SLAS942E November 2015 – December 2019 MSP430FR2532 , MSP430FR2533 , MSP430FR2632 , MSP430FR2633
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.5 Active Mode Supply Current Per MHz
- 5.6 Low-Power Mode LPM0 Supply Currents Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.7 Low-Power Mode (LPM3 and LPM4) Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.8 Low-Power Mode LPMx.5 Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.9 Typical Characteristics - Low-Power Mode Supply Currents
- Table 5-1 Typical Characteristics – Current Consumption Per Module
- 5.10 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 5.11 Timing and Switching Characteristics
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 CPU
- 6.3 Operating Modes
- 6.4 Interrupt Vector Addresses
- 6.5 Bootloader (BSL)
- 6.6 JTAG Standard Interface
- 6.7 Spy-Bi-Wire Interface (SBW)
- 6.8 FRAM
- 6.9 Memory Protection
- 6.10
Peripherals
- 6.10.1 Power-Management Module (PMM)
- 6.10.2 Clock System (CS) and Clock Distribution
- 6.10.3 General-Purpose Input/Output Port (I/O)
- 6.10.4 Watchdog Timer (WDT)
- 6.10.5 System (SYS) Module
- 6.10.6 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
- 6.10.7 Enhanced Universal Serial Communication Interface (eUSCI_A0, eUSCI_B0)
- 6.10.8 Timers (Timer0_A3, Timer1_A3, Timer2_A2 and Timer3_A2)
- 6.10.9 Hardware Multiplier (MPY)
- 6.10.10 Backup Memory (BAKMEM)
- 6.10.11 Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- 6.10.12 10-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 6.10.13 CapTIvate Technology
- 6.10.14 Embedded Emulation Module (EEM)
- 6.11 Input/Output Diagrams
- 6.12 Device Descriptors
- 6.13 Memory
- 6.14 Identification
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.11.1 Port P1 Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
Figure 6-1 shows the port diagram. Table 6-17 summarizes the selection of pin function.
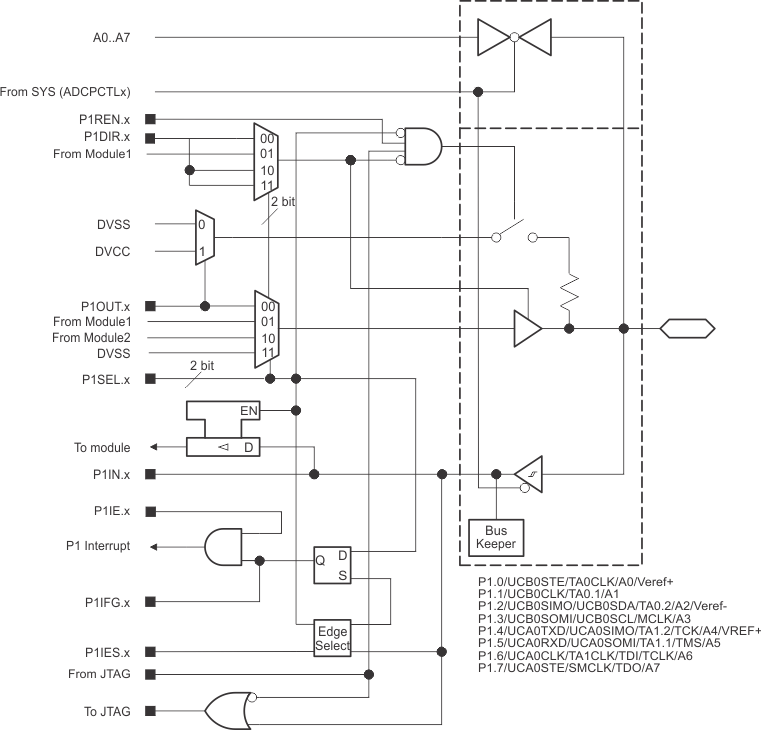 Figure 6-1 Port P1 (P1.0 to P1.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
Figure 6-1 Port P1 (P1.0 to P1.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger Table 6-17 Port P1 (P1.0 to P1.7) Pin Functions
| PIN NAME (P1.x) | x | FUNCTION | CONTROL BITS AND SIGNALS(2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1DIR.x | P1SELx | ADCPCTLx(1) | JTAG | |||
| P1.0/UCB0STE/ TA0CLK/A0 | 0 | P1.0 (I/O) | I: 0; O: 1 | 00 | 0 | N/A |
| UCB0STE | X | 01 | 0 | N/A | ||
| TA0CLK | 0 | 10 | 0 | N/A | ||
| A0/Veref+ | X | X | 1 (x = 0) | N/A | ||
| P1.1/UCB0CLK/TA0.1/ A1 | 1 | P1.1 (I/O) | I: 0; O: 1 | 00 | 0 | N/A |
| UCB0CLK | X | 01 | 0 | N/A | ||
| TA0.CCI1A | 0 | 10 | 0 | N/A | ||
| TA0.1 | 1 | |||||
| A1 | X | X | 1 (x = 1) | N/A | ||
| P1.2/UCB0SIMO/ UCB0SDA/TA0.2/A2 | 2 | P1.2 (I/O) | I: 0; O: 1 | 00 | 0 | N/A |
| UCB0SIMO/UCB0SDA | X | 01 | 0 | N/A | ||
| TA0.CCI2A | 0 | 10 | 0 | N/A | ||
| TA0.2 | 1 | |||||
| A2/Veref- | X | X | 1 (x = 2) | N/A | ||
| P1.3/UCB0SOMI/ UCB0SCL/MCLK/A3 | 3 | P1.3 (I/O) | I: 0; O: 1 | 00 | 0 | N/A |
| UCB0SOMI/UCB0SCL | X | 01 | 0 | N/A | ||
| MCLK | 1 | 10 | 0 | N/A | ||
| A3 | X | X | 1 (x = 3) | N/A | ||
| P1.4/UCA0TXD/ UCA0SIMO/TA1.2/TCK/A4 /VREF+ | 4 | P1.4 (I/O) | I: 0; O: 1 | 00 | 0 | Disabled |
| UCA0TXD/UCA0SIMO | X | 01 | 0 | Disabled | ||
| TA1.CCI2A | 0 | 10 | 0 | Disabled | ||
| TA1.2 | 1 | |||||
| A4, VREF+ | X | X | 1 (x = 4) | Disabled | ||
| JTAG TCK | X | X | X | TCK | ||
| P1.5/UCA0RXD/ UCA0SOMI/TA1.1/TMS/A5 | 5 | P1.5 (I/O) | I: 0; O: 1 | 00 | 0 | Disabled |
| UCA0RXD/UCA0SOMI | X | 01 | 0 | Disabled | ||
| TA1.CCI1A | 0 | 10 | 0 | Disabled | ||
| TA1.1 | 1 | |||||
| A5 | X | X | 1 (x = 5) | Disabled | ||
| JTAG TMS | X | X | X | TMS | ||
| P1.6/UCA0CLK/ TA1CLK/TDI/TCLK/A6 | 6 | P1.6 (I/O) | I: 0; O: 1 | 00 | 0 | Disabled |
| UCA0CLK | X | 01 | Disabled | |||
| TA1CLK | 0 | 10 | 0 | Disabled | ||
| A6 | X | X | 1 (x = 6) | Disabled | ||
| JTAG TDI/TCLK | X | X | X | TDI/TCLK | ||
| P1.7/UCA0STE/SMCLK/ TDO/A7 | 7 | P1.7 (I/O) | I: 0; O: 1 | 00 | 0 | Disabled |
| UCA0STE | X | 01 | 0 | Disabled | ||
| SMCLK | 1 | 10 | 0 | Disabled | ||
| A7 | X | X | 1 (x = 7) | Disabled | ||
| JTAG TDO | X | X | X | TDO | ||
(1) Setting the ADCPCTLx bit in SYSCFG2 register disables both the output driver and input Schmitt trigger to prevent leakage when analog signals are applied.
(2) X = don't care