SLAA638A august 2014 – may 2023 MSP430I2040 , MSP430I2041
- 1
- Single Phase and DC Embedded Metering (Power Monitor) Using MSP430I2040
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Design Details
- 3 Calibration Techniques
- 4 Hardware Setup
- 5 Calibrator Software
- 6 Operating the PC Software Tool
-
7 Serial Communication Commands
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 Communication Protocol
- 7.3
Commands
- 7.3.1 HOST_CMD_GET_METER_NAME
- 7.3.2 HOST_CMD_GET_METER_VER
- 7.3.3 HOST_CMD_GET_METER_CONFIGURATION
- 7.3.4 HOST_CMD_GET_RTC
- 7.3.5 HOST_CMD_ALIGN_WITH_CALIBRATION_FACTORS
- 7.3.6 HOST_CMD_SET_PASSWORD
- 7.3.7 HOST_CMD_GET_READINGS_PHASE_N
- 7.3.8 HOST_CMD_GET_EXTRA_READINGS_PHASE_N
- 7.3.9 HOST_CMD_SUMCHECK_MEMORY
- 7.3.10 HOST_CMD_CLEAR_CALIBRATION_DATA
- 7.3.11 HOST_CMD_SET_CALIBRATION_PHASE_N
- 7.3.12 HOST_CMD_GET_CALIBRATION_PHASE_N
- 7.3.13 HOST_CMD_SET_CALIBRATION_EXTRAS
- 7.3.14 HOST_CMD_GET_CALIBRATION_EXTRAS
-
8 Firmware and Embedded Metering Library API
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2
Embedded Metering LIbrary API
- 8.2.1
Embedded Metering Library Function Calls
- 8.2.1.1
Functions for Metrology Engine Control
- 8.2.1.1.1 Functions for Metrology Engine Control
- int metrology_init (void)
- int metrology_init_from_nv_data (void)
- void align_metrology_with_calibration_data (void)
- void metrology_switch_to_normal_mode (void)
- void metrology_init_analog_front_end_normal_mode (void)
- void metrology_disable_analog_front_end (void)
- 8.2.1.2 Procedure for Metrology Engine Initialization
- 8.2.1.3
Functions for Calculate and Reading the Readings
- 8.2.1.3.1 Functions for Calculate and Reading the Readings
- power_t calculate_phase_readings (void
- power_t active_power (int ph)
- power_t reactive_power (int ph)
- power_t apparent_power (int ph)
- power_t fundamental_active_power(int ph)
- power_t fundamental_reactive_power(int ph)
- power_factor_t power_factor (int ph)
- rms_voltage_t rms_voltage (int ph)
- rms_voltage_t fundamental_rms_voltage(int ph)
- thd_t voltage_thd(int ph)
- rms_current_t rms_current (int ph)
- rms_current_t fundamental_rms_current(int ph)
- thd_t current_thd(int ph)
- int16_t mains_frequency (int ph)
- uint16_t phase_status (int ph)
- 8.2.1.1
Functions for Metrology Engine Control
- 8.2.2 Embedded Metering LIbrary Callbacks
- 8.2.3
Application Level Calibration Functions
- 8.2.3.1
Functions for Reading and Writing Calibration Parameters
- 8.2.3.1.1 Functions for Reading and Writing Calibration Parameters
- int get_calibration_status (void)
- void set_calibration_status (int value)
- int clear_calibration_data (void)
- int16_t get_temperature_intercept (void)
- int16_t get_temperature_slope (void)
- void set_temperature_parameters (int16_t temperature_at_calibration, int16_t temperature_sensor_intercept, int16_t temperature_sensor_slope)
- calibration_scaling_factor_t get_P_scaling (int phx)
- void set_P_scaling (int phx, calibration_scaling_factor_t value)
- calibration_scaling_factor_t get_V_rms_scaling (int phx)
- void set_V_rms_scaling (int phx, calibration_scaling_factor_t value)
- int16_t get_v_dc_estimate (int phx)
- int16_t get_initial_v_dc_estimate (int phx)
- void set_v_dc_estimate (int phx, int16_t value)
- int32_t get_v_ac_offset (int phx)
- void set_v_ac_offset (int phx, int32_t value)
- calibration_scaling_factor_t get_I_rms_scaling(int phx);
- void set_I_rms_scaling(int phx, calibration_scaling_factor_t value);
- int32_t get_i_dc_estimate(int phx);
- int32_t get_initial_i_dc_estimate(int phx)
- void set_i_dc_estimate(int phx, int32_t value);
- int32_t get_i_ac_estimate(int phx);
- void set_i_ac_offset (int phx, int32_t value)
- uint16_t get_compensate_capacitor_value (int phx)
- void set_compensate_capacitor_value (int phx, uint16_t value)
- uint16_t get_compensate_resistance (int phx)
- void set_compensate_resistance (int phx, uint16_t value)
- int16_t get_phase_corr (int phx)
- void set_phase_corr (int phx, int16_t value)
- 8.2.3.1
Functions for Reading and Writing Calibration Parameters
- 8.2.4 Setting Default Calibration Parameters
- 8.2.1
Embedded Metering Library Function Calls
- 9 Example Application Code
- 10Hardware Design Files
- 11EVM Specification and Performance
- 12Running on MSP430i2040 and MSP430i2041
- 13Revision History
2.2.3 Shunt Resistor
For an accurate measurement, the choice of shunt is another important factor. In general, it is suggested that a shunt of smaller value is a better choice. Smaller shunt value benefits the power dissipated on the shunt and the respective rise in temperature. The lower rise in temperature reduces the need for a very low temperature coefficient shunt resistor to sustain the accuracy over temperature. However, there is also drawback of using a small value shunt that the signal to noise ratio of a small value shunt is worse than using a larger value one. In this sense, there may be chance that a shunt of higher value is desired, for example when measuring a very small current and the range of current to be measured is also in a small range. In this design, a few factors are considered: the maximum current, the current dynamic range, the power dissipation.
In this application, the maximum current for each socket is 15A, the desired dynamic range of current keeping flat error percentage is 1000:1. It is preferred that the power dissipated on the shunt resistor be as small as possible.
To achieve the best accuracy, it is desired to have the current signal present to the SD24 ADC have maximum swing when measuring maximum current, since the SD24 ADC has an input range of approximately 900 mV at x1 gain. Using x16 gain, the input range for the AC root mean square is:
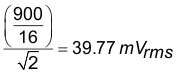
With this number, 2mΩ shunt resistance should be good for this input range. Yet due to the limited area of copper attached to the shunt resistor, it is better to use a smaller valued shunt to keep the heat accumulation on the shunt resistor low; therefore, 0.5 mΩ shunt resistance is chosen.
In addition to value, the physical size of the shunt is also an important factor for accuracy. Not the size directly but the heat generated when current is flowing. A smaller sized shunt heats up more easily due to the limited surface area. If there is significant current to flow though the shunt, it is suggested to have a large enough sized shunt and there should also be sufficient ventilation on the PCB to prevent heat being accumulated. In this design, a 2512 size shunt is chosen. At 0.5 mΩ, the power dissipate on the shunt at maximum current is 162 × 0.5 = 0.128W, which is about 1/8 the rated power of a 2512 size 1W shunt resistor.