SLLU374 November 2024 MCF8329A
5.1 Speed Input Mode
The MCF8329A offers four options to control the speed of the motor: PWM, frequency, Analog, and I2C. The desired speed mode can be set by changing the value of the SPEED_MODE register on the Advanced Tuning page. A description of how to configure these control methods is provided in the Motor Control Input Options section of the MCF8329A Sensorless Field Oriented Control (FOC) Three-phase BLDC Gate Driver Data Sheet.
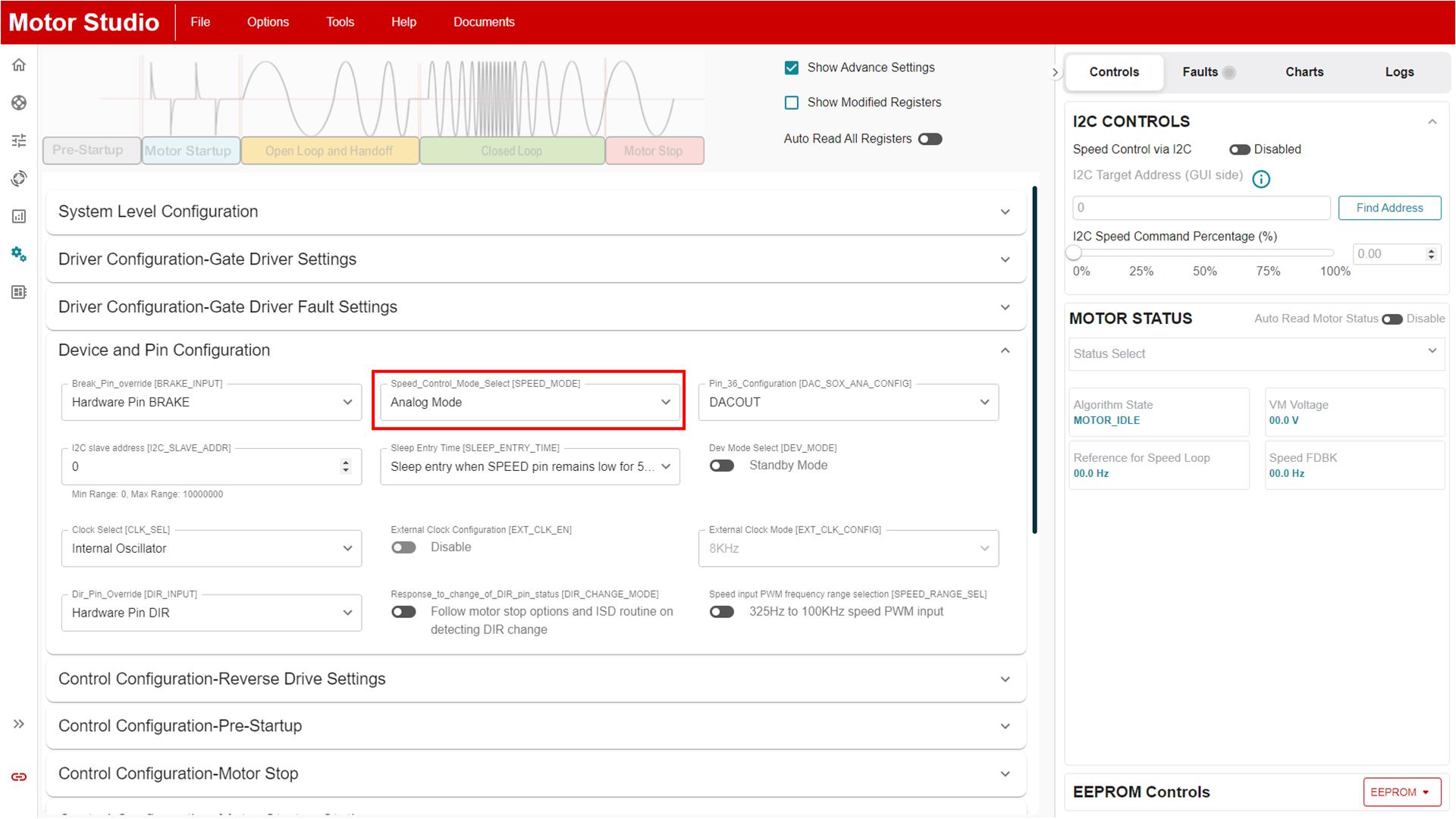 Figure 5-1 Speed Mode Selection
Figure 5-1 Speed Mode SelectionIf I2C speed input is chosen, flip SW1 away from the other switches, see Figure 5-2, this will provide a the wake switch signal to the SPEED/WAKE pin to keep the MCF8329A out of sleep/standby mode. If a speed mode other than I2C is being used, flip the switch to the opposite as what is shown in Figure 5-2 to connect the speed pin to J13. For information on how to set J13, see the Description of User-Selectable Settings on MCF8329EVM (Default in Bold) table in the MCF8329EVM User's Guide.
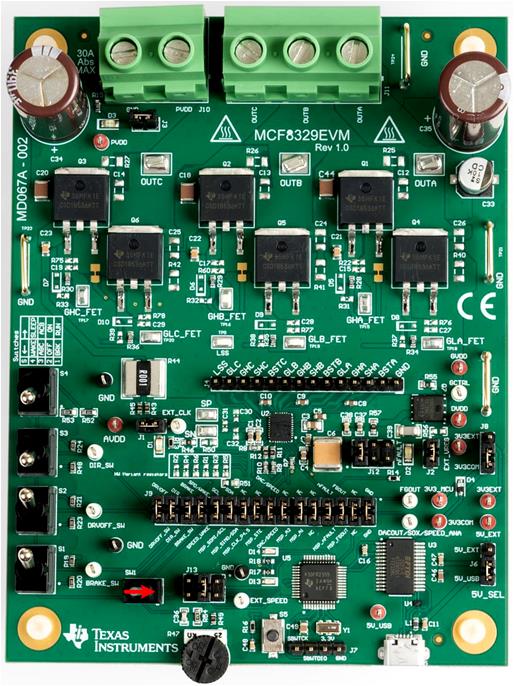 Figure 5-2 SW1 Position for I2C Speed
Mode
Figure 5-2 SW1 Position for I2C Speed
Mode