SLUSAO7C September 2011 – July 2024 UCC28063
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Principles of Operation
- 7.3.2 Natural Interleaving
- 7.3.3 On-Time Control, Maximum Frequency Limiting, and Restart Timer
- 7.3.4 Distortion Reduction
- 7.3.5 Zero-Current Detection and Valley Switching
- 7.3.6 Phase Management and Light-Load Operation
- 7.3.7 External Disable
- 7.3.8 Improved Error Amplifier
- 7.3.9 Soft Start
- 7.3.10 Brownout Protection
- 7.3.11 Dropout Detection
- 7.3.12 VREF
- 7.3.13 VCC
- 7.3.14 Control of Downstream Converter
- 7.3.15
System Level Protections
- 7.3.15.1 Failsafe OVP - Output Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.15.2 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.15.3 Open-Loop Protection
- 7.3.15.4 VCC Undervoltage Lock-Out (UVLO) Protection
- 7.3.15.5 Phase-Fail Protection
- 7.3.15.6 CS-Open, TSET-Open and -Short Protection
- 7.3.15.7 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 7.3.15.8 AC-Line Brownout and Dropout Protections
- 7.3.15.9 Fault Logic Diagram
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.2 ZCD Resistor Selection (RZA, RZB)
- 8.2.2.3 HVSEN
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Selecting (RS) For Peak Current Limiting
- 8.2.2.6 Power Semiconductor Selection (Q1, Q2, D1, D2)
- 8.2.2.7 Brownout Protection
- 8.2.2.8 Converter Timing
- 8.2.2.9 Programming VOUT
- 8.2.2.10 Voltage Loop Compensation
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.3.1 Input Ripple Current Cancellation with Natural Interleaving
Figure 8-2 through Figure 8-4 show the input current (M1= IL1 + IL2), Inductor Ripple Currents (IL1, IL2) versus rectified line voltage. From these graphs, it can be observed that natural interleaving reduces the overall magnitude of input (and output) ripple current caused by the individual inductor current ripples.
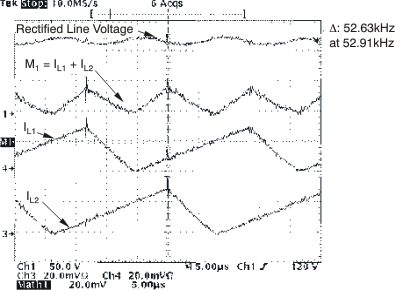 Figure 8-2 Inductor and Input Ripple Current at 85 VRMS at Peak of Line Voltage
Figure 8-2 Inductor and Input Ripple Current at 85 VRMS at Peak of Line Voltage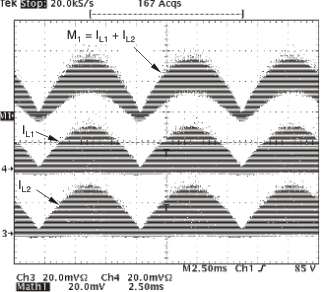 Figure 8-4 Inductor and Input Ripple Current at VIN = 85 VRMS, POUT = 300 W
Figure 8-4 Inductor and Input Ripple Current at VIN = 85 VRMS, POUT = 300 W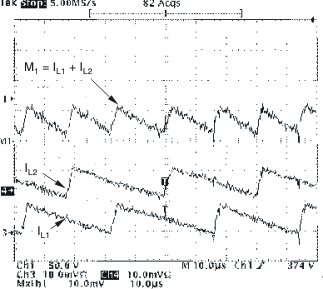 Figure 8-3 Inductor and Input Ripple Current at 265 VRMS Input at Peak Line Voltage
Figure 8-3 Inductor and Input Ripple Current at 265 VRMS Input at Peak Line Voltage