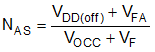SLUSD71A April 2018 – May 2018 UCC28742
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 VDD Capacitance, CDD
- 8.2.2.3 VDD Start-Up Resistance, RSTR
- 8.2.2.4 Input Bulk Capacitance and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 8.2.2.5 Transformer Turns Ratio, Inductance, Primary-Peak Current
- 8.2.2.6 Transformer Parameter Verification
- 8.2.2.7 VS Resistor Divider and Line Compensation
- 8.2.2.8 Standby Power Estimate
- 8.2.2.9 Output Capacitance
- 8.2.2.10 Feedback Loop Design Consideration
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Do's and Don'ts
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
-
11Device and Documentation Support
- 11.1
Device Support
- 11.1.1 Development Support
- 11.1.2
Device Nomenclature
- 11.1.2.1 Capacitance Terms in Farads
- 11.1.2.2 Duty Cycle Terms
- 11.1.2.3 Frequency Terms in Hertz
- 11.1.2.4 Current Terms in Amperes
- 11.1.2.5 Current and Voltage Scaling Terms
- 11.1.2.6 Transformer Terms
- 11.1.2.7 Power Terms in Watts
- 11.1.2.8 Resistance Terms in Ω
- 11.1.2.9 Timing Terms in Seconds
- 11.1.2.10 Voltage Terms in Volts
- 11.1.2.11 AC Voltage Terms in VRMS
- 11.1.2.12 Efficiency Terms
- 11.2 Documentation Support
- 11.3 Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates
- 11.4 Community Resources
- 11.5 Trademarks
- 11.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution
- 11.7 Glossary
- 11.1
Device Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.2.5 Transformer Turns Ratio, Inductance, Primary-Peak Current
The maximum primary-to-secondary turns ratio can be determined by the target maximum switching frequency at full load, the minimum input capacitor bulk voltage, and the estimated DCM resonant time.
Initially determine the maximum available total duty cycle of the on time and secondary conduction time based on target switching frequency and DCM resonant time. For DCM resonant time, assume 500 kHz if you do not have an estimate from previous designs. For the transition mode operation limit, the period required from the end of secondary current conduction to the first valley of the VDS voltage is ½ of the DCM resonant period, or 1 µs assuming 500-kHz resonant frequency. DMAX can be determined using Equation 10.

Once DMAX is known, the maximum turns ratio of the primary to secondary can be determined with the equation below. DMAGCC is defined as the secondary diode conduction duty cycle when load current reaches a specified limit operation. It is set internally by the UCC28742 at 0.475. The total voltage on the secondary winding needs to be determined; which is the sum of VOCV and the secondary rectifier VF.
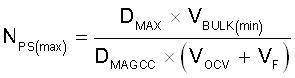
NPS is determined also with other design factors such as voltage and current ratings of primary MOSFET, secondary rectifier diode, as well as secondary MOSFET if synchronous rectifier is used. Once an optimum turns-ratio is determined from a detailed transformer design, use this ratio for the following parameters.
The UCC28742 controller constant current limit is achieved by maintaining DMAGCC = 0.475 at the maximum primary current setting. The transformer turns ratio and current limit determine the current sense resistor for a target constant current limit.
Since not all of the energy stored in the transformer is transferred to the secondary, a transformer efficiency term is included. This efficiency number includes the core and winding losses, leakage inductance ratio, and bias power ratio to rated output power. A bias power can be initially estimated at 0.1% to 0.5% rated power depending on power rating. An overall transformer efficiency of 94.5% is a good estimation of assuming 2% leakage inductance, 3% core and winding loss, and 0.5% bias power.
RCS is used to program the primary-peak current with Equation 12:

The primary transformer inductance can be calculated using the standard energy storage equation for flyback transformers. Primary current, maximum switching frequency, output and transformer efficiency are included in Equation 14.
Initially the transformer primary current should be determined. Primary current is simply the maximum current sense threshold divided by the current sense resistance.
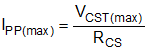

The primary inductance LP in Equation 14 also needs to consider primary MOSFET minimum turn on time as described in Transformer Parameter Verification.
The auxiliary winding to secondary winding transformer turns-ratio (NAS) is determined by the lowest target operating output voltage VOVL at current limit and above the VDD(off) of the UCC28742. The output voltage reaches VOVL when output current reaches its limit IOCC; VOVL is determined by IOCC and the expected minimum load resistance RLOAD at IOCC, i.e., VOVL = IOCC x RLOAD. Note that VOVL can only be maintained within typical 120ms, and after that time, the output voltage will enter the cycle of shutdown and auto-start retry, as described in Constant Current Limit and Delayed Shutdown, and shown in Figure 14 and Figure 15. There is additional energy supplied to VDD from the transformer leakage inductance energy which may allow a slightly lower turns-ratio to be used in a design. The NAS is then determined by the below equation.