SLLU363 may 2023 MCF8315A
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Essential Controls
-
3Basic Controls
- 3.1 Device and Pin Configuration
- 3.2 System Level Configuration
- 3.3
Control Configurations
- 3.3.1 Motor Parameter Estimation to Minimize Motor Parameter Variation Effects
- 3.3.2 Initial Speed Detection of the Motor for Reliable Motor Resynchronization
- 3.3.3 Unidirectional Motor Drive Detecting Backward Spin
- 3.3.4 Preventing Back Spin of Rotor During Startup
- 3.3.5 Faster Startup Timing
- 3.3.6 Gradual and Smooth Start up Motion
- 3.3.7 Improving Speed Regulation
- 3.3.8 Stopping Motor Quickly
- 3.3.9 Preventing Supply Voltage Overshoot During Motor Stop.
- 3.3.10 Protecting Against Rotor Lock or Stall Condition
- 3.3.11 Maximizing Thermal Efficiency and Increasing Thermal Performance
- 3.3.12 Mitigating Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
- 3.3.13 Faster deceleration
2.6.1 MPET IPD Fault [MPET_IPD_Fault]
This fault gets triggered when there is no motor connected to the phase pins of the device or when the MPET IPD Current threshold [MPET_IPD_CURRENT_LIMIT] is set low for motors with high resistance. If this fault is triggered, then please follow the below suggestions.
Step 1: After confirming this fault triggers consistently from multiple start up attempts, check if all the phases of the motor are connected to the phase pins of the device.
Step 2: If the fault persists, increase the MPET IPD Current threshold [MPET_IPD_CURRENT_LIMIT]
Step 3: If the fault still persists, check motor data sheet for motor resistance and inductance. Open the “Control configuration – Motor Parameters” tab in All tuning settings section in the GUI and program motor phase resistance and motor phase inductance.
Step 4: If the motor does not have a data sheet, then measure the phase to phase resistance across any two phases using a Digital Multimeter and calculate the phase resistance by dividing the phase to phase resistance by 2 as shown in equation Equation 2. The motor phase resistance refers to the equivalent phase to center tap resistance, RPH as shown in Figure 2-2. This measurement holds good for both star wound and delta wound motors.
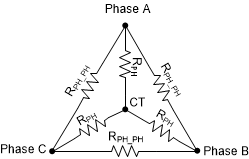 Figure 2-2 Motor Resistance
Figure 2-2 Motor ResistanceTo know the motor inductance, measure the phase to phase inductance at 1 kHz across any two phases using an LCR meter. Calculate the phase inductance by dividing the phase to phase inductance by 2. Motor phase inductance refers to the inductance from the phase output to the center tap, LPH as shown in Figure 2-3. For motors with different phase-phase inductances, measure all three phase to phase inductances and calculate their average and use this value as the phase to phase inductance. This measurement holds good for both star wound and delta wound motors.
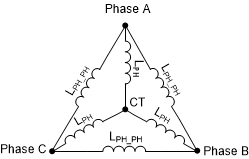 Figure 2-3 Motor Inductance
Figure 2-3 Motor Inductance