SCPS290A April 2024 – June 2024 TCAL6416R
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.2.1 Minimizing ICC When I/Os Control LEDs
As shown in Figure 8-2, normally I/Os are connected to VCCP through a resistor when the I/Os are used to control LEDs. For a P-port configured as an input, current consumption increases as VI becomes lower than VCCP. The LEDs are diodes with threshold voltage VT, and are off when a P-port is configured as an input, but the voltages at the P-port will be equal to VCCPCC minus VT.
For battery-powered applications, it is essential that the voltage of P-ports controlling the LEDs is greater than or equal to VCCP when the P-ports are configured as input to minimize current consumption. Figure 8-2 shows a high-value resistor in parallel with the LED. Figure 8-3 shows VCCP less than the LED supply voltage by at least VT. Both of these methods maintain the I/O VI at or above VCCP and prevent additional supply current consumption when the P-port is configured as an input and the LED is off.
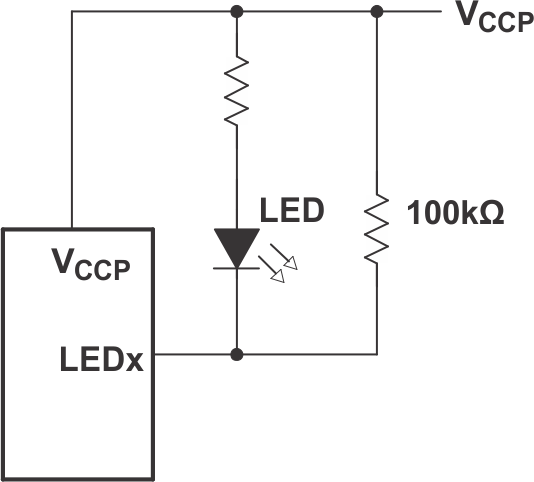 Figure 8-2 High-Value Resistor in Parallel with LED
Figure 8-2 High-Value Resistor in Parallel with LED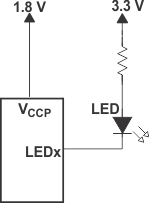 Figure 8-3 Device
Supplied by a Lower Voltage
Figure 8-3 Device
Supplied by a Lower Voltage