SCLS739E September 2013 – March 2024 SN74LV1T08
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Related Products
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.2.1 Up Translation
Input signals can be up translated using the SN74LV1T08. The voltage applied at VCC will determine the output voltage and the input thresholds as described in the Recommended Operating Conditions and Electrical Characteristics tables. When connected to a high-impedance input, the output voltage will be approximately VCC in the HIGH state, and 0V in the LOW state.
The inputs have reduced thresholds that allow for input HIGH state levels, which are much lower than standard values. For example, standard CMOS inputs for a device operating at a 5V supply will have a VIH(MIN) of 3.5V. For the SN74LV1T08, VIH(MIN) with a 5V supply is only 2V, which would allow for up-translation from a typical 2.5V to 5V signals.
Ensure that the input signals in the HIGH state are above VIH(MIN) and input signals in the LOW state are lower than VIL(MAX) as shown in Figure 8-2.
Up Translation Combinations are as follows:
- 1.8V VCC – Inputs from 1.2V
- 2.5V VCC – Inputs from 1.8V
- 3.3V VCC – Inputs from 1.8V and 2.5V
- 5.0V VCC – Inputs from 2.5V and 3.3V
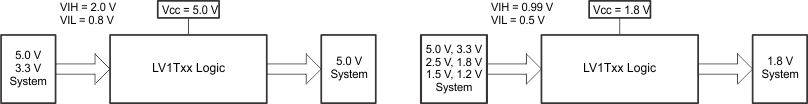 Figure 8-2 LVxT Up and Down Translation
Example
Figure 8-2 LVxT Up and Down Translation
Example