SLOS638C November 2011 – June 2022 TPA2015D1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
12.1.3 Pad Size
In making the pad size for the DSBGA balls, TI recommends that the layout use nonsolder mask defined (NSMD) land.
With this method, the solder mask opening is made larger than the desired land area, and the opening size is defined by the copper pad width. Figure 12-1 and Table 12-1 show the appropriate diameters for a DSBGA layout.
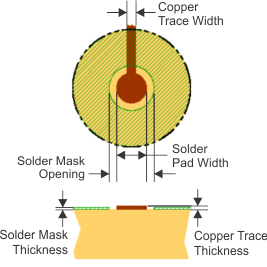 Figure 12-1 Land Pattern Dimensions
Figure 12-1 Land Pattern DimensionsTable 12-1 Land Pattern Dimensions(1)(3)(2)(4)
| SOLDER PAD DEFINITIONS | COPPER PAD | SOLDER MASK (5) OPENING | COPPER THICKNESS | STENCIL (6)(7) OPENING | STENCIL THICKNESS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonsolder mask defined (NSMD) | 275 μm (+0.0, -25 μm) | 375 μm (+0.0, -25 μm) | 1 oz max (32 μm) | 275 μm x 275 μm Sq. (rounded corners) | 125 μm thick |
(1) Circuit traces from NSMD defined PWB lands should be 75 μm to 100 μm wide in the exposed area inside the solder mask opening. Wider trace widths reduce device stand off and impact reliability.
(2) Recommend solder paste is Type 3 or Type 4.
(3) Best reliability results are achieved when the PWB laminate glass transition temperature is above the operating the range of the intended application.
(4) For a PWB using a Ni/Au surface finish, the gold thickness should be less 0.5 mm to avoid a reduction in thermal fatigue performance.
(5) Solder mask thickness should be less than 20 μm on top of the copper circuit pattern
(6) Best solder stencil performance is achieved using laser cut stencils with electro polishing. Use of chemically etched stencils results in inferior solder paste volume control.
(7) Trace routing away from DSBGA device should be balanced in X and Y directions to avoid unintentional component movement due to solder wetting forces.