SLLSEJ2G July 2015 – March 2020 SN65DP159 , SN75DP159
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Power Supply Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Differential Input Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 HDMI and DVI TMDS Output Electrical Characteristics
- 7.8 AUX, DDC, and I2C Electrical Characteristics
- 7.9 HPD Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 HDMI and DVI Main Link Switching Characteristics
- 7.11 AUX Switching Characteristics (Only for RGZ Package)
- 7.12 HPD Switching Characteristics
- 7.13 DDC and I2C Switching Characteristics
- 7.14 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Reset Implementation
- 9.3.2 Operation Timing
- 9.3.3 I2C-over-AUX to DDC Bridge (SNx5DP159 48-Pin Package Version Only)
- 9.3.4 Input Lane Swap and Polarity Working
- 9.3.5 Main Link Inputs
- 9.3.6 Main Link Inputs Debug Tools
- 9.3.7 Receiver Equalizer
- 9.3.8 Termination Impedance Control
- 9.3.9 TMDS Outputs
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Register Maps
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
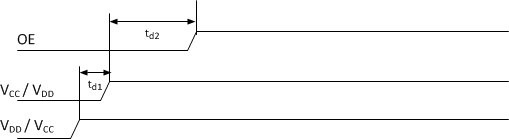
9.3.2 Operation Timing
SNx5DP159 starts to operate after the OE signal goes high (see Figure 22, Figure 23, and Table 1). Keeping OE low until VDD and VCC become stable avoids any timing requirements as shown in Figure 22.
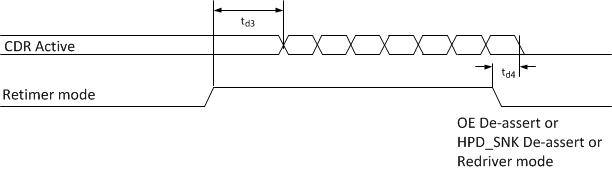 Figure 23. CDR Timing for SNx5DP159
Figure 23. CDR Timing for SNx5DP159