SLOS073H March 1976 – October 2024 RC4558
PRODUCTION DATA
7.2 Typical Application
Some applications require differential signals. Figure 7-1 shows a simple circuit to convert a single-ended input of 2V to 10V into differential output of ±8V on a single 15V supply. The output range is intentionally limited to maximize linearity. The circuit is composed of two amplifiers. One amplifier acts as a buffer and creates a voltage, VOUT+. The second amplifier inverts the input and adds a reference voltage to generate VOUT–. Both VOUT+ and VOUT– range from 2V to 10V. The difference, VDIFF, is the difference between VOUT+ and VOUT–.
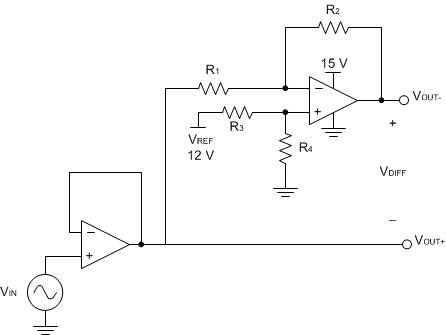 Figure 7-1 Schematic for Single-Ended Input to Differential Output Conversion
Figure 7-1 Schematic for Single-Ended Input to Differential Output Conversion