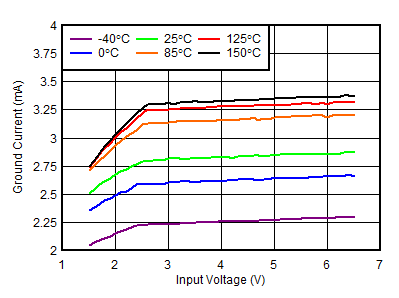
| VBIAS = 0 V, IOUT = 5 mA |
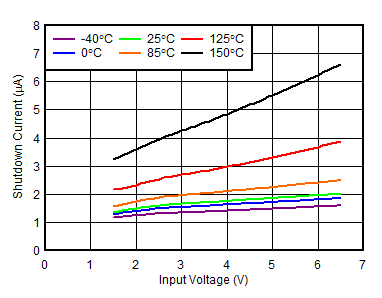
| VBIAS = 0 V |
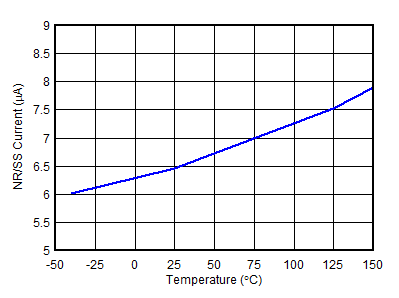
| VBIAS = 0 V |
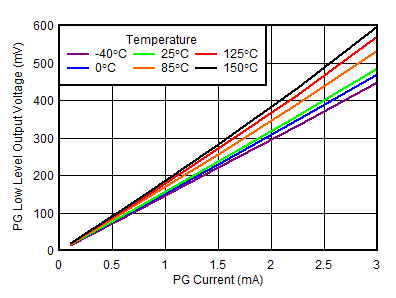
| VIN = 1.1 V |
| IOUT = 2 A, VBIAS = 5 V,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10 nF |
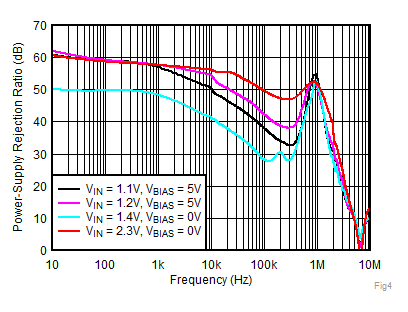
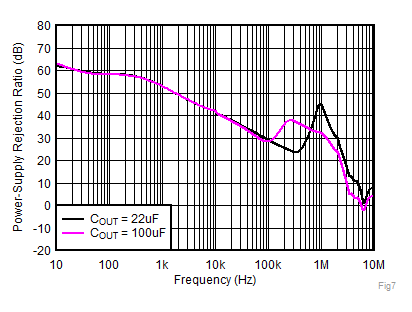
| IOUT = 1 A,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10 nF |
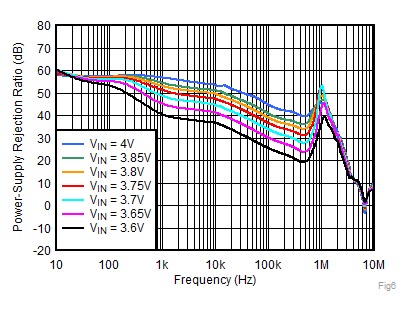
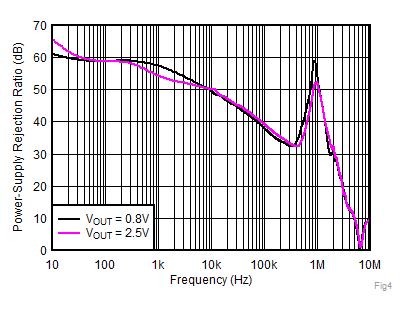
| VOUT = 3.3 V, IOUT = 2 A,
CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10 nF |
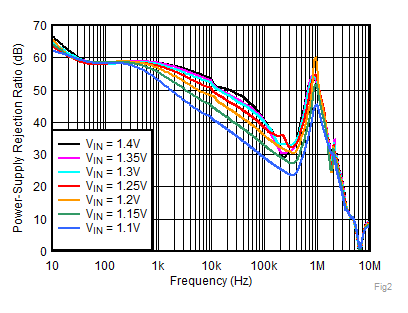
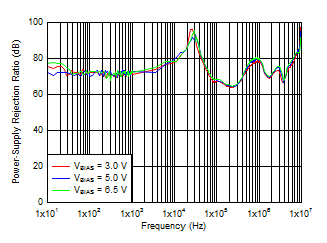 Figure 8. VBIAS PSRR vs Frequency and VBIAS
Figure 8. VBIAS PSRR vs Frequency and VBIAS 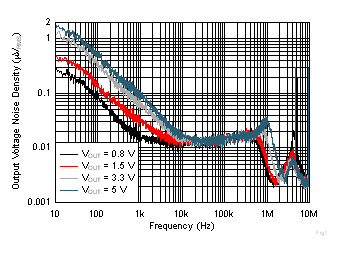
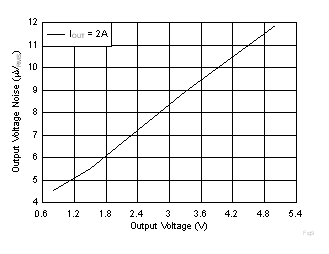
| VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V and VBIAS = 5 V for VOUT ≤ 2.2 V, IOUT = 2 A,, CNR/SS = 10 nF, CFF = 10 nF,
RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz |

| VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V, VBIAS = 5 V, IOUT = 2 A,
CFF = 10 nF, RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz |
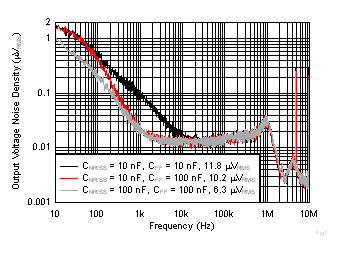
| VOUT = 5 V, IOUT = 2 A, CFF = 10 nF,
RMS noise BW = 10 Hz to 100 kHz |
||
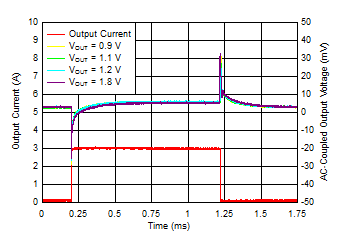
| VIN = VOUT + 0.3 V, VBIAS = 5 V, IOUT, DC = 100 mA, slew rate = 1 A/µs, CNR/SS = CFF = 10 nF |
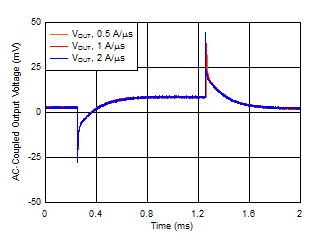
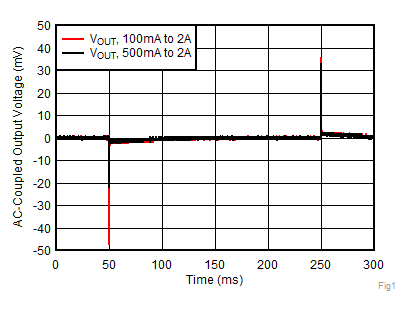
| VOUT = 5 V, IOUT, DC = 100 mA, IOUT = 100 mA to 2 A,
CNR/SS = CFF = 10 nF |
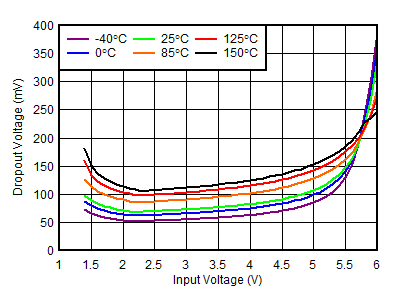
| IOUT = 2 A, VBIAS = 0 V | ||
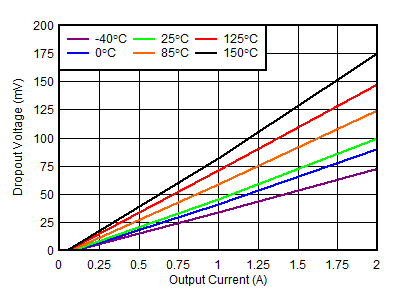
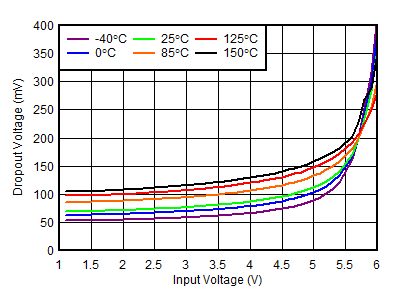
| RGR package, VIN = 1.4 V, VBIAS = 0 V |
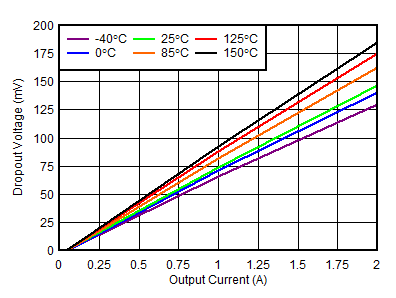
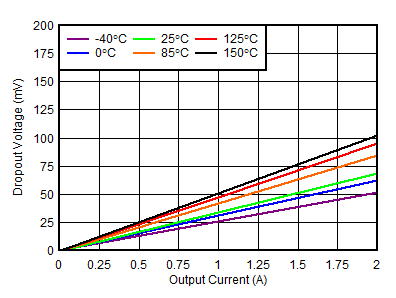
| RGR package, VIN = 5.5 V |
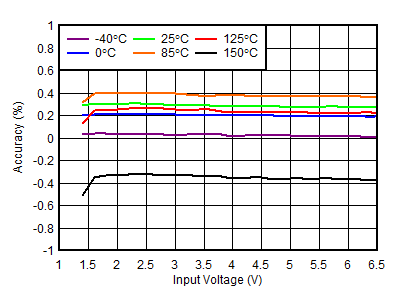
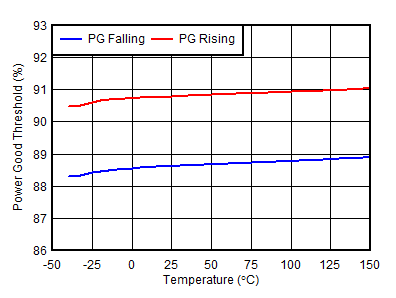
| VOUT = 0.8 V, VBIAS = 0 V, IOUT = 5 mA |
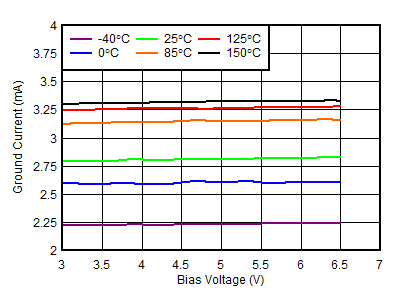
| VIN = 1.1 V, IOUT = 5 mA |
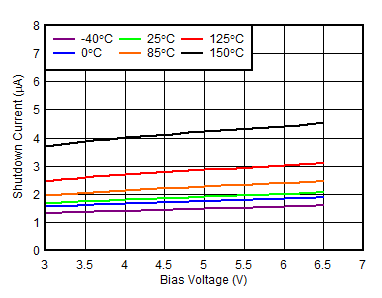
| VIN = 1.1 V |
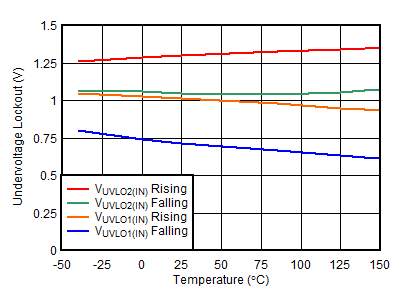
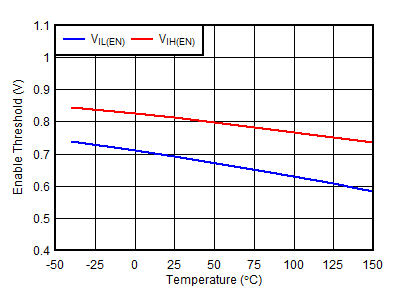
| VIN = 1.4 V, 6.5 V |
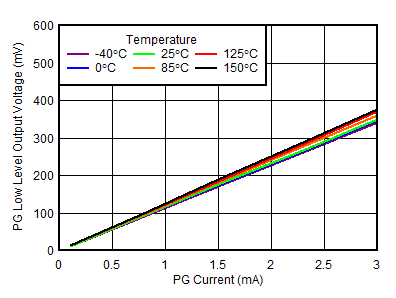
| VIN = 6.5 V |
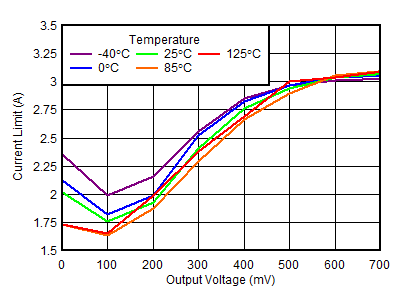
| Temperature limited because of power dissipation |