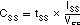SLUS714E January 2007 – June 2019 TPS40077
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Minimum Pulse Duration
- 7.3.2 Slew Rate Limit On VDD
- 7.3.3 Setting The Switching Frequency (Programming The Clock Oscillator)
- 7.3.4 Loop Compensation
- 7.3.5 Shutdown and Sequencing
- 7.3.6 Boost and LVBP Bypass Capacitance
- 7.3.7 Internal Regulators
- 7.3.8 Power Dissipation
- 7.3.9 Boost Diode
- 7.3.10 Synchronous Rectifier Control
- 7.4 Programming
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Buck Regulator 8-V to 16-V Input, 1.8-V Output at 10 A
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1
Power Train Components
- 8.2.1.2.1.1 Output Inductor, LOUT
- 8.2.1.2.1.2 Output Capacitor, COUT, ELCO and MLCC
- 8.2.1.2.1.3 Input Capacitor, CIN ELCO and MLCC
- 8.2.1.2.1.4 Switching MOSFET, QSW
- 8.2.1.2.1.5 Rectifier MOSFET, QSR
- 8.2.1.2.1.6 Timing Resistor, RT
- 8.2.1.2.1.7 Feed-Forward and UVLO Resistor, RKFF
- 8.2.1.2.1.8 Soft-Start Capacitor, CSS
- 8.2.1.2.1.9 Short-Circuit Protection, RILIM and CILIM
- 8.2.1.2.1.10 Boost Voltage, CBOOST and DBOOST (Optional)
- 8.2.1.2.1.11 Closing the Feedback Loop, RZ1, RP1, RPZ2, RSET1, RSET2, CZ2, CP2, and CPZ1
- 8.2.1.2.1
Power Train Components
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Buck Regulator 8-V to 16-V Input, 1.8-V Output at 10 A
- 8.3 Additional System Examples
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.4.2 Programming Soft Start
TPS40077 uses a closed-loop approach to ensure a controlled ramp on the output during start-up. Soft start is programmed by connecting an external capacitor (CSS) from the SS pin to GND. This capacitor is charged by a fixed current, generating a ramp signal. The voltage on SS is level-shifted down approximately 1 V and fed into a separate noninverting input to the error amplifier. The loop is closed on the lower of the level-shifted SS voltage or the 700-mV internal reference voltage. Once the level-shifted SS voltage rises above the internal reference voltage, output-voltage regulation is based on the internal reference. To ensure a controlled ramp-up of the output voltage, the soft-start time should be greater than the L-COUT time constant or Equation 11.
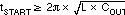
Note that there is a direct correlation between tSTART and the input current required during start-up. The lower tSTART is, the higher the input current required during start-up, because the output capacitance must be charged faster. For a desired soft-start time, the soft-start capacitance, CSS, can be found from Equation 12.