SLAA732A February 2017 – April 2021 PGA460 , PGA460-Q1
6.1.1.1 Frequency Diagnostic Feature of PGA460
The PGA460 device offers a feature to measure the ringing-decay frequency of the transducer. The user has the ability to set the start time (FDIAG_START) and window length (FDIAG_LEN) of the frequency measurement to validate the performance and proper tuning of the transducer. In addition, a frequency error feature is implemented in the PGA460 device to signify that the measured transducer frequency is outside of the limits set by the FDIAG_ERR_TH threshold parameter. Both the measured frequency and error status can be read through any of the interface options.
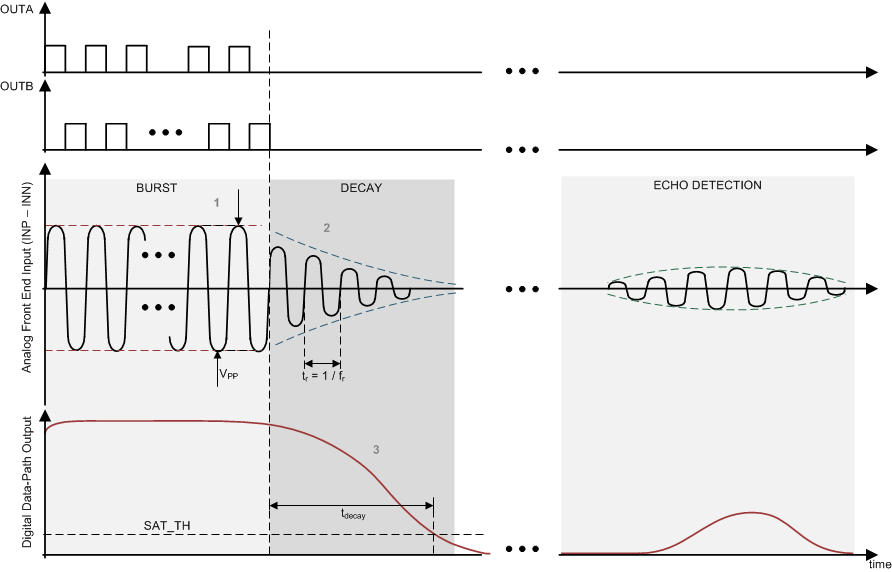 Figure 6-1 Frequency Diagnostic Timing Diagram
Figure 6-1 Frequency Diagnostic Timing Diagram