SLLSFF7A may 2021 – december 2021 ISOW1044
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description Continued
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 ThermalInformation
- 8.5 Power Ratings
- 8.6 Insulation Specifications
- 8.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 8.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 8.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 8.10 Supply Current Characteristics
- 8.11 Switching Characteristics
- 8.12 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 8.13 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
- 10Detailed Description
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11.2.2.2 CAN Termination
The ISO11898 standard specifies the interconnect to be a single twisted pair cable (shielded or unshielded) with 120-Ω characteristic impedance (ZO). Resistors equal to the characteristic impedance of the line should be used to terminate both ends of the cable to prevent signal reflections. Unterminated drop-lines (stubs) connecting nodes to the bus should be kept as short as possible to minimize signal reflections. The termination may be in a node, but if nodes are removed from the bus, the termination must be carefully placed so that it is not removed from the bus.
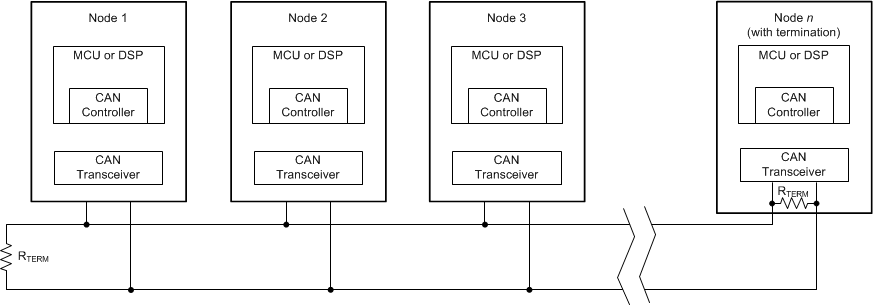 Figure 11-2 Typical CAN
Bus
Figure 11-2 Typical CAN
BusTermination may be a single 120-Ω resistor at the end of the bus, either on the cable or in a terminating node. If filtering and stabilization of the common-mode voltage of the bus is desired, then split termination can be used as below termination concepts. Split termination improves the electromagnetic emissions behavior of the network by eliminating fluctuations in the bus common-mode voltages at the start and end of message transmissions.
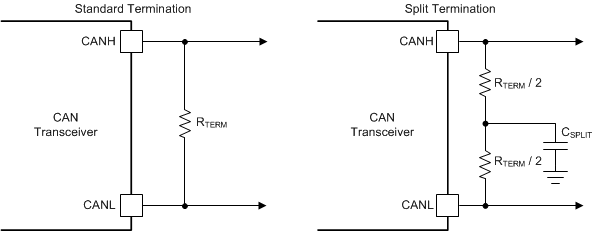 Figure 11-3 CAN Bus
Termination Concepts
Figure 11-3 CAN Bus
Termination Concepts