SLOS638C November 2011 – June 2022 TPA2015D1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
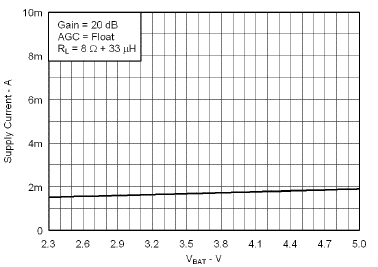
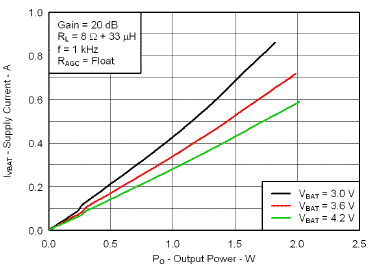
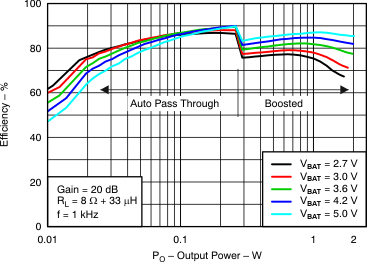
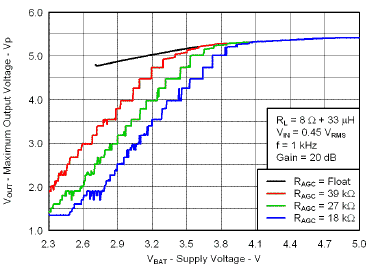
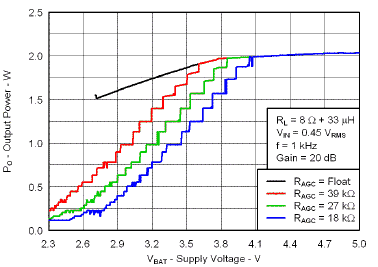
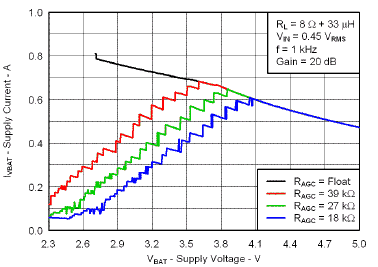
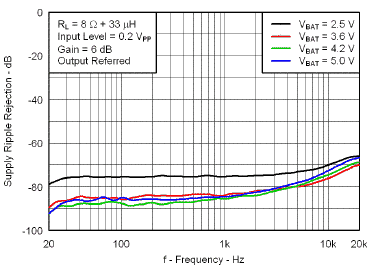
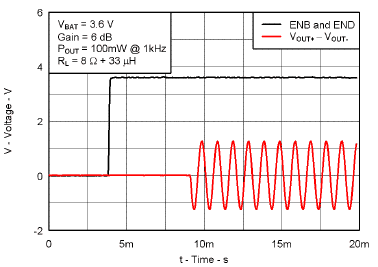
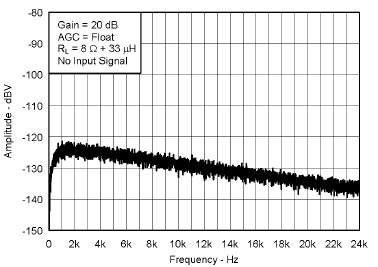
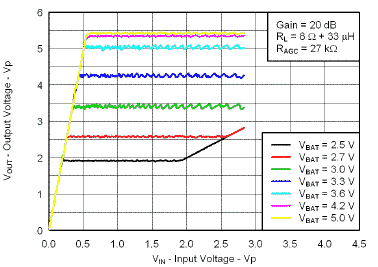
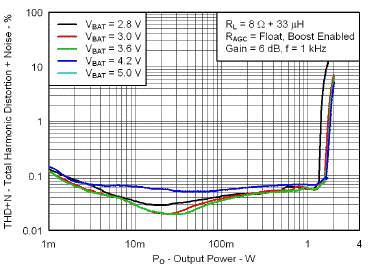
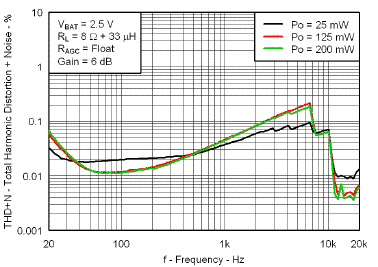
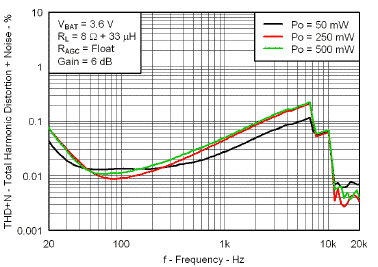
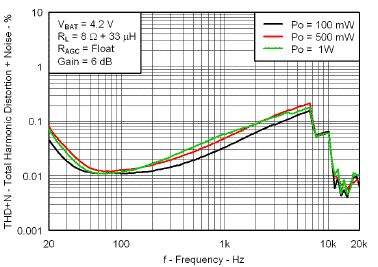
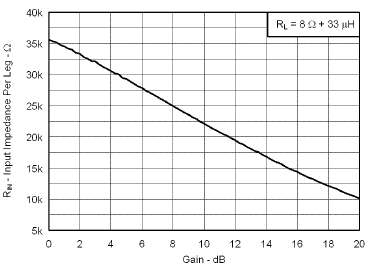
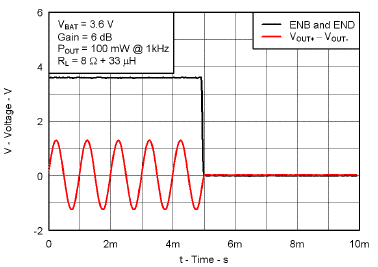
7.7 Typical Characteristics
VBAT = 3.6 V, Gain = 6 dB, CI = 1 µF, CBOOST = 22 µF, LBOOST = 2.2 µH, AGC = Float, ENB = END = VBAT, and Load = 8 Ω + 33 µH unless otherwise specified.