SLUS907K January 2009 – June 2019 TPS2421-1 , TPS2421-2
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.4.1 Startup
Large inrush current occurs when power is applied to discharged capacitors and load. During the inrush period, the TPS2421 device operates in power limit (or SOA protect mode) managing the current as VVOUT rises. In SOA protect mode, the internal MOSFET power dissipation ([VVIN – VVOUT] × IVOUT) is regulated at 5 W typical while the fault timer starts and CCT ramps up. As the charge builds on CLOAD, the current increases towards ILIM. When the capacitor is fully charged, IVOUT drops to the dc load value, the fault timer stops, and CCT ramps down. In order for the TPS2421 device to start properly, the fault timer duration must exceed CLOAD startup time, tON. Startup time without additional dc loading is calculated using Equation 5 where PLIM = 5 W (typical).
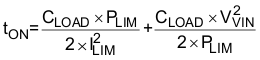
When the load has a resistive component in addition to CLOAD, the fault time must be extended because the resistive load current is unavailable to charge CLOAD. Use Table 1 and Table 2 to predict startup time in the presence of resistive dc loading.
Refer to the TPS2421 Design Calculator Tool (SLUC427) for assistance with design calculations.
Table 1. Startup Time (ms) with DC Loading: VIN = 5 V, PLIM = 3 W, ILIM = 5 A
| RLOAD_(Ω) | CLOAD_ = 100 µF | CLOAD_ = 220 µF | CLOAD_ = 470 µF | CLOAD_ = 1000 µF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 0.43 | 0.95 | 2.03 | 4.33 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 1.11 | 2.36 | 5.03 |
| 5 | 0.61 | 1.34 | 2.87 | 6.1 |
| 3 | 0.91 | 2 | 4.28 | 9.11 |
| 2.5 | 1.31 | 2.88 | 6.14 | 13.07 |
Table 2. Startup Time (ms) with DC Loading: VIN = 12 V, PLIM = 3 W, ILIM = 5 A
| RLOAD_(Ω) | CLOAD_ = 100 µF | CLOAD_ = 220 µF | CLOAD_ = 470 µF | CLOAD_ = 1000 µF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10000 | 2.46 | 5.41 | 11.56 | 24.59 |
| 100 | 2.67 | 5.87 | 12.55 | 26.69 |
| 50 | 2.93 | 6.45 | 13.79 | 29.34 |
| 15 | 6.7 | 14.74 | 31.5 | 67.01 |
| 13 | 11.68 | 25.69 | 54.87 | 116.75 |