SLUSBP5E March 2014 – July 2018 TPS92601-Q1 , TPS92602-Q1
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope-Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Boost-Current Limit
- 7.3.4 Oscillator and PLL
- 7.3.5 Control Loop Compensation
- 7.3.6 LED Open-Circuit Detection
- 7.3.7 Output Short-Circuit and Overcurrent Detection
- 7.3.8 Measuring LED Current During a Non-Failure Condition
- 7.3.9 LED Dimming Options
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Boost Regulator With Separate or Paralleled Channels
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.2 Maximum Output-Current Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Overvoltage-Protection Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.4 Duty Cycle Estimation
- 8.2.1.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.6 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.2.1.2.7 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 8.2.1.2.10 Switching MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.1.2.11 Loop Compensation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2
Boost-to-Battery Regulator
- 8.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.2.1 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2.2 Maximum Output-Current Set Point
- 8.2.2.2.3 Output Overvoltage-Protection Set Point
- 8.2.2.2.4 Duty Cycle Estimation
- 8.2.2.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.2.6 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.2.2.2.7 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.2.8 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.2.9 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 8.2.2.2.10 Switching MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.2.2.11 Loop Compensation
- 8.2.2.3 TPS92602y-Q1 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Boost Regulator With Separate or Paralleled Channels
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.6 Rectifier Diode Selection
The circuit uses a low-forward-voltage-drop Schottky diode as a rectifier diode to reduce power dissipation and improve efficiency. Use 80% derating for the diode on VOUTx to allow for for ringing on the switch node. Equation 24 gives the rectifier-diode minimum reverse-breakdown voltage.
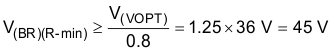
The diode must have a reverse-breakdown voltage greater than 45 V. Equation 25 and Equation 26 estimate the rectifier diode peak and average currents.
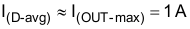

For this design, average current is 1 A and peak current is 5.26 A.
Equation 27 estimates the power dissipation in the diode.
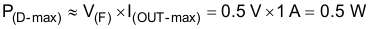
For this design, the maximum power dissipation is estimated as 0.5 W. After reviewing 45-V and 60-V Schottky diodes, the selection is the 30BQ060PbF diode, Schottky, 60 V, 3 A, SMC. This diode has a forward voltage drop of 0.5 V at 1 A, so the conduction power dissipation is approximately 500 mW, less than half its rated power dissipation.