SCDS419E November 2020 – July 2024 TMUX6208 , TMUX6209
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Thermal Information
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Source or Drain Continuous Current
- 6.6 ±15 V Dual Supply: Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 ±15 V Dual Supply: Switching Characteristics
- 6.8 36 V Single Supply: Electrical Characteristics
- 6.9 36 V Single Supply: Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 12 V Single Supply: Electrical Characteristics
- 6.11 12 V Single Supply: Switching Characteristics
- 6.12 ±5 V Dual Supply: Electrical Characteristics
- 6.13 ±5 V Dual Supply: Switching Characteristics
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7.1 On-Resistance
- 7.2 Off-Leakage Current
- 7.3 On-Leakage Current
- 7.4 Transition Time
- 7.5 tON(EN) and tOFF(EN)
- 7.6 Break-Before-Make
- 7.7 tON (VDD) Time
- 7.8 Propagation Delay
- 7.9 Charge Injection
- 7.10 Off Isolation
- 7.11 Crosstalk
- 7.12 Bandwidth
- 7.13 THD + Noise
- 7.14 Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.7 Ultra-Low Charge Injection
Figure 8-1 shows that the TMUX620x have a transmission gate topology. Any mismatch in the stray capacitance associated with the NMOS and PMOS causes an output level change whenever the switch is opened or closed.
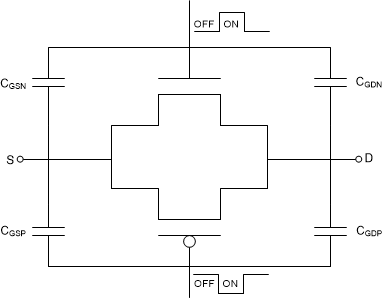 Figure 8-1 Transmission Gate Topology
Figure 8-1 Transmission Gate TopologyThe TMUX620x contain specialized architecture to reduce charge injection on the Drain (D). To further reduce charge injection in a sensitive application, a compensation capacitor (Cp) can be added on the Source (Sx). This will ensure that excess charge from the switch transition will be pushed into the compensation capacitor on the Source (Sx) instead of the Drain (D). As a general rule of thumb, Cp should be 20x larger than the equivalent load capacitance on the Drain (D). Figure 8-2 shows charge injection variation with different compensation capacitors on the Source side. This plot was captured on the TMUX6219 as part of the TMUX62xx family with a 100pF load capacitance.
 Figure 8-2 Charge Injection Compesation
Figure 8-2 Charge Injection Compesation