SLUSDE4A August 2019 – August 2019 TPS56C230
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
The inductor ripple current is filtered by the output capacitor. A higher inductor ripple current means the output capacitor should have a ripple current rating higher than the inductor ripple current. See Table 3 for recommended inductor values.
The RMS and peak currents through the inductor can be calculated using Equation 5 and Equation 6. It is important that the inductor is rated to handle these currents.
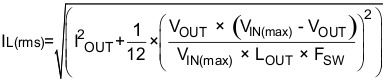
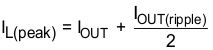
During transient and short-circuit conditions, the inductor current can increase up to the current limit of the device, so it is safe to choose an inductor with a saturation current higher than the peak current under current limit condition.