SCLS739E September 2013 – March 2024 SN74LV1T08
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Related Products
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.2 LVxT Enhanced Input Voltage
The SN74LV1T08 belongs to TI's LVxT family of logic devices with integrated voltage level translation. This family of devices was designed with reduced input voltage thresholds to support up-translation, and inputs tolerant of signals with up to 5.5V levels to support down-translation. For proper functionality, input signals must remain at or above the specified VIH(MIN) level for a HIGH input state, and at or below the specified VIL(MAX) for a LOW input state. Figure 8-1 shows the typical VIH and VIL levels for the LVxT family of devices, as well as the voltage levels for standard CMOS devices for comparison.
The inputs are high impedance and are typically modeled as a resistor in parallel with the input capacitance given in the Electrical Characteristics. The worst case resistance is calculated with the maximum input voltage, given in the Absolute Maximum Ratings, and the maximum input leakage current, given in the Electrical Characteristics, using Ohm's law (R = V ÷ I).
Input signals must transition between valid logic states quickly, as defined by the input transition rate in the Recommended Operating Conditions table. Failing to meet this specification will result in excessive power consumption and could cause oscillations. More details can be found in the Implications of Slow or Floating CMOS Inputs application report.
Do not leave inputs floating at any time during operation. Unused inputs must be terminated at a valid high or low voltage level. If a system will not be actively driving an input at all times, then a pull-up or pull-down resistor can be added to provide a valid input voltage during these times. The resistor value will depend on multiple factors; however, a 10kΩ resistor is recommended and will typically meet all requirements.
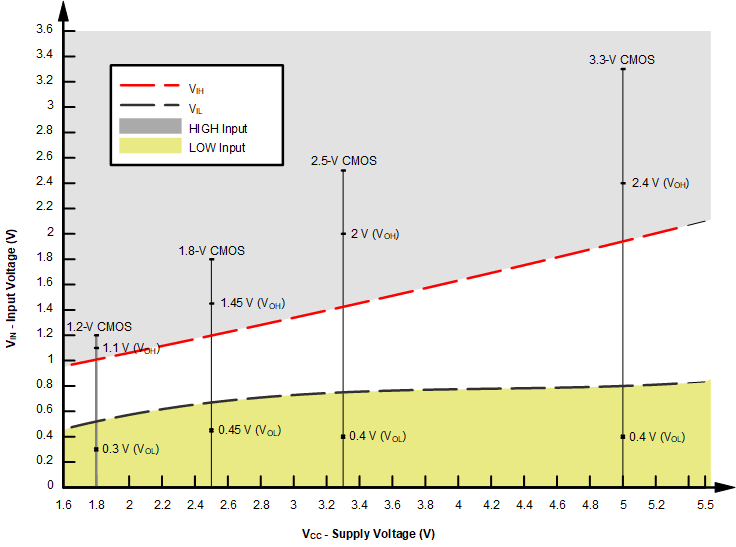 Figure 8-1 LVxT Input Voltage
Levels
Figure 8-1 LVxT Input Voltage
Levels