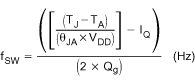SLUS714E January 2007 – June 2019 TPS40077
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Minimum Pulse Duration
- 7.3.2 Slew Rate Limit On VDD
- 7.3.3 Setting The Switching Frequency (Programming The Clock Oscillator)
- 7.3.4 Loop Compensation
- 7.3.5 Shutdown and Sequencing
- 7.3.6 Boost and LVBP Bypass Capacitance
- 7.3.7 Internal Regulators
- 7.3.8 Power Dissipation
- 7.3.9 Boost Diode
- 7.3.10 Synchronous Rectifier Control
- 7.4 Programming
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Buck Regulator 8-V to 16-V Input, 1.8-V Output at 10 A
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1
Power Train Components
- 8.2.1.2.1.1 Output Inductor, LOUT
- 8.2.1.2.1.2 Output Capacitor, COUT, ELCO and MLCC
- 8.2.1.2.1.3 Input Capacitor, CIN ELCO and MLCC
- 8.2.1.2.1.4 Switching MOSFET, QSW
- 8.2.1.2.1.5 Rectifier MOSFET, QSR
- 8.2.1.2.1.6 Timing Resistor, RT
- 8.2.1.2.1.7 Feed-Forward and UVLO Resistor, RKFF
- 8.2.1.2.1.8 Soft-Start Capacitor, CSS
- 8.2.1.2.1.9 Short-Circuit Protection, RILIM and CILIM
- 8.2.1.2.1.10 Boost Voltage, CBOOST and DBOOST (Optional)
- 8.2.1.2.1.11 Closing the Feedback Loop, RZ1, RP1, RPZ2, RSET1, RSET2, CZ2, CP2, and CPZ1
- 8.2.1.2.1
Power Train Components
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Buck Regulator 8-V to 16-V Input, 1.8-V Output at 10 A
- 8.3 Additional System Examples
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.8 Power Dissipation
The power dissipation in the TPS40077 is largely dependent on the MOSFET driver currents and the input voltage. The driver current is proportional to the total gate charge, Qg, of the external MOSFETs. Driver power (neglecting external gate resistance) can be calculated with Equation 5.
where
The total power dissipation in the TPS40077, assuming the same MOSFET is selected for both the high-side and synchronous rectifier, is described in Equation 6 or Equation 7.
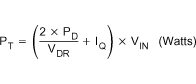
or
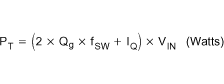
where
The maximum power capability of the TPS40077 PowerPAD package is dependent on the layout as well as air flow. The thermal impedance from junction to air, assuming 2-oz. copper trace and thermal pad with solder and no air flow, is 37°C/W. See the application report titled PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package (SLMA002) for detailed information on PowerPAD package mounting and usage.
The maximum allowable package power dissipation is related to ambient temperature by Equation 8. For θJA, see Table 1.
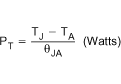
Table 1. Package Dissipation Ratings
| THERMAL IMPEDANCE,
JUNCTION-TO-AMBIENT(1) |
TA = 25°C POWER RATING | TA = 85°C POWER RATING | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural convection | 37°C/W | 2.7 W | 1.08 W |
| 150 LFM airflow | 30°C/W | 3.33 W | 1.33 W |
| 250 LFM airflow | 28°C/W | 3.57 W | 1.42 W |
| 500 LFM airflow | 26°C/W | 3.84 W | 1.52 W |
Substituting Equation 8 into Equation 7 and solving for fSW yields the maximum operating frequency for the TPS40077. The result is described in Equation 9.