-
TPS25830A-Q1Functional Safety FIT Rate, FMD and Pin FMA
TPS25830A-Q1Functional Safety FIT Rate, FMD and Pin FMA
Trademarks
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1 Overview
This document contains information for the TPS25830A-Q1 (VQFN package) to aid in a functional safety system design. Information provided are:
- Functional safety failure in time (FIT) rates of the semiconductor component estimated by the application of industry reliability standards
- Component failure modes and their distribution (FMD) based on the primary function of the device
- Pin failure mode analysis (pin FMA)
Figure 1-1 shows the device functional block diagram for reference.
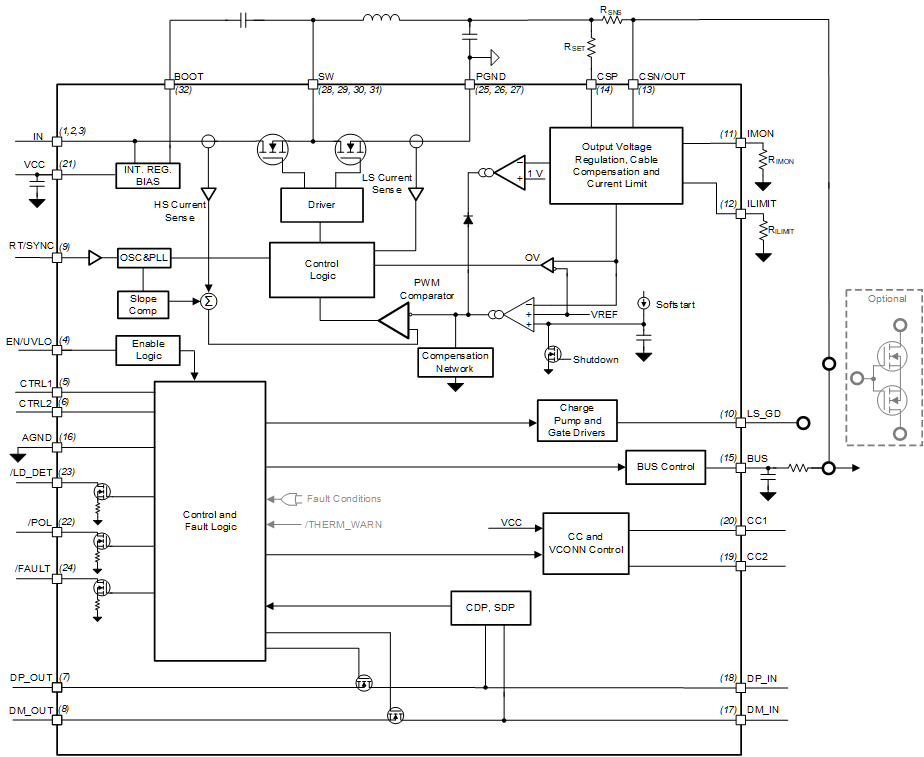 Figure 1-1 Functional Block
Diagram
Figure 1-1 Functional Block
DiagramThe TPS25830A-Q1 was developed using a quality-managed development process, but was not developed in accordance with the IEC 61508 or ISO 26262 standards.
2 Functional Safety Failure In Time (FIT) Rates
This section provides functional safety failure in time (FIT) rates for the TPS25830A-Q1 based on two different industry-wide used reliability standards:
- Table 2-1 provides FIT rates based on IEC TR 62380 / ISO 26262 part 11
- Table 2-2 provides FIT rates based on the Siemens Norm SN 29500-2
| FIT IEC TR 62380 / ISO 26262 | FIT (Failures Per 109 Hours) |
|---|---|
| Total component FIT rate | 27 |
| Die FIT rate | 8 |
| Package FIT rate | 19 |
The failure rate and mission profile information in Table 2-1 comes from the reliability data handbook IEC TR 62380 / ISO 26262 part 11:
- Mission profile: Motor control from table 11
- Power dissipation: 1300 mW
- Climate type: World-wide table 8
- Package factor (lambda 3): Table 17b
- Substrate material: FR4
- EOS FIT rate assumed: 0 FIT
| Table | Category | Reference FIT Rate | Reference Virtual TJ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Digital, Analog, Mixed | 25 FIT | 55°C |
The reference FIT rate and reference virtual TJ (junction temperature) in Table 2-2 come from the Siemens Norm SN 29500-2 tables 1 through 5. Failure rates under operating conditions are calculated from the reference failure rate and virtual junction temperature using conversion information in SN 29500-2 section 4.
3 Failure Mode Distribution (FMD)
The failure mode distribution estimation for the TPS25830A-Q1 in Table 3-1 comes from the combination of common failure modes listed in standards such as IEC 61508 and ISO 26262, the ratio of sub-circuit function size and complexity, and from best engineering judgment.
The failure modes listed in this section reflect random failure events and do not include failures resulting from misuse or overstress.
| Die Failure Modes | Failure Mode Distribution (%) |
|---|---|
| SW no output | 25% |
| CSP and CSN/OUT not in specification – voltage or timing | 20% |
| LS_GD no output | 5% |
| LS_GD not in specification – voltage or timing | 5% |
| DP_IN, DM_IN – no output | 10% |
| DP_IN, DM_IN – not in specification – voltage or timing | 10% |
| CC1, CC2 no output | 5% |
| CC1, CC2 not in specification – voltage or timing | 10% |
| FAULT, POL, LD_DET false trip or fails to trip | 5% |
| Short circuit any two pins | 5% |
The FMD in Table 3-1 excludes short circuit faults across the isolation barrier. Faults for short circuit across the isolation barrier can be excluded according to ISO 61800-5-2:2016 if the following requirements are fulfilled:
- The signal isolation component is OVC III according to IEC 61800-5-1. If a SELV/PELV power supply is used, pollution degree 2/OVC II applies. All requirements of IEC 61800-5-1:2007, 4.3.6 apply.
- Measures are taken to ensure that an internal failure of the signal isolation component cannot result in excessive temperature of its insulating material.
Creepage and clearance requirements should be applied according to the specific equipment isolation standards of an application. Care should be taken to maintain the creepage and clearance distance of a board design to ensure that the mounting pads of the isolator on the printed-circuit board do not reduce this distance.
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a failure mode analysis (FMA) for the pins of the TPS25830A-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality. |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality. |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation. |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance. |
Figure 4-1 shows the TPS25830A-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins, see the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the TPS25830A-Q1 data sheet.
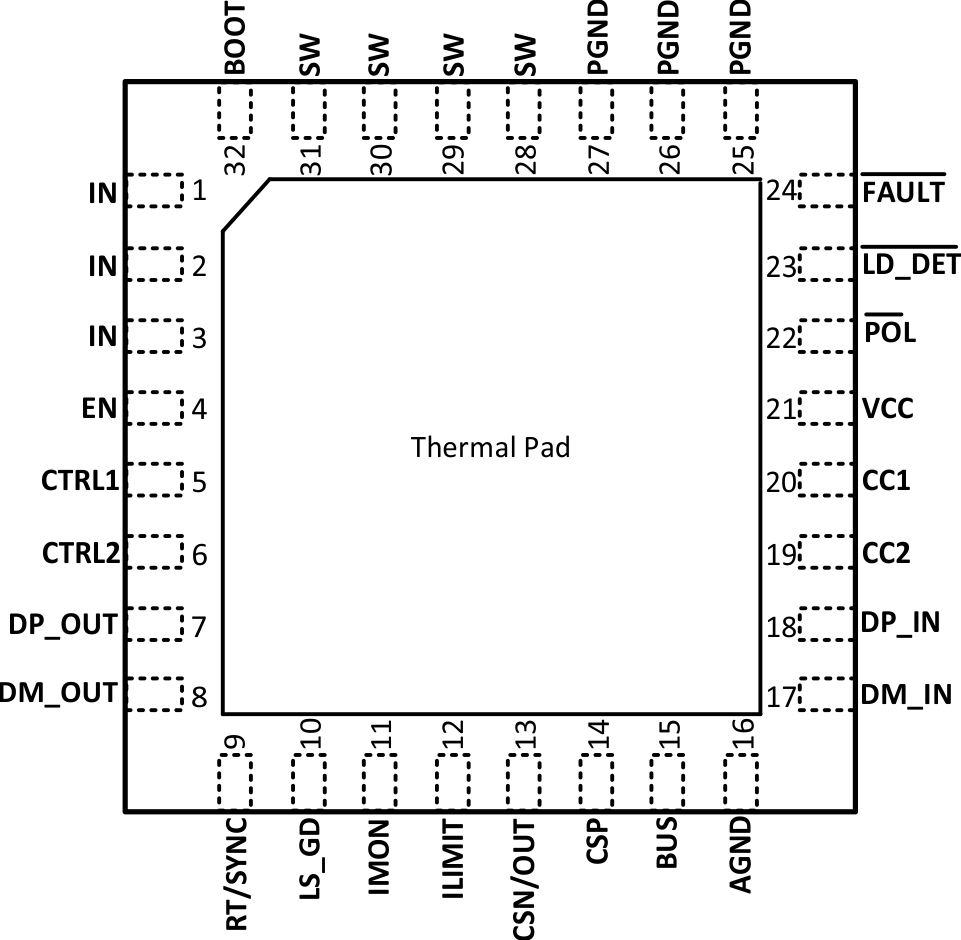 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
-
Device used within the 'Recommended Operating Conditions' and the 'Absolute Maximum Ratings' found in the appropriate device data sheet.
-
Configuration as shown in the 'Example Application Circuit' found in the appropriate device data sheet.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | Device does operate. No output voltage is generated. | B |
| VIN | 2 | Device does operate. No output voltage is generated. | B |
| VIN | 3 | Device does operate. No output voltage is generated. | B |
| EN | 4 | Loss of ENABLE functionality. Device remains in shutdown mode. | B |
| CTRL1 | 5 | Device stays at RESERVED mode or DCP auto mode. When in the RESERVED mode, the output charging is abnormal. | B |
| CTRL2 | 6 | Device stays at RESERVED mode or SDP mode. When in the RESERVED mode, the output charging is abnormal. | B |
| DP_OUT | 7 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/Client mode, device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| DM_OUT | 8 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/Client mode, device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| RT/SYNC | 9 | Device internal buck switching frequency goes up to 4.6 MHz, and the CSN pin voltage up to 7 V. It makes the output charging abnormal. | B |
| LS_GD | 10 | Device cannot drive external FET for current limit. | B |
| IMON | 11 | Loss of Cable Compensation functionality. Device cannot make a cable compensation. | C |
| ILIMT | 12 | Loss of Current Limit functionality. Device uses the maximum current limit value of 3.5 A. | C |
| CSN/OUT | 13 | Device internal buck output short-circuits. Device enters hiccup mode. | B |
| CSP | 14 | Device internal buck output short-circuits. Device enters hiccup mode. | B |
| BUS | 15 | Device hiccups and output current limit does work. | B |
| AGND | 16 | No effect | D |
| DM_IN | 17 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/Client mode, device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| DP_IN | 18 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/Client mode, device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| CC2 | 19 | Device hiccups and output voltage is abnormal. | B |
| CC1 | 20 | Device hiccups and output voltage is abnormal. | B |
| VCC | 21 | Device hiccups and cannot be powered on. | B |
| /POL | 22 | Loss of /POL functionality, device always appears to the CC2 pin is connected to the CC line in the cable. | C |
| /LD_DET | 23 | Loss of /LD_DET functionality, device always appears to a Type-C UFP is identified on the CC lines. | C |
| /FAULT | 24 | Loss of /FAULT functionality, device always appears to be in the fault condition. | C |
| PGND | 25 | No effect | D |
| PGND | 26 | No effect | D |
| PGND | 27 | No effect | D |
| SW | 28 | Device internal buck hiccup, long-term reliability may impact. | A |
| SW | 29 | Device internal buck hiccup, long-term reliability may impact. | A |
| SW | 30 | Device internal buck hiccup, long-term reliability may impact. | A |
| SW | 31 | Device internal buck hiccup, long-term reliability may impact. | A |
| BOOT | 32 | Device internal buck stop switching. No output voltage in VSN/OUT. | B |
| Thermal Pad | — | No effect | D |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| VIN | 2 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| VIN | 3 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| EN | 4 | Device off and on cannot be controlled and is off and on depending on how EN floats. | B |
| CTRL1 | 5 | Device DCP auto/SDP/CDP/RESERVED mode cannot be controlled, and is DCP auto/SDP/CDP/RESERVED mode depending on how CTRL1 floats. | B |
| CTRL2 | 6 | Device DCP auto/SDP/CDP/RESERVED mode cannot be controlled, and is DCP auto/SDP/CDP/RESERVED mode depending on how CTRL2 floats. | B |
| DP_OUT | 7 | Device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| DM_OUT | 8 | Device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| RT/SYNC | 9 | Device internal buck switching frequency drop and loading current are limited to about a small value. It causes abnormal charging. | B |
| LS_GD | 10 | Device cannot drive external FET for current limit. | B |
| IMON | 11 | VOUT/CSN goes up to 6.9 V. It may cause VBUS voltage over compensation and fail at the BC1.2 certification test. | B |
| ILIMT | 12 | Device internal buck hiccups. | B |
| CSN/OUT | 13 | Device internal buck output voltage is abnormal. | B |
| CSP | 14 | Device cannot sense the output current signal. The output current limit and VBUS cable compensation do not work. | C |
| BUS | 15 | Loss of VBUS OVP functionality, short to battery test and IEC ESD test is impacted. | B |
| AGND | 16 | The device tries to power up by forward-biasing the ESD diode from the GND to another pin. Strange results are observed. | B |
| DM_IN | 17 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/Client mode, device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| DP_IN | 18 | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/Client mode, device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| CC2 | 19 | Device Nothing attached/UFP connected/No UFP connected cannot be controlled, it depends on the state of CC1. | B |
| CC1 | 20 | Device Nothing attached/UFP connected/No UFP connected cannot be controlled, it depends on the state of CC2. | B |
| VCC | 21 | Device cannot start up. Internal buck stops switching. | B |
| /POL | 22 | Loss of /POL functionality, cannot give cable orientation information. | C |
| /LD_DET | 23 | Loss of /LD_DET functionality, cannot identify the Type-C UFP. | C |
| /FAULT | 24 | Loss of /FAULT functionality, cannot check whether the device is in the fault condition. | C |
| PGND | 25 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| PGND | 26 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| PGND | 27 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| SW | 28 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| SW | 29 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| SW | 30 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| SW | 31 | Long-term reliability may impact due to lower bonding-wire count. | C |
| BOOT | 32 | Device internal buck HS FET cannot be turned on. VSN/OUT cannot get up to target voltage. | B |
| Thermal Pad | — | Long-term reliability may impact if the device operates beyond the rate junction temperature for extended time because a heat path is interrupted. | C |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | VIN | No effect | D |
| VIN | 2 | VIN | No effect | D |
| VIN | 3 | EN | Device is enabled and cannot be disabled. | D |
| EN | 4 | CTRL1 | Device DCP auto/SDP/CDP/Reserve mode and enable/disable cannot be controlled. It is DCP auto/SDP/CDP/ Reserve mode and enable/disable depending on how EN and CTRL1 circuits interact. | B |
| CTRL1 | 5 | CTRL2 | Device DCP auto/SDP/CDP/Reserve mode cannot be controlled. It is DCP auto/SDP/CDP/Reserve mode depending on how CTRL1 and CTRL2 circuits interact. | B |
| CTRL2 | 6 | DP_OUT | Device is client/SDP/CDP mode depending on how CTRL2 and DP_OUT driving circuits interact. DP_OUT is fixed at high or low voltage; the data communication is impacted. | B |
| DP_OUT | 7 | DM_OUT | Device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| DM_OUT | 8 | RT/SYNC | Device unable to communicate with host and attached device. Device internal buck switching is interrupted by DM_OUT. | B |
| RT/SYNC | 9 | LS_GD | The LS_GD goes down from 11.3 V to 0.5 V, and the internal buck switching frequency is abnormal. The device cannot drive the external FET for current limit. | B |
| LS_GD | 10 | IMON | LS_GD voltage set low. The device cannot drive the external FET for current limit. | B |
| IMON | 11 | ILIMT | Current limit threshold and cable compensation value are impacted. | C |
| ILIMT | 12 | CSN/OUT | Ilimit is pulled up over 1 V. The device behaves as average current limit and keeps hiccup. | B |
| CSN/OUT | 13 | CSP | Average current limit, external FET current limit and cable compensation function are bypassed. | C |
| CSP | 14 | BUS | Average current limit, external FET current limit and cable compensation function are bypassed. | C |
| BUS | 15 | AGND | Device goes into hiccup mode. | B |
| AGND | 16 | DM_IN | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/Client mode. Device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| DM_IN | 17 | DP_IN | Device cannot support SDP/CDP/Client mode. Device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| DP_IN | 18 | CC2 | If shorted before charging, the device cannot charge, if shorted after charge, device unable to communicate with host and attached device. | B |
| CC2 | 19 | CC1 | Pin short before power up, device internal buck is not switching. Pin short during normal condition, no impact. | B |
| CC1 | 20 | VCC | Device stops working, CSN/OUT does not output voltage. | B |
| VCC | 21 | /POL | Loss of /POL functionality, the /POL always goes into high, device always appears to have the CC1 pin connected to the CC line. | C |
| /POL | 22 | /LD_DET | Loss of /POL and /LD_LET functionality | C |
| /LD_DET | 23 | /FAULT | Loss of /FAULT and /LD_LET functionality | C |
| /FAULT | 24 | PGND | Loss of /FAULT functionality, device always appears to be in the fault condition. | C |
| PGND | 25 | PGND | No effect | D |
| PGND | 26 | PGND | No effect | D |
| PGND | 27 | SW | Device internal buck hiccups, long-term reliability may be impacted. | A |
| SW | 28 | SW | No effect | D |
| SW | 29 | SW | No effect | D |
| SW | 30 | SW | No effect | D |
| SW | 31 | BOOT | Device internal buck HS FET stops working, no output voltage in CSN/OUT. | B |
| Thermal Pad | — | Any of the numbered pins in the above rows. | The thermal pad is connected to the board ground. Treat shorts to the thermal pad as shorts to ground. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | No effect | D |
| VIN | 2 | No effect | D |
| VIN | 3 | No effect | D |
| EN | 4 | Device is enabled and cannot be disabled. | D |
| CTRL1 | 5 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| CTRL2 | 6 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| DP_OUT | 7 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| DM_OUT | 8 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| RT/SYNC | 9 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| LS_GD | 10 | External FET cannot do current limit. | C |
| IMON | 11 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| ILIMT | 12 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| CSN/OUT | 13 | VBUS OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| CSP | 14 | VBUS OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| BUS | 15 | VBUS OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| AGND | 16 | Former power supply may be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |
| DM_IN | 17 | DM_IN OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| DP_IN | 18 | DP_IN OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| CC2 | 19 | CC OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| CC1 | 20 | CC OVP protection. FAULT pin asserts. | B |
| VCC | 21 | Device broken, VCC pin voltage exceeds the ABS maximum value. | A |
| /POL | 22 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| /LD_DET | 23 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| /FAULT | 24 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| PGND | 25 | Former power supply may be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |
| PGND | 26 | Former power supply may be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |
| PGND | 27 | Former power supply may be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |
| SW | 28 | Device internal buck stops working. | B |
| SW | 29 | Device internal buck stops working. | B |
| SW | 30 | Device internal buck stops working. | B |
| SW | 31 | Device internal buck stops working. | B |
| BOOT | 32 | Above ABS voltage, device may be damaged. | A |
| Thermal Pad | — | Thermal pad is connected to PGND on the PCB board. Former power supply may be pulled down. Device is not powered up. | B |