SLASFC5 September 2024 TAS2320
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Device Functional Modes
- 6.4 Feature Description
- 6.5 Programming
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.4.2.4 Supply Tracking Limiters with Brown Out Prevention
TAS2320 monitors class-D supply voltage (VBAT or PVDD) along with the audio signal to automatically decrease gain when the audio signal peaks exceed a programmable threshold. This helps prevent clipping and extends playback time through end of charge battery conditions. The limiter and brown out module calculates the signal attenuation required based on the condition of the signal level, channel gain and the selected supply voltage.
The Brown Out Prevention (BOP) module provides a priority input to provide a fast response to transient dips in the battery supply. The BOP feature can be enabled by configuring the register bit BOP_EN high. The supply voltage that is tracked to determine Brown out conditions can be configured as VBAT or PVDD based on system configuration needs by using BOP_SRC register bit. When the selected supply dips below the brown-out threshold configured by setting register BOP_THR_LVL[23:0], the BOP will begin reducing gain. The rate of gain reduction (db/sample) can be configured by setting the BOP_ATK_RATE[23:0] registers . When the VBAT supply rises above the brownout threshold, the BOP will begin to release the gain after the programmed hold timer, BOP_HLD_COUNT[23:0]. The BOP feature uses the LIM_RLS_RATE[23:0] register setting to release after a brown out event. The release rate is rate of gain increase in db/sample ratio. During a BOP event the limiter updates will be paused. This is to prevent a limiter from releasing during a BOP event.
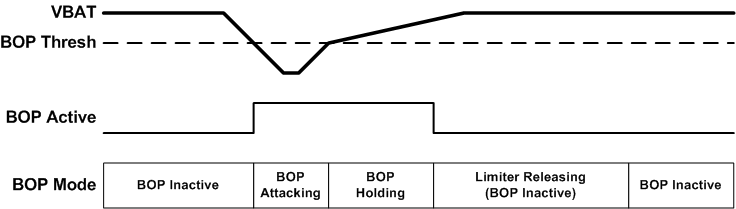 Figure 6-2 Brown Out
Prevention Event
Figure 6-2 Brown Out
Prevention EventThe device can be configured to hold the gain attenuation once a BOP event is detected by setting the register bit BOP_INF_HLD high. When the bit is programmed high, the Limiter and BOP module does not release the gain attenuation and holds the device in the programmed min gain attenuation level until the infinite hold is cleared by setting the register bit BOP_HLD_CLR high. The hold clearing bit is self clearing and will automatically reset to low state once the hold is cleared.
A hard brownout level can be set to shutdown the device if the BOP gain attenuation cannot mitigate the drop in battery voltage. The brown out based shutdown of the device is enabled when BOPSD_EN bit is set high and shuts down when the battery voltage falls below the voltage threshold set by BOSD_THR_LVL[23:0] register bits.
A maximum level of attenuation applied by the limiters and brown out prevention feature is configurable via the LIM_MAX_ATN register. This attenuation limit is shared between the features. For instance, if the maximum attenuation is set to 6 dB and the limiters have reduced gain by 4 dB, the brown out prevention feature will only be able to reduce the gain further by another 2 dB. If the limiter or brown out prevention feature is attacking and it reaches the maximum attenuation, gain will not be reduced any further.
 Figure 6-3 Limiter and Brown out gain attenuation
Figure 6-3 Limiter and Brown out gain attenuation