SLAU927B June 2024 – November 2024 MSPM0G3507
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
-
2Hardware Setup
- 2.1 EVM Hardware Setup
- 2.2 Pin Configurations for IPD Usage
- 2.3 Pin Configurations for PWM Outputs
- 2.4 Pin Configurations for ADC Currents
- 2.5 Pin Configurations for ADC Voltages
- 2.6 Pin Configurations for Faults
- 2.7 Pin Configurations for GPIO Output Functions
- 2.8 Pin Configurations for SPI Communication
- 2.9 Pin Configurations for UART Communication
- 2.10 External Connections for Evaluation Boards
- 3Software Setup
- 4GUI Setup
-
5Register Map
- 5.1 Register Map Page in GUI
- 5.2
User Control Registers (Base Address = 0x20200400h)
- 5.2.1 Speed Control Register (Offset = 0h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.2.2 Algo Debug Control 1 Register (Offset = 4h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.2.3 Algo Debug Control 2 Register (Offset = 8h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.2.4 Algo Debug Control 3 Register (Offset = Ch) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.2.5 DAC Configuration Register (Offset = 10h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3
User Input Registers (Base Address = 0x20200000h)
- 5.3.1 SYSTEM_PARAMETERS (Offset = 0h)
- 5.3.2 ISD_CONFIG Register (Offset = 38h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.3 RVS_DRV_CONFIG Register (Offset = 3Ch) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.4 MOTOR_STARTUP1 Register (Offset = 40h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.5 MOTOR_STARTUP2 Register (Offset = 44h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.6 CLOSED_LOOP1 Register (Offset = 48h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.7 CLOSED_LOOP2 Register (Offset = 4Ch) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.8 FIELD_CTRL Register (Offset = 50h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.9 FAULT_CONFIG1 Register (Offset = 54h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.10 FAULT_CONFIG2 Register (Offset = 58h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.11 MISC_ALGO Register (Offset = 5Ch) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.12 PIN_CONFIG Register (Offset = 60h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.3.13 PERI_CONFIG Register (Offset = 64h) [Reset = 00000000h]
- 5.4 User Status Registers (Base Address = 0x20200430h)
- 6Basic Tuning
-
7Advanced Tuning
- 7.1
Control Configurations Tuning
- 7.1.1 Control Mode of Operation
- 7.1.2 Initial Speed Detection of the Motor for Reliable Motor Resynchronization
- 7.1.3 Unidirectional Motor Drive Detecting Backward Spin
- 7.1.4 Preventing Back Spin of Rotor During Startup
- 7.1.5 Gradual and Smooth Start up Motion
- 7.1.6 Faster Startup Timing
- 7.1.7 Stopping Motor Quickly
- 7.1.8 Flux Weakening: Operating Motor at Speeds Higher than Rated Speed
- 7.1.9 Maximum Torque Per Ampere : Improve Efficiency of IPMSM Motors
- 7.1.10 Preventing Supply Voltage Overshoot During Motor Stop.
- 7.1.11 Protecting the Power Supply
- 7.1.12 FOC Bandwidth Selection
- 7.1
Control Configurations Tuning
- 8Hardware Configurations
- 9Revision History
6.2.2.2 Testing for Successful Startup Into Closed Loop
- Apply a nonzero speed command
Change the "Speed Input Command" to a nonzero value. When the speed command is issued, the device starts to commutate and the motor spins at a speed that is proportional to Speed Command × MAXIMUM MOTOR SPEED / 32767.
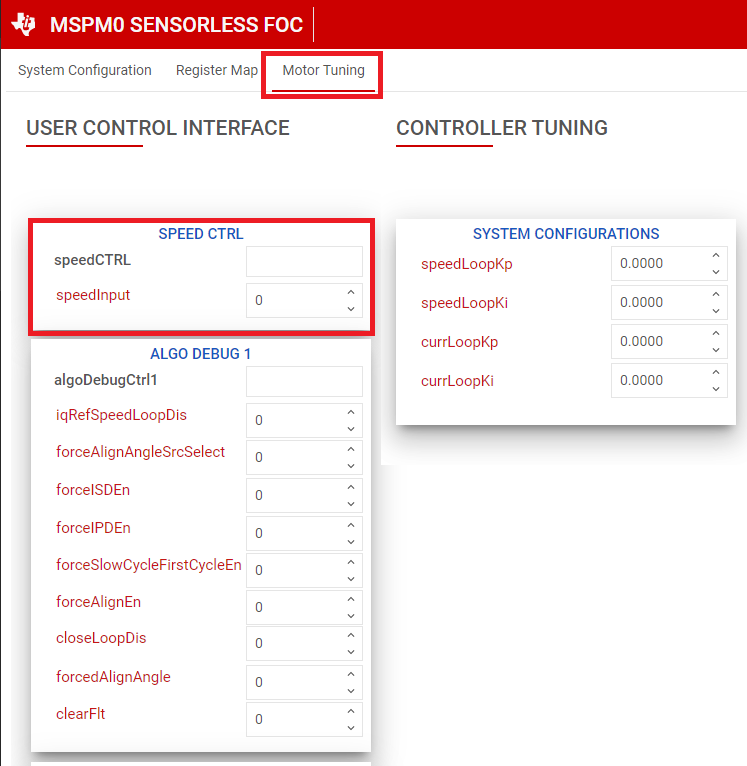
Figure 6-10 Setting Speed Input From GUI - Check if motor spins
in closed loop at commanded speed.
Enable the "Continuous Read status" toggle button towards the bottom right corner of the GUI and monitor the Fault Status register. If no faults is triggered, move to the Section 7.
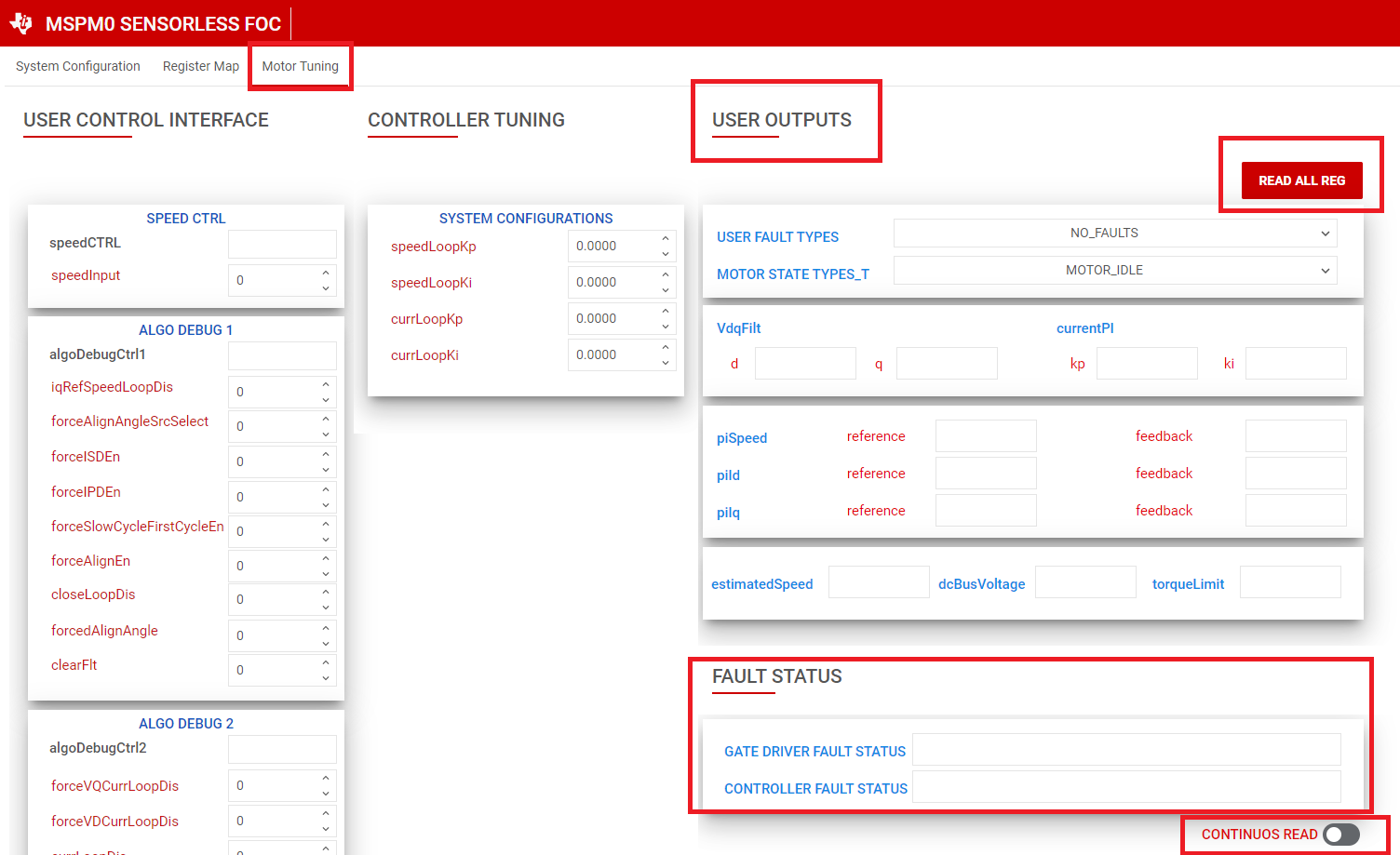
Figure 6-11 Reading Fault Status From GUI - If any fault is triggered, tune the configuration
for fault handling using these steps:
- Set zero speed command by setting the Speed Input command to 0.
- Clear the fault status registers by setting the clear fault bit (ClearFlt) bit in the ALGO DEBUG CTRL1 register.
- Check Section 6.3 for steps to debug faults.