SLLS567F May 2003 – July 2024 MAX211
PRODUCTION DATA
6 Parameter Measurement Information
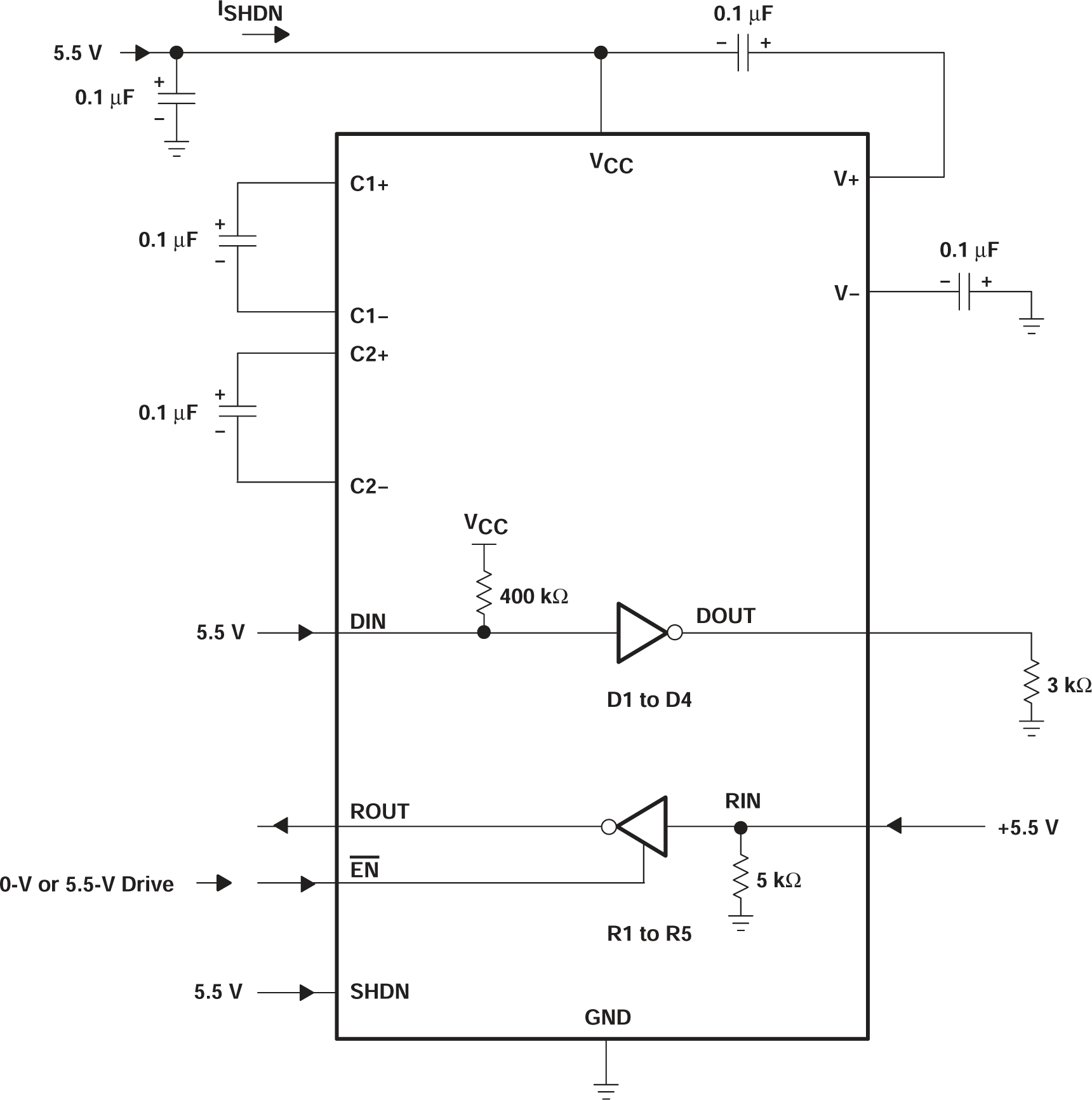 Figure 6-1 Shutdown Current Test Circuit
Figure 6-1 Shutdown Current Test Circuit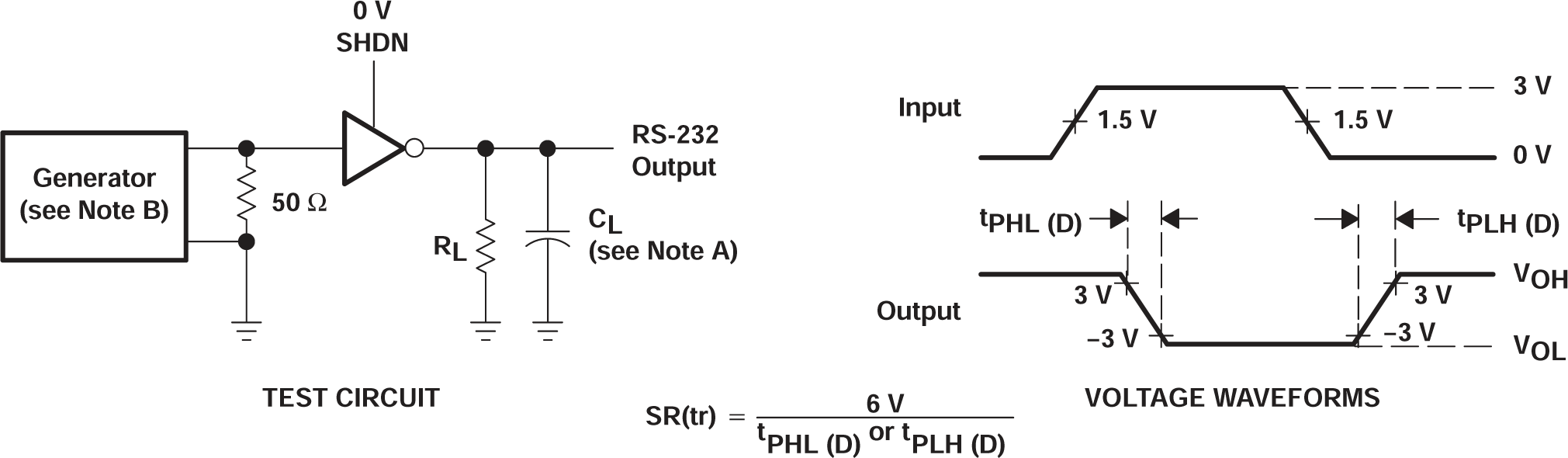
A. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
B. The pulse generator
has the following characteristics: PRR = 120kbit/s, ZO = 50Ω, 50%
duty cycle, tr ≤ 10ns, tf ≤ 10ns.
Figure 6-2 Driver Slew Rate and Propagation Delay Times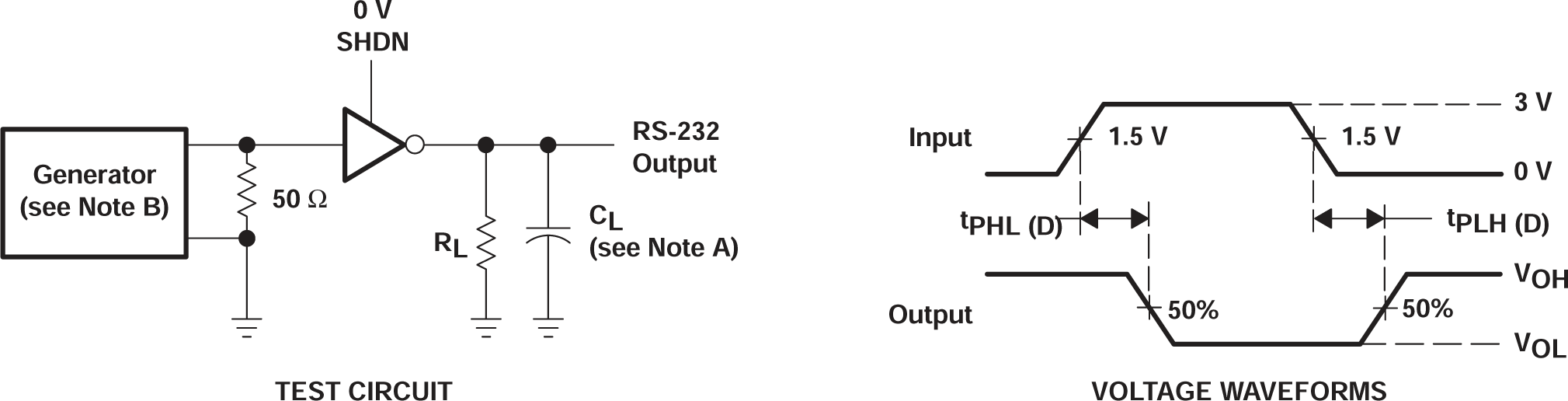
A. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
B. The pulse generator
has the following characteristics: PRR = 120kbit/s, ZO = 50Ω, 50%
duty cycle, tr ≤ 10ns, tf ≤ 10ns.
Figure 6-3 Driver Pulse Skew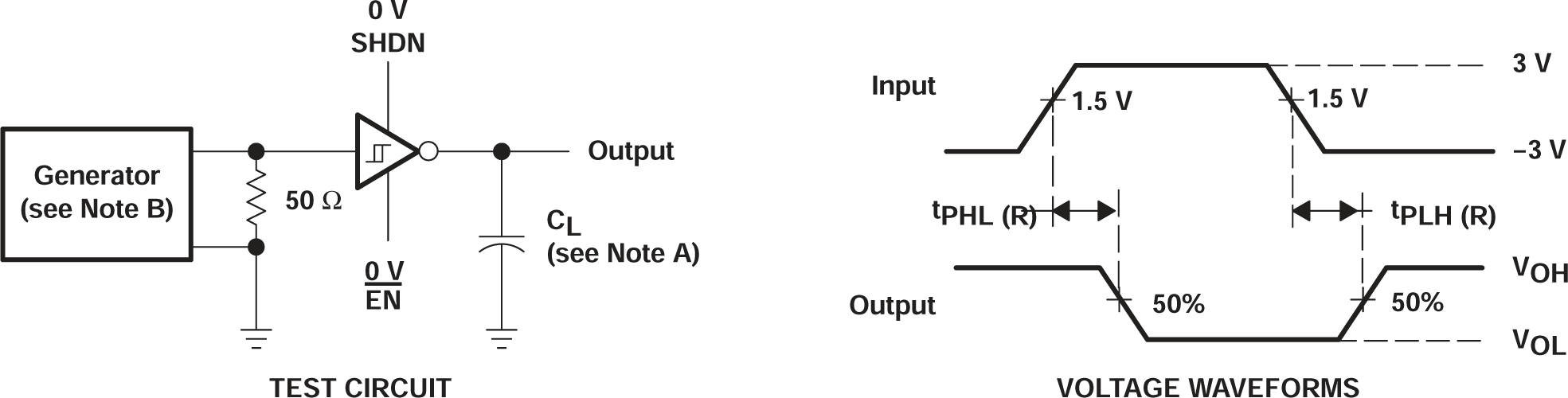
A. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
B. The pulse generator
has the following characteristics: ZO = 50Ω, 50% duty cycle,
tr ≤ 10ns, tf ≤ 10ns.
Figure 6-4 Receiver Propagation Delay Times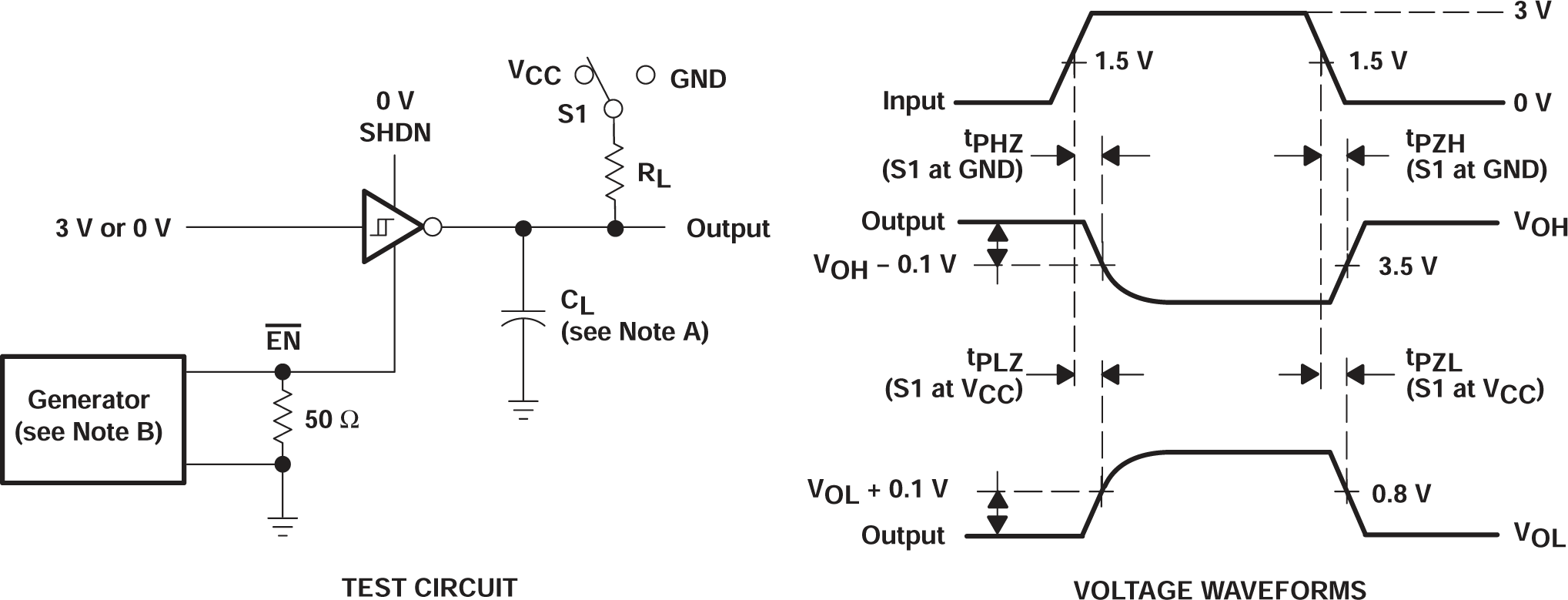
A. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
B. The pulse generator
has the following characteristics: ZO = 50Ω, 50% duty cycle,
tr ≤ 10ns, tf ≤ 10ns.
C. tPLZ and tPHZ are the same as tdis.
D. tPZL and tPZH are the same as ten.
Figure 6-5 Receiver Enable and Disable Times