SLAU320AJ July 2010 – May 2021
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
-
2Programming Using the JTAG Interface
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.2
Interface and Instructions
- 2.2.1 JTAG Interface Signals
- 2.2.2 JTAG Access Macros
- 2.2.3 Spy-Bi-Wire (SBW) Timing and Control
- 2.2.4 JTAG Communication Instructions
- 2.3
Memory Programming Control Sequences
- 2.3.1 Start-Up
- 2.3.2 General Device (CPU) Control Functions
- 2.3.3 Accessing Non-Flash Memory Locations With JTAG
- 2.3.4 Programming the Flash Memory (Using the Onboard Flash Controller)
- 2.3.5 Erasing the Flash Memory (Using the Onboard Flash Controller)
- 2.3.6 Reading From Flash Memory
- 2.3.7 Verifying the Target Memory
- 2.3.8 FRAM Memory Technology
- 2.4
JTAG Access Protection
- 2.4.1 Burning the JTAG Fuse - Function Reference for 1xx, 2xx, 4xx Families
- 2.4.2 Programming the JTAG Lock Key - Function Reference for 5xx, 6xx, and FRxx Families
- 2.4.3 Testing for a Successfully Protected Device
- 2.4.4 Unlocking an FRAM Device in Protected and Secured Modes
- 2.4.5 Memory Protection Unit Handling
- 2.4.6 Intellectual Property Encapsulation (IPE)
- 2.4.7 FRAM Write Protection
- 2.5 JTAG Function Prototypes
- 2.6 JTAG Features Across Device Families
- 2.7 References
- 3JTAG Programming Hardware and Software Implementation
- 4Errata and Revision Information
- 5Revision History
2.2.2.1.3 DR_SHIFT20 (20-Bit Address) (Applies Only to MSP430X Devices)
The MSP430X architecture is based on a 20-bit memory address bus (MAB), to address up to 1 MB of continuous memory. No new JTAG instructions are needed to control the 20-bit MAB (for details on instructions, see Section 2.2.4.1), only the JTAG address register itself has been extended to 20 bits. This macro loads a 20-bit address word into the 20-bit wide JTAG MAB register. The address word is shifted, MSB first, into the TDI input of the target MSP430 device. Each bit is captured from TDI on a rising edge of TCK. At the same time, TDO shifts out the last captured and stored value in the JTAG MAB register. A new bit is present at TDO with a falling edge of TCK. TCLK should not change state while this macro is executing. This macro should only be used when IR_ADDR_16BIT or IR_ADDR_CAPTURE has been loaded into the JTAG instruction register before the MAB is manipulated through JTAG. On a 20-bit shift access, the upper four bits (19:16) of the JTAG address register are shifted out last. Therefore, bit 15 of the MAB is read first when the lower part of the MAB is accessed by performing a 16-bit shift. This implementation ensures compatibility with the original MSP430 architecture and its JTAG MAB register implementation.
The DR_SHIFT20 (20-bit Address) macro in the associated C-code software example application automatically reconstructs the swapped TDO (15:0) (19:16) output to a continuous 20-bit address word (19:0) and simply returns a 32-bit LONG value.
Figure 2-5 shows how to load a 20-bit address word into the JTAG address register and read out a stored value through TDO.
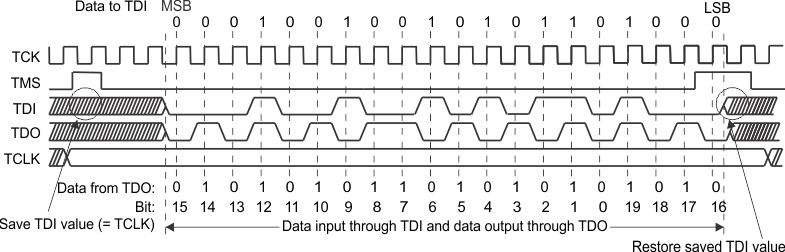 Figure 2-5 Address Register I/O: DR_SHIFT20 (0x12568) (TDO Output Is 0xA55AA)
Figure 2-5 Address Register I/O: DR_SHIFT20 (0x12568) (TDO Output Is 0xA55AA)