SLUS720F February 2007 – June 2019 TPS40195
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Typical Application 1
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Output Inductor, LOUT
- 9.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor, COUT
- 9.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor, CIN
- 9.2.1.2.4 Switching MOSFET, QSW
- 9.2.1.2.5 Rectifier MOSFET, QSR
- 9.2.1.2.6
Component Selection for the TPS40195
- 9.2.1.2.6.1 Timing Resistor, RT
- 9.2.1.2.6.2 Setting UVLO
- 9.2.1.2.6.3 Setting the Soft-Start Time
- 9.2.1.2.6.4 Short-Circuit Protection, RILIM
- 9.2.1.2.6.5 Voltage Decoupling Capacitors, CBP, and CVDD
- 9.2.1.2.6.6 Boost Voltage, CBOOST and DBOOST (optional)
- 9.2.1.2.6.7 Closing the Feedback Loop RZ1, RP1, RPZ2, RSET1, RSET2, CZ2, CP2 AND CPZ1
- 9.2.1.2.7 Application Curve
- 9.2.2 Typical Application 2
- 9.2.3 Typical Application 3
- 9.2.1
Typical Application 1
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.1.2.5 Rectifier MOSFET, QSR
Similar criteria as used above apply to the rectifier MOSFET. One significant difference however, is that the rectifier MOSFET switches with nearly zero voltage across its drain and source so its switching losses are nearly zero. There are losses from the source to drain body diode that occur as it conducts during the delay before the FET turns on. The equations used to calculate the losses in the rectifier MOSFET are shown below.
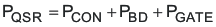
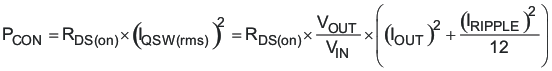

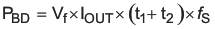
where
- PBD is the body diode loss
- t1 is the body diode conduction prior to turn-on of channel (57nS)
- t2 is the body diode conduction after turn-off of channel (14nS)
- Vf is the body diode forward voltage
Estimating the body diode losses based on a forward voltage of 1.0 V yields 0.162 W. The gate losses are unknown at this time so assume 0.1 W gate losses. This leaves 0.338 W for conduction losses. Using this figure a target RDS(on) of 4.0 mΩ was calculated. The SI7886ADP has an RDS(on) maximum of 4.8 mΩ and was used for this design.
Using the parameters from its data sheet the actual expected power losses were calculated. Conduction loss is 0.394 W, body diode loss is 0.210 W and the gate loss was 0.063 W. This totals 0.667 W associated with the rectifier MOSFET.
The ratio between Cgs and Cgd should be greater than one. The Si7886 capacitor meets this criterion and helps reduce the risk of dv/dt induced turn on of the rectifier MOSFET. If this is likely to be a problem a small resistor may be added in series with the boost capacitor, CBOOST. to slow the turn on speed of QSW at the expense of increased switching losses in that device.