SFFS845 April 2024 CD74HCT4067-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
- Pin short-circuited to ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1 TI Classification of Failure
Effects
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance |
Figure 4-1 shows the CD74HCT4067-Q1 pin diagram for the SOIC package. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the CD74HCT4067-Q1 data sheet.
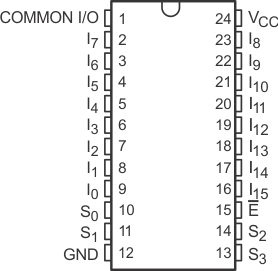 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram (SOIC) Package
Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram (SOIC) PackageTable 4-2 Pin FMA for Device Pins
Short-Circuited to Ground
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMMON I/O | 1 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the selected Ix pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I7 | 2 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I6 | 3 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I5 | 4 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I4 | 5 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I3 | 6 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I2 | 7 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I1 | 8 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I0 | 9 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| S0 | 10 | Address stuck low. Cannot control switch states. | B |
| S1 | 11 | Address stuck low. Cannot control switch states. | B |
| GND | 12 | No effect, normal operation. | D |
| S3 | 13 | Address stuck low. Cannot control switch states. | A |
| S2 | 14 | Address stuck low. Cannot control switch states. | A |
| E/ | 15 | Enable stuck low. Can no longer disable the device without power down. | B |
| I15 | 16 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I14 | 17 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I13 | 18 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I12 | 19 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I11 | 20 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I10 | 21 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I9 | 22 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I8 | 23 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| VDD | 24 | Device is unpowered. Device is not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met; otherwise device damage may be possible. | A |
Table 4-3 Pin FMA for Device
Open-Circuited
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMMON I/O | 1 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the Ix pins | B |
| I7 | 2 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I6 | 3 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I5 | 4 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I4 | 5 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I3 | 6 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I2 | 7 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I1 | 8 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I0 | 9 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| S0 | 10 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| S1 | 11 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| GND | 12 | Device unpowered. Device not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| S3 | 13 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| S2 | 14 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| E/ | 15 | Loss of control of the E/ pin. Cannot control the device. | B |
| I15 | 16 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I14 | 17 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I13 | 18 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I12 | 19 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I11 | 20 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I10 | 21 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I9 | 22 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| I8 | 23 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin | B |
| VDD | 24 | Device is unpowered. Device is not functional. | B |
Table 4-4 Pin FMA for Device Pins
Short-Circuited to Adjacent Pin
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMMON I/O | 1 | I7 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the IX and COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I7 | 2 | I6 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I6 | 3 | I5 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I5 | 4 | I4 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I4 | 5 | I3 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I3 | 6 | I2 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I2 | 7 | I1 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I1 | 8 | I0 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I0 | 9 | S0 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| S0 | 10 | S1 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| S1 | 11 | GND | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| GND | 12 | S3 | Not considered, corner pin. | D |
| S3 | 13 | S2 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| S2 | 14 | E/ | Control of the address and Enable pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| E/ | 15 | I15 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| I15 | 16 | I14 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I14 | 17 | I13 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I13 | 18 | I12 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I12 | 19 | I11 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I11 | 20 | I10 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I10 | 21 | I9 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I9 | 22 | I8 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. | B |
| I8 | 23 | VCC | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| VCC | 24 | COMMON I/O | Not considered, corner pin. | D |
Table 4-5 Pin FMA for Device Pins
Short-Circuited to VDD
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMMON I/O | 1 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the Ix pins. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I7 | 2 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I6 | 3 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I5 | 4 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I4 | 5 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I3 | 6 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I2 | 7 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I1 | 8 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I0 | 9 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| S0 | 10 | Address stuck high. Cannot control switch. | B |
| S1 | 11 | Address stuck high. Cannot control switch. | B |
| GND | 12 | Device is unpowered. Device is not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be possible. | A |
| S3 | 13 | Address stuck high. Cannot control switch. | B |
| S2 | 14 | Address stuck high. Cannot control switch. | B |
| E/ | 15 | E/ stuck high. Can no longer disable the device | B |
| I15 | 16 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I14 | 17 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I13 | 18 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I12 | 19 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I11 | 20 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I10 | 21 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I9 | 22 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| I8 | 23 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COMMON I/O pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| VDD | 24 | No effect, normal operation. | D |