SLLSF83A May 2021 – November 2021 TCAN11623-Q1 , TCAN11625-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configurations and Functions (TCAN11625)
- 7 Pin Configurations and Functions (TCAN11623)
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3 Feature Description
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
- 11Application Information
- 12Power Supply Requirements
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11.2.2.1 CAN Termination
Termination may be a single 120-Ω resistor at the end of the bus on either the cable or in a terminating node. If filtering and stabilization of the common mode voltage of the bus is desired then split termination may used, see Figure 11-3. Split termination improves the electromagnetic emissions behavior of the network by filtering higher-frequency common-mode noise that may be present on the differential signal lines..
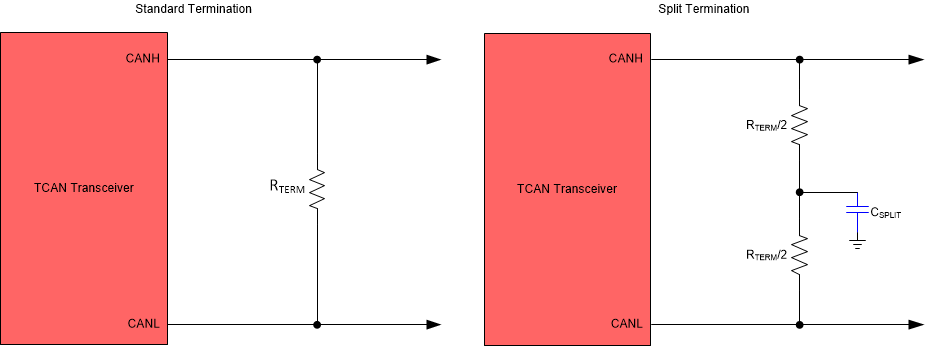 Figure 11-3 CAN Bus Termination Concepts
Figure 11-3 CAN Bus Termination Concepts