SLOA294A June 2020 – April 2024 TPS3851-Q1 , TPS7A16A-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Types of Faults and Quantitative Random Hardware Failure Metrics
- 3 Random Failures Over a Product Lifetime and Estimation of BFR
- 4 BFR Estimation Techniques
- 5 Siemens SN 29500 FIT model
- 6 IEC TR 62380
- 7 Recommended Assumptions for BFR Calculations
- 8 Special Considerations for Transient Faults
- 9 BFR Differences (Due to Package) Between IEC TR 62380 and SN 29500
- 10Effect of Power-on Hours on BFR
- 11What Can You Expect for TI Products
- 12Summary
- 13References
- 14Revision History
5 Siemens SN 29500 FIT model
SN 29500 uses a look-up table to find reference FIT rate and temperature for various component types such as:
- Integrated circuits (ICs)
- Discrete semiconductors
- Passive components
- Switches, relays, lamps, connectors, and so on
The method for estimating the FIT rate of an IC starts by looking up a reference FIT rate value and reference die temperature value from tables. The tables are separated into three types: one table for integrated circuits, a second one for discrete semiconductors and a third one for passive components. These three tables are further divided into subcategories of IC/component type and then by a range of how many transistors are in the IC or discrete semiconductor component.
In the excerpt shown in Figure 5-1, which is from a TI functional safety FIT document for a bipolar operational amplifier, the λref FIT rate is 12 FIT and the reference die temperature is 55°C. This information is sourced from the SN 29500 standard.
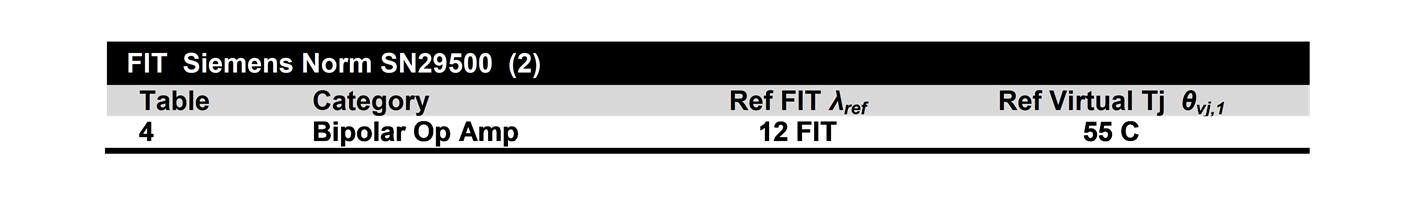 Figure 5-1 TI Standard Functional Safety FIT Documentation for
the SN 29500 Standard
Figure 5-1 TI Standard Functional Safety FIT Documentation for
the SN 29500 StandardThe SN 29500 standard includes calculations for adjusting the FIT rate from the reference condition to the FIT rate for the actual expected system operating conditions. Simply plug in the expected temperature profile and reference values into the equations, and calculate the component’s FIT rate in the context of the component’s use in the intended application.
The following expresses the general equation for all types of components as:
Application FIT
rate = reference FIT rate and temperature × temperature factors ×
voltage factors
× current factors × % time stress
factors
System integrators need to refer to the information in the SN 29500 standard to derive the specific FIT rate of the application for a TI-supplied component.