SLUAAG7 October 2021 BQ25720
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
-
2Design Considerations for Notebook
Applications
- 2.1 Vmin Active Protection (VAP)
- 2.2 Fast Role Swap (FRS)
- 2.3 Processor Hot Indication
- 2.4 Two-Level Battery Discharge Current Limit
- 2.5 Pass Through Mode (PTM) Operation
- 2.6 Seamless Mode Transition
- 2.7 Current and Power Monitor
- 2.8 Input Source Dynamic Power Management
- 2.9 Power Up USB Port From Battery (USB OTG)
- 3Test Results
- 4Summary
- 5References
2.2 Fast Role Swap (FRS)
This device integrates Fast Role Swap which is a great new feature which is defined in the latest USB PD version 3.0 specifications, affects further Type-C interface power design. The charger quickly swaps from power sink role to power source role to provide OTG output voltage to accessories when the original power source is disconnected
Figure 2-2 shows a traditional power solution for FRS. Notebook uses a USB PD controller to detect the FRS signal and notify the host. After FRS event is detected, the buck-boost charger stops operation, and 5 V DCDC converter is enabled with its input from battery pack. It needs a complicated power mux, and only supports a fixed OTG voltage which is set by DCDC output voltage.
 Figure 2-2 Traditional Power Solution for
FRS
Figure 2-2 Traditional Power Solution for
FRSFigure 2-3 shows a new solution that the buck-boost charger is able to operate in forward and reverse operation due to its symmetrical architecture. To compare with the traditional power solution (Figure 2-2), the new solution (Figure 2-3) eliminates the DCDC converter and power mux. Most importantly, the new solution provides USB On-the-Go (OTG) full 5 V - 20 V seamlessly after FRS event, while the typical solution cannot.
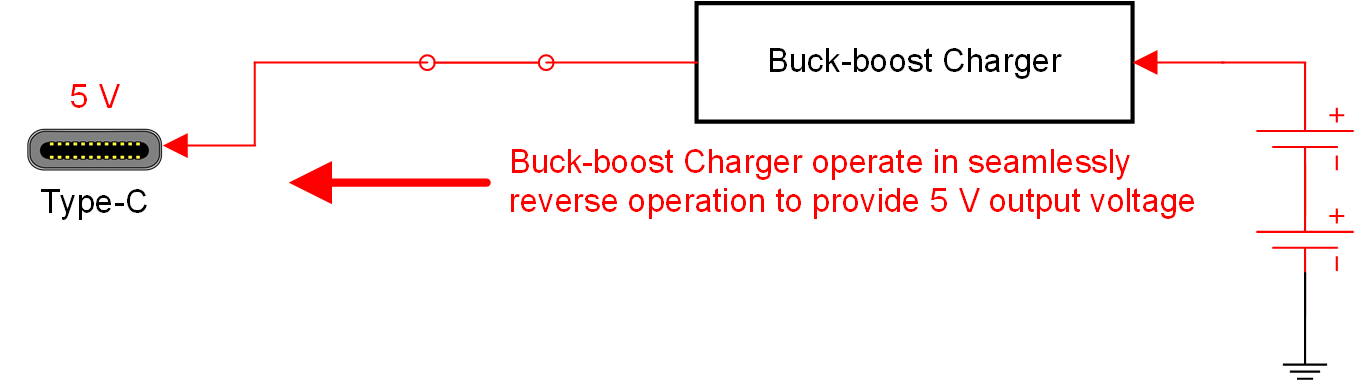 Figure 2-3 New Power Solution for FRS
Figure 2-3 New Power Solution for FRS