SFFS926 June 2024 PGA308
4.2 VSON (DRK) Package
Figure 4-2 shows the PGA308 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins, see the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the PGA308 data sheet.
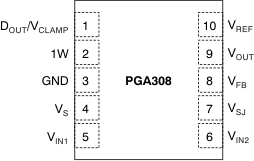 Figure 4-2 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-2 Pin Diagram| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| DOUT/VCLAMP | 1 | If configured as DOUT, approaches the absolute maximum rating for PIN 1 voltage, potentially degrading performance long term. If configured as VCLAMP, sets clamping voltage to VEE resulting in a loss of output signal. | B |
| 1W | 2 | Loss of communication with device, PIN 1 remains in previous configuration. | D |
| VS | 4 | Op-amp supplies are shorted together, leaving the VS pin at some voltage between the VS and GND sources (depending on the source impedance). | A |
| VIN1 | 5 | VIN1 pin is shorted to ground, leaving the device outside the linear range, resulting in an unpredictable device output voltage. | B |
| VIN2 | 6 | VIN2 pin is shorted to ground, leaving the device outside the linear range, resulting in an unpredictable device output voltage. | B |
| VSJ | 7 | There is potential for device damage depending on circuit configuration. | A |
| VFB | 8 | Loss of device functionality, damage to the device is not likely. | B |
| VOUT | 9 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the device can be forced into a short-circuit condition with the VOUT voltage ultimately forced to the GND voltage. Prolonged exposure to short-circuit conditions can result in long-term reliability issues. | A |
| VREF | 10 | Loss of device functionality, damage to the device is not likely. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| DOUT/VCLAMP | 1 | If configured as DOUT, digital communication is lost with external sensors resulting in a loss of device functionality. If configured as VCLAMP, clamping voltage, at some voltage between VEE and VCC, potentially results in the device output not functioning as intended. | B |
| 1W | 2 | Loss of communication with device, PIN 1 remains in previous configuration. | D |
| GND | 3 | Negative supply is left floating. The op amp ceases to function because no current can source or sink to the device. | B |
| VS | 4 | Positive supply is left floating. The op amp ceases to function because no current can source or sink to the device. | B |
| VIN1 | 5 | Signal input voltage 1 is left floating. VIN1 voltage can end up at the positive or negative rail because of leakage on the ESD diodes, potentially resulting in a device output voltage between the negative and positive rails. | B |
| VIN2 | 6 | Signal input voltage 2 is left floating. VIN2 voltage can end up at the positive or negative rail because of leakage on the ESD diodes, potentially resulting in a device output voltage between the negative and positive rails. | B |
| VSJ | 7 | Loss of external compensation, device potentially continues to function. | D |
| VFB | 8 | Depending on circuit configuration, VOUT is forced to either VCC or VEE. | B |
| VOUT | 9 | No negative feedback or ability for VOUT to drive the application. | B |
| VREF | 10 | Loss of functionality for course offset DAC, fine offset DAC, underscale DAC, overscale DAC, and fault monitor. | D |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOUT / VCLAMP | 1 | 2 | If configured as DOUT, results in a loss of device functionality. If configured as VCLAMP, clamping voltage is set to 1W voltage, potentially resulting in the device output not functioning as intended. | B |
| 1W | 2 | 3 | Loss of communication with device, PIN 1 remains in previous configuration. | D |
| GND | 3 | 4 | Op-amp supplies are shorted together, leaving the GND pin at some voltage between the GND and VS sources (depending on the source impedance). | A |
| VS | 4 | 5 | VIN1 pin is shorted to supply, leaving the device outside the linear range, resulting in unpredictable device output voltage. | B |
| VIN1 | 5 | 6 | Both inputs are tied together. Output voltage is set to some value-based device gain configuration and the course offset value is set by VREF voltage. | B |
| VIN2 | 6 | 7 | Oscillation is possible due to additional capacitance on the VSJ pin, resulting in erratic behavior on the output. | B |
| VSJ | 7 | 8 | Depending on circuit configuration, erroneous gain can result in a loss of intended functionality. Potential stability issues can arise by shorting the isolation resistor, typically found between VSJ and VFB. | B |
| VFB | 8 | 9 | No loss of functionality and no potential damage to the device. If an external filter is used, the filter is bypassed. | D |
| VOUT | 9 | 10 | Device output behaves unpredictably, resulting in a loss of functionality. No potential damage to the device. | B |
| VREF | 10 | 1 | If PIN 1 is configured as DOUT, output voltage is unpredictable, resulting in a loss of functionality, If PIN 1 is configured as VCLAMP, clamping voltage is set to VREF voltage, potentially resulting in an erroneous output voltage if the VREF voltage is less than the intended output. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| DOUT | 1 | If configured as DOUT, approaches the absolute maximum rating for PIN 1 voltage, potentially degrading performance long term. If configured as VCLAMP, sets clamping voltage to VCC allowing the full output range. | C |
| 1W | 2 | Loss of communication with device, PIN 1 remains in previous configuration. | D |
| GND | 3 | Op-amp supplies are shorted together, leaving the GND pin at some voltage between the GND and VS sources (depending on the source impedance). | A |
| VIN1 | 5 | VIN1 pin is shorted to supply, leaving the device outside the linear range, resulting in an unpredictable device output voltage. | B |
| VIN2 | 6 | VIN2 pin is shorted to supply, leaving the device outside the linear range, resulting in an unpredictable device output voltage. | B |
| VSJ | 7 | Device damage is possible, depending on circuit configuration. | A |
| VFB | 8 | Loss of device functionality, damage to the device is not likely. | B |
| VOUT | 9 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the device can be forced into a short-circuit condition with the VOUT voltage ultimately forced to the VS voltage. Prolonged exposure to short-circuit conditions can result in long-term reliability issues. | A |
| VREF | 10 | Loss of device functionality, damage to the device is not likely. | B |