SLLA603 March 2023
5 Stationary Target Detection
The test procedure used focuses on two different scenarios at a variety of distances. The Field of View (FOV) of the device is limited. This is because as the mirror rotates in front of the sensor, the visible portion of the mirror becomes less due to the angle of the mirror. Therefore, two scenarios were tested, one with the target directly in the middle of the FOV of the device, and one with the subject at the edge.
For all testing, the mirror was rotated constantly through the entire range of the mirror at a rate of 3.24 seconds to rotate to the maximum extent of the mirror and back.
A baseline test of nothing in the field of view was performed. The baseline test in #GUID-0D0796AA-FD30-4D5D-9D8B-606429153A02 shows that the sensor correctly identified zero people in the FOV, because no voltage response was produced.
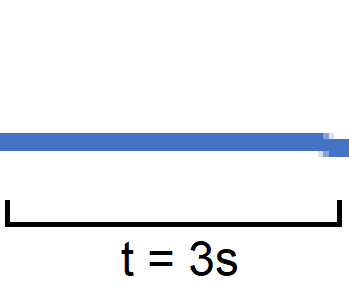 Figure 5-2 Baseline Test Voltage
Response
Figure 5-2 Baseline Test Voltage
ResponseThe next test performed was with a subject in the middle of the FOV of the device. #GUID-DAA0FA8F-77F8-4121-B226-63E666699D91 shows that a stationary subject up to 10 ft produces a consistent voltage response in the PIR.
 Figure 5-3 Object in Middle of FOV at
Ranges of 4, 8, and 10 ft From Left to Right
Figure 5-3 Object in Middle of FOV at
Ranges of 4, 8, and 10 ft From Left to RightTwo tests were performed with the subject at the edge of the FOV of the sensor, one at 5 feet, and one at 8 feet.
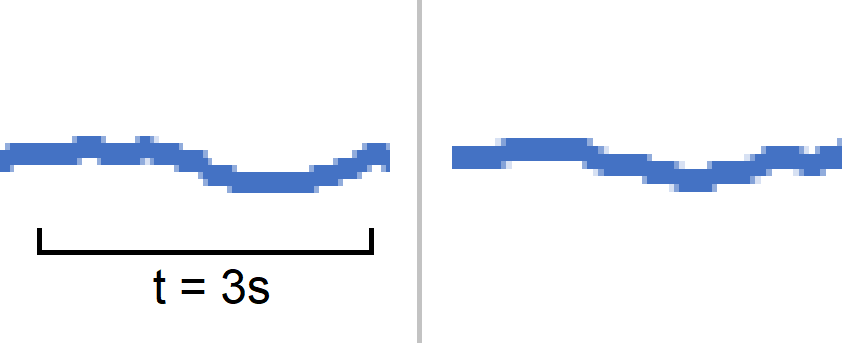 Figure 5-4 Subject at the Edge of FOV at
Ranges of 5 ft and 8 ft, From Left to Right
Figure 5-4 Subject at the Edge of FOV at
Ranges of 5 ft and 8 ft, From Left to RightThe PIR sensor can still accurately detect a stationary object at the edge of the field of view up to a range of 8 feet. The use of larger mirrors can be used to increase the accuracy of the system, but at the expense of creating a larger form factor.