SLAAEH2A December 2023 – June 2024 TAA5212 , TAC5111 , TAC5112 , TAC5211 , TAC5212 , TAD5112 , TAD5212
3.1 ADC Sampling Rate Conversion
An overview of ADC SRC flow in default mode is shown in the block diagram below where an ADC input running at higher sampling rate (main Fs) is converted to a lower sampling rate (auxiliary Fs) and be available on the other ASI. User has the choice to choose Primary ASI or Secondary ASI with the higher or lower rate interface. The flow applies also when main Fs is chosen from the lower rate thus SRC is converting from lower to higher rate.
The SRC process has option to mix with a DAC loopback data for example adding audio data from host to the recorded voice data.
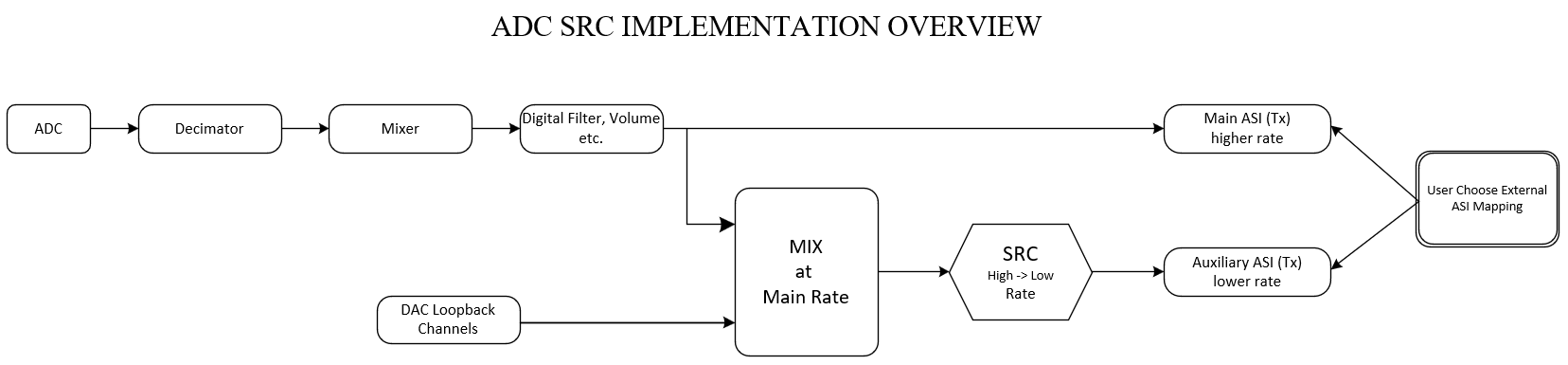 Figure 3-1 TAx5x1x ADC SRC Overview - Default Mode
Figure 3-1 TAx5x1x ADC SRC Overview - Default ModeUsers can watch the levels when mixing, set the coefficients so the output does not exceed the maximum allowed as higher level causes clipping or distortion. The mixer output levels are defined by the following equations.
For ADC mixer, the equation to set the mixing coefficients is given below where w represents the weight or scale of magnitude. For example w=0.5 represents half of the magnitude which translates into 'h40000000 in the 32-bit DAC mixer coefficients. The default on some of the path coefficients are 'h7FFFFFFF for the full scale magnitude of 1. The ADC mixer coefficients are configured through register page address 0x0A and register address from 0x08 to 0x47.
For Digital Loopback (ADC to DAC) mixer, the equation to set the mixing coefficients is the same as the ADC mixer equation given above and is set through register page address 0x0A with register address from 0x48 to 0x67.
For ADC Auxiliary mixer, the equation to set the mixing coefficients is given below where w represents the weight or scale of magnitude. This Auxiliary ADC mixer coefficients are configured through register page address 0x0B and register address from 0x30 to 0x37.
Examples for this ADC SRC are demonstrated in the subsequent section.