SCEA065B November 2018 – March 2021 SN74AVC4T774 , SN74AXC1T45 , SN74AXC4T245 , SN74AXC4T774 , SN74AXC8T245 , SN74AXC8T245-Q1 , SN74AXCH1T45 , SN74AXCH4T245 , SN74AXCH8T245
2.1 General Purpose Input Output (GPIO)
All microprocessors have General purpose input output (GPIO) ports for communication with the peripheral devices. However, the core and peripheral chips might work at different voltage levels, which is why the system would need a level shifter. If the required signals are not shifted to the voltage at which the microprocessor is operating, it impacts the reliability of communication. The SN74AXC1T45 can be implemented as part of the I/O circuit, especially in single channel signals such as control inputs. The SN74AXC1T45 provides a solution for voltage translating I/O pins such as the following:
- Enable
- Restart
- Clock buffering
- Power good
- Error flag
- Reset
- Memory error
- Processor overheat
- LED driving as shown in Figure 2-1
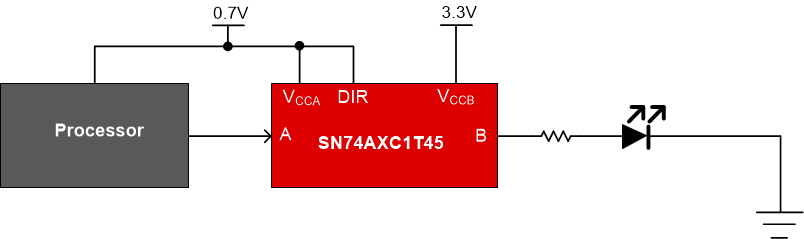 Figure 2-1 GPIO Translation Using SN74AXC1T45 for LED
Driving
Figure 2-1 GPIO Translation Using SN74AXC1T45 for LED
Driving