SLLU374 November 2024 MCF8329A
4.1.6 Maximum Electrical Speed (Hz)
Go to the Motor Information Section of the GUI on the Quick Spin tab and use the following steps to set the motor's max speed:
- Select Speed in RPM or Speed in Hz depending on the unit of speed provided by the motor's data sheet.
- Input the speed in the Max Speed box. If inputting a speed in RPM, also input the number of pole pairs the motor has using the Pole Pairs box.
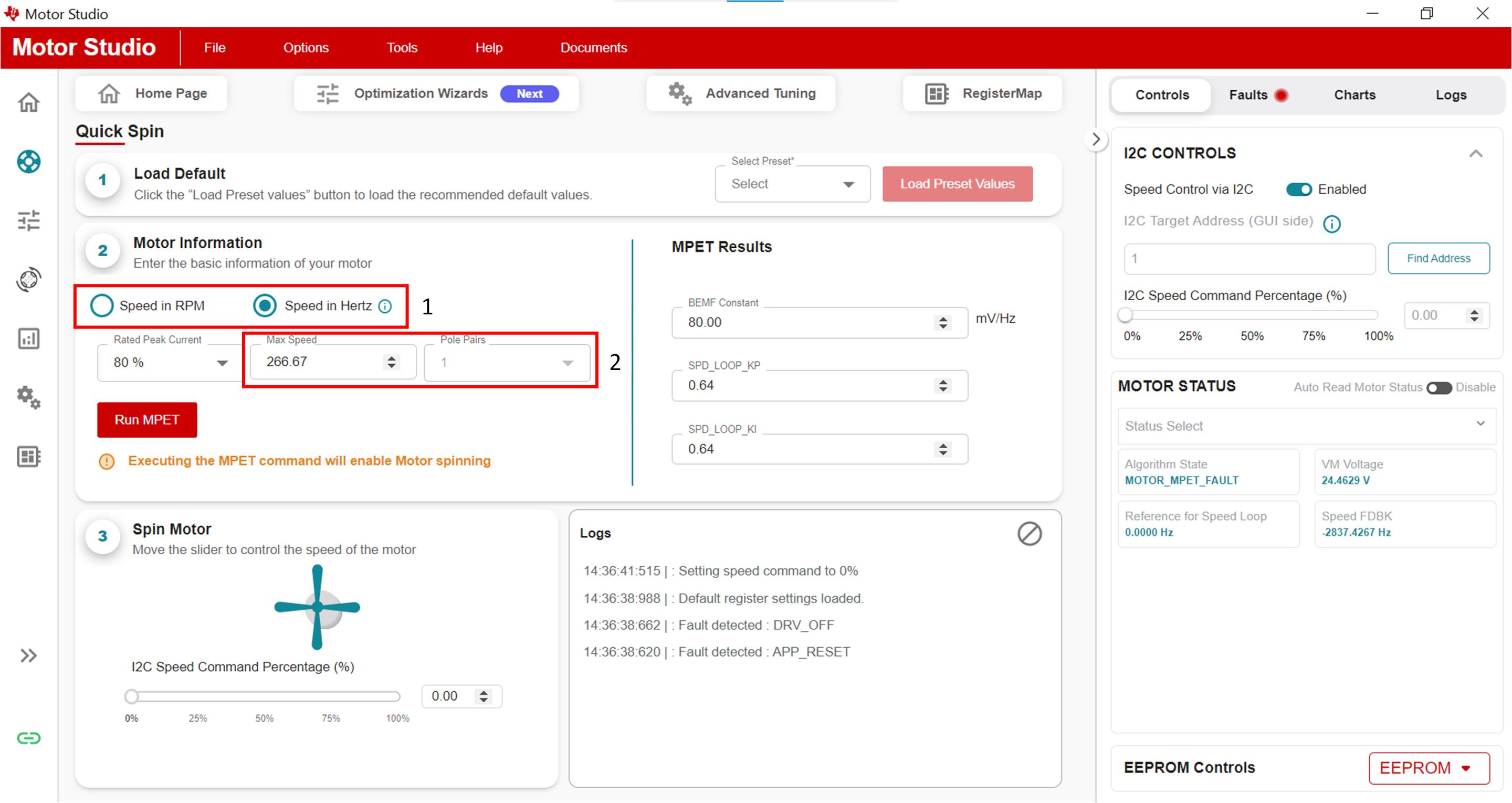 Figure 4-9 Motor Max Speed
Figure 4-9 Motor Max SpeedNote: Determining number of motor poles
without a motor data sheet:
- Use a lab power supply and make sure it's current limit is set to less than the motor rated current. Do not turn on the supply.
- Connect V+ of the supply to phase A and V- of the supply to phase B of the motor. Any 2 of the 3 phases can be chosen at random if they are not labeled.
- Turn on supply. The rotor should have settled at one position with the injecting current.
- Manually rotate the rotor until rotor snaps to another settle position. It will have several settle-down positions around one mechanical cycle.
- Count the number of settle-down positions for one fully mechanical cycle, which is the number of pole pairs. Multiplying by two calculates the number of poles.
Be careful of gearing systems within a motor. The gear ratio determines how many rotor revolutions correlate to the shaft’s mechanical revolution.